| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 58.45% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vote on recall | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shall Gavin Newsom be recalled (removed) from the office of Governor? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
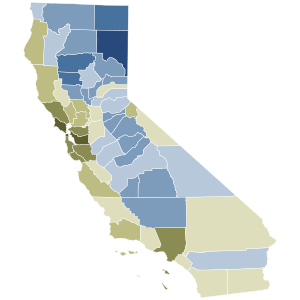
No: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Yes: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2021 California gubernatorial recall election was a special recall election that began in August 2021 and concluded on September 14, 2021, when California voters chose not to recall incumbent Democratic Governor Gavin Newsom, elected for the term January 2019 to January 2023.
Had the recall been successful, the replacement candidate with the most votes on the second part of the ballot would have assumed the office. The election followed the same format used in the November 2020 general election: in August, county election offices sent an official ballot to the mailing address of every registered voter, giving them the option to vote by mail on or before election day, or, when polling places opened statewide, to vote in-person.[3][4] The recall petition was filed in February 2020 and signatures were collected from June 2020 to March 2021, with the signature drive gaining critical momentum in late 2020 regarding Newsom's personal behavior and leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Voters' ability to recall an elected official in California is the result of Progressive Era democratic reforms intended to reduce corruption, enacted alongside the introduction of the ballot initiative and women's suffrage in 1911. Following a petition drive collecting signatures amounting to at least 12 percent of voters in the previous election for the political office in question, a special election is held. The election was the fourth gubernatorial recall election in American history and the second in state history after the 2003 recall election, which resulted in the successful recall of Governor Gray Davis, who was replaced with Arnold Schwarzenegger.
The ballot asked voters two separate questions: whether to recall Newsom as governor, and which candidate should replace Newsom as governor if he were recalled. All voters could answer the second question regardless of their vote (if any) on the first. Allies of Newsom were successful in dissuading any high-profile Democrats from entering the field of candidates seeking to replace Newsom if he was recalled. His campaign encouraged voters to vote "no" on the first question (whether to recall Newsom) while abstaining from voting on the second question (who should replace Newsom if he were recalled). Largely as consequence of this, while 12,838,565 voters answered the first question, only 7,361,568 voters answered the second.
Due to the wide margin of the results, most major news outlets projected the race for Newsom within an hour of polls closing; later that night, Larry Elder, the frontrunner replacement candidate, conceded defeat.[5] Official certification of the results occurred on October 22, 2021.
Background[edit]
| Elections in California |
|---|
 |
Following their ascension into power in 1911, California's progressive Republican reformers introduced direct democracy with the recall (Proposition 8) and the initiative and referendum (Proposition 7) processes, alongside other sweeping democratic reforms like women's suffrage (Proposition 4),[6] to weaken the corrupting power of private interests over the state's government (especially that of the enormously influential Southern Pacific Railroad), and restore, according to newly elected Governor Hiram Johnson, "the people's rule".[6][7]
Prior to this election, the only other gubernatorial recall attempt in California to qualify for the ballot happened in 2003, which resulted in Gray Davis being replaced by Arnold Schwarzenegger.[8][9] This election was the result of one of 179 attempts to recall a state-level elected official in California since voters gained the right to recall in 1911, one of 55 attempts to recall a governor, and one of six such efforts to remove Newsom.[10][8][9] Every California governor since 1960 has experienced some form of a recall attempt.[11] Of the ten prior recall attempts on state-level elected officials in California which led to special recall elections, six ultimately resulted in their removal from office by voters.[10] The recall election was the fourth gubernatorial recall election ever held in the United States;[12] the other three were in North Dakota in 1921, California in 2003, and Wisconsin in 2012.
Newsom recall petition (June 2020–March 2021)[edit]

During Newsom's tenure as governor, a total of seven recall petitions have been launched against him. On February 20, 2020, the petition which led to the 2021 recall election was served against Newsom. It stated, "People in this state suffer the highest taxes in the nation, the highest homelessness rates, and the lowest quality of life as a result."[13] The timing of the recall attempt coincided with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.[14] The basis for previous recall attempts included the state's "Universal Healthcare and laws regarding illegal aliens" and "homelessness".[15][12][16][17]
On June 10, 2020, then-Secretary of State Alex Padilla approved petitioners' petitions for circulation.[18] The recall petition focused on a variety of grievances, on issues such as sanctuary policies, homelessness, high taxes, and water rationing.[19] Newsom's official response to the petition touted his support for funding education, health care, and infrastructure, noted the State's fiscal health, and warned that the recall campaign was a partisan attack that would result in a costly election.[19]
The recall campaign hired a political consulting firm in late June 2020, and the initial plan was to pay circulators to collect signatures.[18] To ensure a successful validation, the recall campaign sought to gather 2 million signatures.[20][21] Given the difficulties in obtaining signatures during the pandemic, however, the per-signature cost rose dramatically, and petitioners opted to proceed with a team of approximately 5,000 volunteer circulators instead.[18] The first proponent of the recall, Orrin Heatlie, played a grassroots role in the previous attempt led by aspiring Tea Party politician Erin Cruz.[22] Heatlie, a former county sheriff's sergeant, was motivated by his disapproval of a video in which Newsom advised immigrants of their right not to be subject to warrantless searches.[22][23]
The petition was initially given a signature deadline of November 17, 2020, but was extended to March 17, 2021, by Sacramento County Superior Court Judge James P. Arguelles due to the pandemic. Arguelles ruled that recall proponents could have a longer time window to collect signatures than they normally would have under non-pandemic circumstances.[18][24][25][26]
Party at The French Laundry[edit]

Newsom was widely criticized in November 2020 for his attendance at a birthday party with more than three households at The French Laundry restaurant in Yountville in the Napa Valley, despite guidelines issued by his administration ahead of an expected holiday COVID-19 surge, which limited private gatherings to at most three households.[27] Also in attendance were multiple lobbyists, including both the head lobbyist and the CEO of the California Medical Association.[28] Newsom and his office initially defended the outing while saying it was the first time he and his wife dined with others in public since the COVID-19 pandemic began, that public dining recommendations were separate from state guidelines for private gatherings, and that the party was held outdoors.[29][30]

The day after Newsom claimed the party had been held outdoors, photographs showing an enclosed and maskless gathering were published and widely shared.[31] Neighboring diners said Newsom's party was so loud, restaurant staff closed off their garage-like dining space with sliding glass doors, essentially making an indoor dining space.[32] Napa County was in the "orange tier" of pandemic severity at the time, which permitted some indoor dining.[33] Newsom later apologized for attending the celebration.[34] The incident severely damaged Newsom's image and credibility amid the public health crisis.[31]
This incident[35] and voter anger over lockdowns, job losses, and school and business closures[36] were widely credited for the recall petition's surge in support. Other reasons included a $31 billion[37] fraud scandal at the state unemployment agency and pre-pandemic grievances over homelessness and high taxes.[36] By August 2020, the petitioners had submitted 55,000 valid signatures, and from August 2020 through October 2020, a total of 890 new valid signatures were submitted.[38] Coincidentally, both the French Laundry party and the extension of the signature collection deadline happened on November 6, 2020[39] and between November 5, 2020, and December 7, 2020, over 442,000 new signatures were submitted and verified; 1,664,010 valid signatures, representing roughly 111 percent of the 1,495,709 minimum required signatures and 98 percent of the 1,719,900 final certified signature count, would be submitted from November 2020 to the March 2021 deadline.[38]
Reactions[edit]
Though the state's Republican Party establishment was not involved with the launch of the recall petition,[40] the growing recall effort eventually received the attention and support of statewide and nationwide Republicans, with the Republican Governors Association commissioning a poll involving prospective candidates in February 2021.[41] In January 2021, Newsom refused to acknowledge the developing recall movement when questioned by reporters.[42] In January 2021, Rusty Hicks, the chairman of the California Democratic Party, likened it to the storming of the U.S. Capitol, calling it the "California coup".[42][43] The comparison drew bipartisan criticism, with Newsom's former deputy chief of staff, Yashar Ali, saying it was "absolutely insane to frame a recall where the voters go to the polls a coup".[43][44]
Certification[edit]

The recall campaign submitted 2,117,730 signatures by the March 2021 deadline.[45] On April 26, 2021, the office of Secretary of State Shirley Weber announced that the recall effort had gained enough signatures to pass the 1,495,709 threshold and qualify for the ballot, pending official certification after a period of 30 days where voters could retract their signatures[note 1] and where state officials tallied the costs to conduct the election (up to 60 days).[47] The count yielded 1,719,943 valid signatures, which was roughly 13.8 percent of votes cast in 2018, exceeding the 12 percent threshold required to trigger the recall election.[48] On June 23, 2021, the secretary of state announced that only 43 recall signatories withdrew their signatures statewide prior to the withdrawal deadline, resulting in a final count of 1,719,900 signatures (224,191 more than the required total), and all but ensuring a special election to recall Newsom from the governor's office.[49]
After official certification, Lieutenant Governor Eleni Kounalakis was legally required to call the election within 60 to 80 days (per recent changes in recall election procedures signed by Governor Newsom, which eliminated the election cost review requirements if sufficient funding had been appropriated for the election).[50] The signature drive was officially certified on July 1, 2021[51] and on the same day, Kounalakis called the election for September 14, 2021 (76 days later and the last Tuesday within the 60 to 80 day time period available to Kounalakis).[52]
Recall campaigning (March 2021–September 2021)[edit]
Newsom's opponents said he was being dishonest when in a March 16, 2021, interview with Jake Tapper of CNN, he said, "I've been living through Zoom school and all of the challenge related to it," since his children had been receiving in-person instruction at their private school since October 2020, unlike schoolchildren in many densely-populated and urban public school districts in California. Newsom made the comments while conducting a public outreach effort to address the all-but-certain recall.[53][54][55] The COVID-19 pandemic in California led to widespread school closures, the emergence of distance learning, and student mental health and academic challenges, and by the summer of 2021, education became a prominent issue in the recall campaign.[56] Republican candidates said the public K-12 school system failed to adequately serve students after teachers unions' demands led to extended shutdowns, and proposed a statewide voucher system, whereby parents could use their share of per-pupil state funding on the public, charter, or private school of their choice.[56]
Ahead of the September recall election, President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris campaigned for Newsom.[57][58][59][60][61] At a rally in Long Beach on the eve of the election, Biden said, "Folks, send a message to the nation: Courage matters, leadership matters, science matters. Vote to keep Gavin Newsom." Both Biden and Newsom likened the frontrunner candidate Larry Elder to Trump, with Newsom warning, "We may have defeated Donald Trump, but we have not defeated Trumpism. Trumpism is still on the ballot in California."[60]
Newsom's campaign ran television ads in September 2021 that called his Republican opponents' positions "anti-vax" and called the outcome of the recall vote "a matter of life and death.[62] All four major Republican candidates (Elder, Faulconer, Kiley, and Cox) opposed vaccine mandates, although none contended that the vaccines were dangerous and all said that they had been vaccinated against the virus.[62] Among the Republican candidates, Faulconer was the strongest advocate of COVID-19 vaccination; Cox had an "evolving position" but eventually recommended that everyone get vaccinated against COVID-19, and Elder and Kiley said that individuals should make up their own minds.[62] Elder pledged, if elected, to repeal all face-covering and COVID-19 testing requirements for state workers.[62]
Newsom under recall[edit]
Although the recall petition was introduced in February 2020, before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, Newsom's response faced scrutiny by recall supporters and the news media.[63] Many in favor of recalling Newsom cited issues unrelated to the pandemic as reasons for their support.[64]
Newsom presided over an unexpected surplus in the state's 2021 finances, attributable to the recovery in the stock market, the state's progressive tax code, and $26 billion in federal aid, and announced a $100 billion post-pandemic spending proposal in May 2021 which would expand the eligibility for stimulus checks issued by the state to higher-wage earners with an additional payment to those with children, provide rental and utility assistance, and give funds to small businesses.[65][66] While Newsom was required to return some of the surplus to taxpayers due to the Gann limit, which requires surplus funds to "be returned by a revision of tax rates or fee schedules", the Howard Jarvis Taxpayers Association said the law was likely being misapplied with the issuance of rebate checks to targeted constituencies rather than with the reduction of tax rates for all taxpayers.[67] A report from the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst's Office, published shortly after the proposal was revealed, said that when considering spending that must go towards public schools, pay off debt, or be placed in the state's main reserve account, the surplus was actually $38 billion, not $75 billion as claimed by Newsom, that the proposal was being rushed since more time was needed to determine which solutions would be effective, and that the proposal was "shortsighted and inadvisable" since it requested $12 billion from the state's existing reserves in spite of the surplus.[68][69][70] Newsom's Democratic predecessor Jerry Brown said the spending plans were "not sustainable" and said, "I would predict, certainly within two years, we're going to see fiscal stress."[71][72] Proponents of Newsom's proposal said the high amount of spending was "historic" and would help the economy recover from the pandemic, while opponents said Newsom's proposal was crafted in response to the imminent recall election.[68][73] According to state officials, a stimulus payment would be issued to eligible individuals starting in September 2021.[74][75] The first round of 600,000 stimulus checks was directly deposited into bank accounts on August 27, 2021, with payments to other recipients scheduled to be disbursed every two weeks.[76]
In May 2021, Kaiser Health News reported that throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, Newsom was "routinely outsourcing life-or-death public health duties to his allies in the private sector" with lucrative no-bid government contracts. The report said the "vast majority" of awardees were Newsom supporters and donors who had collectively donated $113 million to his political campaigns (including to his campaign to fight the recall), charitable causes, or policy initiatives, since his entry into state-level politics in 2010.[77]
In June 2021, The Sacramento Bee reported that the non-profit organization founded by Newsom's wife, Jennifer Siebel Newsom, had received over $800,000 in donations from companies that lobbied or did business with California state government, and paid her over $2.3 million since 2011 for leading the organization and producing documentary films through her production company, Girl's Club Entertainment.[78][79] When questioned about his wife's non-profit, Newsom denied that there was any conflict of interest with the arrangement.[79] In response to the report, several recall challengers called for a ban on donations to non-profit organizations of elected officials' family members from companies engaged in business with the state.[78]
Partisanship[edit]
The recall effort was not launched by state Republican Party apparatus, but by activists who had unsuccessfully attempted to recall Newsom before; the activists said the party establishment did not get involved in a substantial way until the recall effort had almost triggered the election.[40]
Newsom did not acknowledge the recall election until its occurrence became all but certain, calling the effort "partisan, Republican". He recruited nationwide Democrats to help fundraise against it.[80][81] State Democratic leaders warned members of their party against running in the recall election to avoid a potential split electorate, which some attribute to the 2003 recall of Governor Gray Davis, where Democratic Lieutenant Governor Cruz Bustamante was defeated in his candidacy by Republican Arnold Schwarzenegger.[82] A May 2021 UC Berkeley Institute of Government Studies poll sponsored by the Los Angeles Times found that Democratic voters overwhelmingly preferred having a prominent Democratic replacement candidate on the ballot in case the recall was successful, at odds with attempts by party leadership to prevent such a scenario.[83]
Former Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger disputed the supposed partisan motives of the recall, comparing the 2021 effort to the successful 2003 recall and saying,
"It's pretty much the same atmosphere today as it was then. There was dissatisfaction, to the highest level. And it's the same with the momentum. Something that sets it off to a higher level, kind of the straw that breaks the camel's back ... like an explosion."[84]
Democratic strategist Katie Merrill said that the chance for a successful recall in 2021 was low:
"Politically, we're a completely different state than we were in 2003. If you look at the statewide races, the Republican Party has effectively become a third party in California."[85]
Newsom sought to connect the backers of the recall effort to "the RNC, anti-mask and anti-vax extremists, and pro-Trump forces", while recall proponents said that the recall was only about Newsom and his performance as governor, and claimed that around one-third of recall petition signatories were registered Democrats or independents.[86] As of April 30, 2021, nearly a year after the recall campaign was approved for petition circulation by the secretary of state, Trump had yet to personally comment on the recall effort.[87] In September 2021, Trump commented on the recall election, claiming without evidence that it was "probably rigged".[88]
Despite the CDC's mid-May guidance that it was not necessary for persons fully vaccinated against COVID-19 to wear masks in most indoor settings, Newsom's administration decided that California would continue its indoor mask mandate for another month, until June 15, 2021. Reception to the CDC's new guidance among public health experts had been mixed, with some favoring quick implementation and others favoring a delay, including Bob Wachter, chair of the UCSF Department of Medicine, who called the CDC's new guidance "premature".[89] The delayed implementation was criticized by UCSF scientist and COVID-19 expert Dr. Monica Gandhi who said it had no scientific rationale, while potentially causing harm by suggesting there is "still a danger when there isn't one".[90] Isaac Hale, a lecturer of political science at UC Davis, said partisan politics concerning the recall may have been a factor in the decision:
"One of [the] top political priorities Newsom has is keeping the Democratic base together, which is why they're really focused on arguing the recall is a partisan Republican endeavor. The biggest thing that could damage that narrative is if a prominent Democrat or progressive emerged as a candidate in the recall, like Cruz Bustamante did in 2003. The key to Newsom staying in power is keeping the Democratic base happy, consolidated and making sure the California Democratic Party is the party of Gavin Newsom, and Gavin Newsom only. It's smart politics since mask mandates are popular among California Democrats."[91]
Jack Citrin, a political science professor at UC Berkeley, said changing the electoral calendar threatened to reinforce the public's cynicism about politicians using any means available to stay in power, and that they were "trying to create a situation that is most favorable for the partisan outcome that they favor".[92] The changes were heavily criticized by Newsom's Republican opponents.[93]
In August, recall proponents filed suit challenging language proposed by Newsom for the voter information handbook, alleging it falsely or misleading characterized the recall as a "power grab" by "Republicans and Trump supporters".[94] On August 5, 2021, Sacramento County Superior Court Judge Laurie M. Earl ruled against the suit and allowed inclusion of the disputed language, saying, "There is nothing false or misleading about describing the recall effort's leaders as Trump supporters."[95] Judge Earl wrote that while it may have been an exaggeration to describe the election as a "Republican recall", the rhetoric was "common to political debate" and "permissible".[96]
On July 24, 2021, the California Republican Party's steering committee voted to allow the party to endorse a candidate in the recall election, if the candidate received at least 60 percent of delegate votes in an upcoming August 7 meeting. Some Republicans opposed the move out of concern that endorsing a single candidate would reduce Republican voter turnout.[97] On August 7, the party voted to cancel the endorsement vote and issue no endorsement;[98] prior to the cancellation of the endorsement vote, Republican delegates were set to choose an endorsee from the four candidates who each had received the support of at least 200 delegates, which were Larry Elder, Kevin Faulconer, Kevin Kiley, and Doug Ose.[99]
With political allies having successfully dissuaded prospective high-level Democrats from joining the race, Newsom's campaign urged supporters to skip the second question on the recall ballot. The directive was criticized by nonpartisan political observers, who said that it was misleading and could cause voter confusion.[100]
Recall election (September 2021)[edit]
Election administration[edit]
After some blueprints of the Dominion Voting Systems voting machines were leaked, a group of eight cybersecurity experts called, in a letter to Secretary of State Shirley Weber, for rigorous auditing of the recall election with a risk-limiting audit to mitigate any cyberattack risk.[101] The experts wrote that they had no evidence of a hacking threat, and did not cast any blame on Dominion, but said that the state and counties should take steps to ensure that "the release of the Dominion software into the wild" did not increase election security risks.[101] The California Secretary of State's office said the 40 counties in California using Dominion election management system use a different version of the software that meets state requirements, and noted that California election systems have layered security protections, including routine vulnerability testing, pre-election testing, access controls, and physical security.[101] California also uses paper ballots with a voter-verified paper audit trail, another security measure.[101]
Larry Elder's unsubstantiated fraud claim prior to election day[edit]
The day before the end of voting, candidate Larry Elder claimed on his campaign website that fraud had already been detected and linked to a petition for citizens to sign "demanding a special session of the California legislature to investigate and ameliorate the twisted results" of the election,[102] though no vote totals had yet been reported. Elder would concede defeat on election day.[5] His claim that cast doubt on the legitimacy of the election result was accompanied by similar unsubstantiated claims from former President Donald Trump and several right-wing media figures.[103][102]
California's recall process[edit]
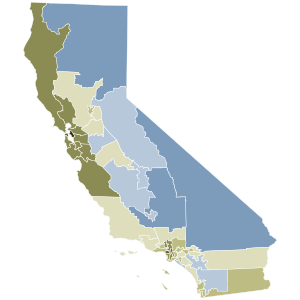
As of 2021, California is one of 19 states to allow recall elections.[105] Under state law, any elected official may be subjected to a recall.[106] To trigger a recall election of a statewide elected official, proponents must gather a certain number of signatures from registered voters within a certain time period. The number must equal at least 12 percent of the votes cast in the previous election for that office.[107][108] Based on the previous gubernatorial election, the 2021 recall petition required 1,495,709 signatures.[108] When the secretary of state confirms that a recall petition meets the required number of signatures, a recall election must be scheduled within 60 to 80 days.[109][110] If the petition qualifies fewer than 180 days prior to the next regularly scheduled election, then the recall becomes part of that regularly scheduled election.[111] In the case of a recall against the governor, the responsibility for scheduling the recall election falls on the lieutenant governor,[112] which for 2021 was Eleni Kounalakis.[110]
A recall ballot in California consists of two parts: whether the incumbent should be recalled, and a selection of replacement candidates in the event they are recalled. If a simple majority of those who cast ballots favors removing the incumbent by selecting "YES" on the first question,[113] then the replacement candidate who receives the most votes (a type of plurality voting) finishes out the incumbent's term in office. A voter is allowed a single unranked vote when choosing a preferred replacement candidate, irrespective of their response to the first question.[114] If the recall had been successful, the new governor would have taken office 38 days after the election and served the remainder of the term through January 2, 2023.[115] Following legislation, all registered voters would be mailed a ballot for any elections held in 2021, including the recall election (subsequent legislation signed by Governor Newsom in September 2021 would mandate the same universal mail-in format for all future state and local elections).[116][110]
Changes to state recall election laws[edit]
Though California's recall process remains fundamentally unchanged since its introduction in 1911,[117] beginning in 2017 and up to the 2021 gubernatorial recall, California's Democratic-led government enacted legislation to change how recall elections are conducted. Several lawmakers and academics also proposed more substantial changes during the 2021 recall campaign that would later fail in the legislature and the courts; similar rule changes were proposed during California's 2003 recall election campaign that targeted Democrat Gray Davis.[117] In addition, a new election law was applied to the 2021 recall election, though its application would later be ruled invalid in court.
Recall election timeline (SB 117 and SB 152)[edit]
In 2017, ahead of the successful recall of State Senator Josh Newman (D-Fullerton), Democratic legislators changed the law concerning recall elections with Senate Bill 117[118] to give voters 30 business days to withdraw their names from the recall petition.[119] The 2017 law change also added a 30-day period for the state Department of Finance to conduct a cost estimate and gave the Joint Legislative Budget Committee 30 days to review the estimate.[120]
On June 28, 2021, Newsom signed Senate Bill 152 into law, which allowed for his recall election to be held as early as August 2021 by allowing for a shorter recall timeline, which had been lengthened prior to the recall of Senator Newman.[121] The changes allowed the lieutenant governor to set a date for the recall without waiting for the Joint Legislative Budget Committee to review the cost estimate "so long as the Legislature has appropriated the funds it determines 'reasonably necessary' to conduct the recall election".[122] With the same law change, the legislature appropriated $250 million to administer the recall election.[123]
Election cost[edit]
While Newsom's pre-pandemic response to the recall effort in early 2020 warned that a special recall election would cost $81 million,[124][19] county officials estimated in June 2021 that a statewide recall election, which at the time was expected to be held in the fall of 2021, would cost taxpayers $215 million.[125][126] This higher estimate had presumed higher paper costs due to California's requirements for universal mail-in ballots instituted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which covered all elections held in 2020 and 2021, as well as a lengthy recall calendar featuring the rule changes enacted in 2017, ahead of Senator Newman's recall.[126][127]
With the shortened timeline from SB 152 now ensuring a summertime election, California's county election clerks nonetheless urged Lieutenant Governor Kounalakis to schedule the election as late as possible, citing an inability to guarantee a successful August election, possible voter confusion, and the potential for costs far beyond the original estimate.[126] A summertime election, held in late August or early September, could have helped Newsom defeat the recall by avoiding political fallout over fires, virus variants, or school reopenings, which could coincide with what had been anticipated to be a late October or early November recall election; this strategic advantage was the rationale for public advocacy for an earlier election by Democratic State Senator Steve Glazer.[128] On July 1, the Department of Finance released an estimate of the cost of the September 14, 2021 election at $276 million, an increase of $61 million from the prior $215 million estimated by county election offices.[129][125]
Newsom's campaign and Democratic legislative leaders of both state houses had criticized the recall election as a waste of taxpayer money, while recall proponents said, "You can't put a price on democracy," and that some costs could have been avoided if officials allowed for a "traditional" election without universal mail-in ballots.[130] While the projected $276 million cost of the recall was close to the $292 million spent on the 2020 general election in California, which was the first to feature universal mail-in ballots, the cost per voter was significantly higher than in the 2018 midterm elections.[130]
Secretary of State Weber said in an interview with KABC-TV that the recall election's total cost by election day had surpassed $276 million and was on track to eventually exceed $300 million.[131] On February 3, 2022, election officials released a final tally of the costs for the recall election, at a little over $200.2 million.[132]
Incumbent's party preference (SB 151)[edit]
In 2019, Newsom signed Senate Bill 151 into law,[133] which gave recall targets the right to state their party preference on the recall ballot. Newsom was unable to take advantage of the new law after his campaign missed a February 2020 deadline (when the recall petition was filed) to state his party preference. In June and July 2021, Newsom's campaign sued Secretary of State Shirley Weber (whom he appointed earlier in 2021) over the issue, but lost the case. Weber sided with him, telling the judge that voters would benefit from knowing Newsom's political party preference. The lawyers arguing the case in opposition to Newsom before Judge James P. Arguelles (who had also approved the recall signature deadline extension)[134] represented replacement candidate Caitlyn Jenner and proponents of the recall.[135][136]
Misapplication of tax return disclosure law (SB 27)[edit]
A new requirement for gubernatorial candidates to disclose their most recent tax returns was passed into law in 2019, when Governor Newsom signed Senate Bill 27.[note 2] Although the language of the law says that gubernatorial candidates must publicize the prior five years of their tax returns in order for their names to appear on a "primary ballot", the secretary of state applied the law to the recall election.[138] The law has been cited as a potential reason for the major reduction in recall replacement candidates relative to the number of candidates in the 2003 gubernatorial recall.[139]
The tax return disclosure requirement did not apply to Newsom, who was not considered a "candidate" in the recall. Newsom's campaign nonetheless submitted his tax documents to Secretary of State Shirley Weber, who refused to publish them on the grounds that the governor was not required to disclose them. Newsom's campaign did not respond to a reporter's July 19, 2021, request for his recent tax returns.[140]
On July 21, 2021, Sacramento County Superior Court Judge Laurie Earl invalidated all tax return disclosure requirements for the 2021 recall election. The ruling was on a suit filed by prospective recall challenger Larry Elder against Secretary of State Weber, alleging she overstepped her authority by disqualifying him from his candidacy due to a purported tax return filing error.[141] The judge ruled that Weber had improperly disqualified Elder, who had "substantially complied" with the requirements and that the special recall election was not a primary election and therefore Senate Bill 27 did not even apply.[142] By then, 42 candidates' tax returns had already been made public by the secretary of state's office.[143] Weber's office said it would comply with the ruling and did not appeal.[144]
Constitutional legal challenge[edit]
In August 2021, an essay by UC Berkeley School of Law Dean Erwin Chemerinsky and UC Berkeley Professor of Law and Economics Aaron Edlin appeared in The New York Times claiming California's recall process violates the Constitution of the United States, since more people could vote to retain Newsom than for any particular candidate while still ousting him, thus potentially violating "one person, one vote" legal precedent (conversely, if a majority of voters favored retaining Newsom, but an even greater number of voters favored a particular replacement candidate, Newsom would nonetheless prevail).[145][146] Charles C. W. Cooke, writing in The National Review in the same month, criticized the rationale and timing of the essay's publication and said Chemerinsky had selectively taken issue with California's recall, in which a Democrat was targeted, by not bringing up the pivotal 2020–21 United States Senate election in Georgia, which would also be invalid by his logic.[147] Many experts have said the current recall process would probably survive legal challenges.[148]
On August 13, 2021, two California voters filed a federal lawsuit against California's recall process, with formerly disbarred[149] attorney Stephen Yagman and Joseph Reichmann as counsel,[150] alleging violation of the U.S. Constitution's Equal Protection Clause.[151] California Attorney General Rob Bonta said on August 16, 2021, that he was monitoring the lawsuit and legal debate; by then, millions of ballots had already been sent out.[151] On August 27, 2021, United States District Court for the Central District of California Judge Michael W. Fitzgerald, an Obama appointee, dismissed the lawsuit.[152] Judge Fitzgerald, in his ruling, said of the plaintiffs' grievances: "Such disgruntlement raises no federal constitutional issues and certainly does not give the federal judiciary the right to halt the mammoth undertaking of this gubernatorial recall election."[153] The office of Secretary of State Shirley Weber (the defendant in the case) said they would not appeal the ruling.[153]
Proposed changes to state recall election law[edit]
In April 2021, two bills that could make future recalls less likely were introduced in the California Senate: the first, a bill originally authored by Senator Ben Allen (D-Redondo Beach) two years prior, in response to the recall of Senator Josh Newman, would allow a targeted incumbent to be a candidate on the recall ballot;[154] the second, authored by Senator Josh Newman (who by 2020 had reclaimed his lost state senate seat) would have allowed targets of recall campaigns to access the lists of recall petition signers and try to persuade them to remove their signatures. Neither bill would have impacted the 2021 recall election.[155]
Newman's proposed law (Senate Bill 663)[155] cleared the State Senate's Elections Committee on April 12, but he pulled the bill before it headed to the Judiciary Committee[156][157] after it received fierce opposition from proponents of the 2021 recall over privacy and voter intimidation concerns.[158][159] As of July 2021, Senator Allen's bill (Senate Constitutional Amendment 3)[155] was on hold in the legislative "suspense file".[154][160]
In September 2021, while voting in the recall election was underway, Democratic State Assembly Speaker Anthony Rendon said discussions were being held to alter California's recall process; support and opposition to changes in the recall process in California have fallen along partisan lines.[161] Any major changes to the recall process must be approved by California's voters via an amendment to the Constitution of California.[162]
Fundraising[edit]
California's recall process requires that campaigns supporting challengers adhere to the usual campaign finance limits for political candidates, while there is no dollar limit for a donor's contribution to the campaign of the defending incumbent, nor for donations to groups advocating narrowly for the recall of the incumbent while not supporting any specific challenger.[163] For the 2021 recall election, the maximum amount that a donor could have given to a candidate (other than Newsom) was $32,400.[164]
By June 2021, the three biggest donors to Newsom's campaign against the recall were the California Association of Realtors, the California Democratic Party, and Reed Hastings.[165] Prominent donors against the recall also included Steven Spielberg, George Soros, Jeffrey Katzenberg, Peter Chernin, J.J. Abrams and Katie McGrath, Laurene Powell Jobs, and Marissa Mayer.[166][167] By June 3, 2021, labor unions across the state donated $2 million to Newsom's campaign against the recall and union leaders, while saying their side was already favored by voters, promised a get-out-the-vote drive to "make sure we secure those votes and talk to our members to ensure that base" through a door-to-door canvassing effort.[168]
While organizers of the recall campaign said the effort was driven by grassroots supporters angry over pandemic restrictions and Newsom's attendance at the French Laundry dinner that defied his own guidelines, over half of the $4 million raised by recall proponents by March 2021 originated from two dozen Republican groups, along with wealthy companies and individuals, including Douglas Leone, David O. Sacks and Chamath Palihapitiya.[169] Recall proponents said there was greater voter energy in favor of the recall and that despite having a small budget, an "unparalleled" volunteer base collected more than enough signatures for the "purposeful and organic" recall effort.[168]
By May 26, 2021, $11.1 million and $4.6 million went to the pro-Newsom and pro-recall sides, respectively, with most funding for both sides originating from the same wealthy enclaves around the state.[170] On August 4, 2021, the Los Angeles Times published updated campaign finance data for the upcoming recall election: Newsom's campaign was by far in the lead with $51 million raised, while $5.8 million had been raised by pro-recall committees unaffiliated with a candidate (most of the $5.8 million raised had already been spent during the signature gathering phase). Among challengers who had raised over a million dollars, John Cox reported the most, with $7.6 million (largely self-funded), followed by Faulconer, who reported $3.4 million (raised over a six-month period), and Elder, who reported over $1 million (raised over a three-week period).[171]
After surviving the recall election, Newsom would decide the fate of numerous bills passed in the legislature and determine policy that could affect donors to his anti-recall campaign, which included the film and tech industries, real estate and labor union interests, and Native American tribes, who had collectively donated tens of millions of dollars to fight the recall (being unencumbered by donation limits), in what was described as a unique opportunity to attempt to buy influence in California's government.[172]
Campaign[edit]
Qualified replacement candidates[edit]
To have been listed on the ballot as a replacement candidate, a candidate must have been a United States citizen and registered to vote in California, submitted signatures from 65 registered voters and paid a $4,194.94 filing fee (which could be waived with the submission of 7,000 signatures of registered voters). Candidates who had been convicted of a felony involving bribery or embezzlement of public money were not allowed to run.[139]
The deadline for filing was July 16, 2021. Forty-six candidates qualified to appear on the recall ballot, consisting of 24 Republicans, nine Democrats, two Greens, one Libertarian, and ten no party preference. Four of the 46 candidates qualified after a Sacramento County judge invalidated application of SB 27 on recall elections and ordered California's Secretary of State to add candidates who did not meet requirements for tax return disclosure. The list of candidates on the ballot was certified on July 21, 2021.[141][173][174][175] Additionally, seven write-in candidates were certified by the Secretary of State on September 3.[176] Of the write-in candidates, their party affiliation consisted of two Democrats, one Republican, one American Independent, and three no party preference. Lieutenant Governor of California Eleni Kounalakis declined to run.[177]
Top candidates[edit]
| Candidate | Party | Prior positions | Residence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holly L. Baade | Democratic | Spiritual teacher and coach[173][178] | Fairfax |
 |
Republican | Businessman Perennial Candidate 2018 Republican gubernatorial candidate[179] |
Rancho Santa Fe |
 |
Republican | Conservative talk show host and author[175] | Los Angeles |
 |
Republican | Former mayor of San Diego (2014–2020)[180] | San Diego |
 |
Republican | Reality show personality Former Olympic athlete Transgender rights activist[181][182][183] |
Malibu |
 |
Republican | Assemblyman for California's 6th State Assembly district (2016–2022)[184] | Rocklin |
 |
Democratic | Actor Screenwriter Producer[173][178] |
Los Angeles |
| Jacqueline McGowan |
Democratic | Cannabis advocate and business owner[173][178] | Napa |
 |
Democratic | YouTuber Real estate broker Landlord[185] |
Ventura |
| Armando Perez- Serrato |
Democratic | Business owner[186][15] | Orange |
| Brandon Ross | Democratic | Doctor and lawyer[173][178] | San Diego |
 |
Democratic | Former executive committee member of the Service Employees International Union Retired airport analyst Perennial candidate[187][178] |
San Francisco |
| Daniel Watts | Democratic | Free speech lawyer Green candidate in the 2003 California gubernatorial recall election[173][178] |
Vista |
Debates[edit]
The Richard Nixon Foundation announced plans for two debates during the month of August 2021: the first on August 4, and the second on August 22. The first debate was a 90-minute televised event held at the Nixon Presidential Library in Yorba Linda, California. Six Republican candidates (Faulconer, Elder, Cox, Jenner, Kiley, and Ose) were invited to participate, along with Newsom. The Nixon Foundation announced that all the Republican candidates, with the exception of Jenner, had accepted the invitation, and Gov. Newsom had not responded.[188] A day after the debate was announced with Elder as a participant, the Elder campaign issued a statement that he would not attend the debate.[189][190][188]
During the August 17 debate in Sacramento, Cox was served with a subpoena while on stage, and on camera. The subpoena by a San Diego County court was for failure to pay a debt of about $100,000 from his 2018 gubernatorial campaign. Ose had initially accepted the invitation to appear at the same debate, but dropped out of the race the day of the debate, and therefore did not attend.[191] Elder announced that he would not attend the debate, nor any other debate in which Newsom is not attending.[192]
During the August 25 debate in Sacramento, Kevin Paffrath called on the other three candidates onstage (Faulconer, Cox, and Kiley) to drop out of the race and endorse him, stating he feared a lame-duck governor would get nothing done.[193]
| 2021 California's gubernatorial recall election debates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Date (2021) | Host / Sponsor | Moderator(s) | Link |
| 1 | July 24 | Yes California (virtual format) | Marcus Ruiz Evans & Tom Elias | YouTube video |
| 2 | August 4 | Nixon Presidential Library | Hugh Hewitt (with Robert C. O'Brien, Christine Devine and Elex Michaelson serving as panelists) |
YouTube video |
| 3 | August 17 | Sacramento Press Club | Vicki Gonzalez | YouTube video |
| 4 | August 19 | KRON-TV studios, San Francisco | Nikki Laurenzo & Frank Buckley | YouTube video |
| 5 | August 25 | KCRA-TV studios, Sacramento | Alexei Koseff & Deirdre Fitzpatrick | YouTube video |
Participation[edit]
| Candidate |
P Present A Absent N Not invited W Withdrawn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Debate number (see table above) | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Larry Elder | A | A | A | A | A |
| John Cox | A | P | P | P | P |
| Kevin Faulconer | A | P | P | P | P |
| Kevin Kiley | A | P | P | P | P |
| Caitlyn Jenner | A | A | A | A | A |
| Kevin Paffrath | A | N | N | N | P |
| Doug Ose | P | P | W | W | W |
| Jacqueline McGowan | P | N | N | N | N |
| James G. Hanink | P | N | N | N | N |
| Holly L. Baade | P | N | N | N | N |
| David Alexander Bramante | P | N | N | N | N |
| John R. Drake | P | N | N | N | N |
| David Hillberg | P | N | N | N | N |
| Dan Kapelovitz | P | N | N | N | N |
| Kevin K. Kaul | P | N | N | N | N |
| Daniel R. Mercuri | P | N | N | N | N |
| Joel A. Ventresca | P | N | N | N | N |
| Daniel Watts | P | N | N | N | N |
Endorsements[edit]
On recall question[edit]
- Executive branch officials
- Richard Grenell, former United States Ambassador to Germany (2018–2020), former Acting Director of National Intelligence (2020) and former Special Presidential Envoy for Serbia and Kosovo Peace Negotiations (2019–2021)[194]
- Governors
- Mike Huckabee, former Governor of Arkansas (1996–2007) and candidate for President of the United States in 2008 and 2016[195]
- Pete Wilson, 36th Governor of California (1991–1999), United States Senator from California (1983–1991), and 29th Mayor of San Diego (1971–1983)[196]
- U.S Representatives
- Ken Calvert, U.S. Representative from California's 42nd congressional district (2023–present), California's 41st congressional district (2013–2023), California's 44th congressional district (2003–2023) and California's 43rd congressional district (1993–2003)[197]
- Newt Gingrich, former U.S. Representative from Georgia's 6th congressional district (1979–1999), 50th Speaker of the United States House of Representatives (1995–1999), and candidate for President of the United States in 2012[195]
- Mike Garcia, U.S. Representative from California's 25th congressional district (2020–2023) and California's 27th congressional district (2023–present)[197]
- Dan Crenshaw, U.S. Representative from Texas's 2nd congressional district (2019–present)[198]
- Young Kim, U.S. Representative from California's 39th congressional district (2021–2023) and California's 40th congressional district (2023–present)[197]
- Doug LaMalfa, U.S. Representative from California's 1st congressional district (2013–present)[197]
- Kevin McCarthy, U.S. Representative from California's 23rd congressional district (2007–2023), California's 20th congressional district (2023) and House Minority Leader (2019–present)[197]
- Tom McClintock, U.S. Representative from California's 4th congressional district (2009–2023), California's 5th congressional district (2023–present) and candidate for governor in the 2003 recall election[197]
- Devin Nunes, U.S. Representative from California's 22nd congressional district (2003–2022)[197]
- Jay Obernolte, U.S. Representative from California's 8th congressional district (2021–present)[197]
- Michelle Steel, U.S. Representative from California's 48th congressional district (2021–2023) and California's 45th congressional district (2023–present)[199][197]
- Darrell Issa, U.S. Representative from and California's 48th congressional district (2023–present), California's 50th congressional district (2021–2023), California's 49th congressional district (2003–2019), and California's 48th congressional district (2001–2003); former Director of the USTDA (2019–2021)[200]
- David Valadao, U.S. Representative from California's 21st congressional district (2013–2019; 2021–2023) and California's 22nd congressional district (2023–present)[197]
- Doug Ose, former U.S. Representative for California's 3rd congressional district (1999–2005) and candidate for governor in 2018 and 2021[201][202]
- Burgess Owens, U.S. Representative for Utah's 4th congressional district (2021–present)[203]
- State legislators
- Laurie Davies, state assemblymember from the 73rd district (2020–present)[204]
- Shannon Grove, state senator from the 16th district (2018–present) and former Republican Minority Leader of the California Senate (2019–2021)[205]
- Gloria Romero, former state senator from the 24th district (2001–2009) and former Democratic Majority Leader of the California Senate (2001–2008) (Democrat)[206]
- Dov Hikind, former state assemblymember from New York's 48th Assembly District (1983–2018) (Democrat)[207]
- Local officials
- Clint Eastwood, former mayor of Carmel-by-the-Sea (1986–1988), actor, film director, composer, and producer (Libertarian)[208]
- Mike Feinstein, former mayor of Santa Monica (2000–2002) and candidate for California Secretary of State in 2018 (Green)[209]
- Joel Anderson, member of the San Diego County Board of Supervisors (2021–present) and former state senator from the 38th district (2010–2018)[210]
- Individuals
- David O. Sacks, technology industry executive[211][212]
- Rudy Giuliani, former Mayor of New York City (1994–2001) and former United States Associate Attorney General (1981–1983)[213]
- Rose McGowan, activist and former actress[214][215]
- Kat Von D, tattoo artist and television personality[216]
- Organizations
- California Republican Party[17]
- Howard Jarvis Taxpayers Association[217]
- Libertarian Party of California[218]
- Newspapers and other media
- Executive branch officials
- Joe Biden, 46th President of the United States (2021–present), 47th Vice President of the United States (2009–2017), and former U.S. Senator from Delaware (1973–2009)[222]
- Kamala Harris, 49th Vice President of the United States (2021–present) and former U.S. Senator from California (2017–2021)[222]
- Barack Obama, 44th President of the United States (2009–2017) and former U.S. Senator from Illinois (2005–2008)[223]
- U.S. Senators
- Cory Booker, United States Senator from New Jersey (2013–present) and candidate for President of the United States in 2020[224]
- Barbara Boxer, former U.S. Senator from California (1993–2017)[225]
- Amy Klobuchar, U.S. Senator from Minnesota (2007–present) and candidate for President of the United States in 2020[226]
- Alex Padilla, U.S. Senator from California (2021–present) and former California Secretary of State (2015–2021)[227]
- Bernie Sanders, U.S. Senator from Vermont (2007–present) and candidate for President of the United States in 2016 and 2020 (Independent)[224]
- Chuck Schumer, U.S. Senator from New York (1999–present) and Senate Majority Leader (2021–present)[228]
- Elizabeth Warren, U.S. Senator from Massachusetts (2013–present) and candidate for President of the United States in 2020[224]
- U.S Representatives
- Karen Bass, United States Representative from California's 37th congressional district (2013–2022)[229]
- Julia Brownley, U.S. Representative from California's 26th congressional district (2013–present)[230]
- John Burton, former U.S. Representative from California's 5th congressional district (1975–1983)[231]
- Salud Carbajal, U.S. Representative from California's 24th congressional district (2017–present)[232]
- Judy Chu, U.S. Representative from California's 28th congressional district (2023–present), California's 27th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 32nd congressional district (2009–2013)[233]
- Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, U.S. Representative from New York's 14th congressional district (2019–present)[234]
- Mark DeSaulnier, U.S. Representative from California's 10th congressional district (2023–present) and California's 11th congressional district (2015–2023)[235]
- Nancy Pelosi, U.S. Representative from California's 12th congressional district (1987–present) and 52nd Speaker of the United States House of Representatives (2007–2011; 2019–2023)[236]
- Katie Porter, U.S. Representative from California's 47th congressional district (2023–present) and California's 45th congressional district (2019–2023)[224]
- Ro Khanna, U.S. Representative from California's 17th congressional district (2017–present)[224]
- Barbara Lee, U.S. Representative from California's 12th congressional district (2023–present), California's 13th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 9th congressional district (1998–2013)[237]
- Ted Lieu, U.S. Representative from California's 33rd congressional district (2015–present)[238]
- Zoe Lofgren, U.S. Representative from California's 18th congressional district (2023–present), California's 19th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 16th congressional district (1995–2013)[239]
- Alan Lowenthal, U.S. Representative from California's 42nd congressional district (2023–present) and California's 47th congressional district (2013–2023)[240]
- Doris Matsui, U.S. Representative from California's 7th congressional district (2023–present), California's 6th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 5th congressional district (2005–2013)[241]
- Raul Ruiz, U.S. Representative from California's 36th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 25th congressional district (2023–present)[242]
- Adam Schiff, U.S. Representative from California's 30th congressional district (2023–present), California's 28th congressional district (2013–2023), California's 29th congressional district (2003–2013) and California's 27th congressional district (2001–2003)[243]
- Jackie Speier, U.S. Representative from California's 14th congressional district (2013–2023) and California's 12th congressional district (2008–2013)[244]
- Sara Jacobs, U.S. Representative from California's 51st congressional district (2023–present) and California's 53rd congressional district (2021–2023)[245]
- Maxine Waters, U.S. Representative from California's 43rd congressional district (2013–present) and California's 35th congressional district (1993–2013)[246]
- State officeholders
- Stacey Abrams, former Minority Leader of the Georgia House of Representatives (2011–2017), Democratic nominee for Governor of Georgia in 2018, and founder of Fair Fight Action[224]
- Rob Bonta, California Attorney General (2021–present) and former state assemblymember from the 18th district (2012–2021)[247]
- Jerry Brown, former governor of California (1975–1983; 2011–2019)[220]
- Wendy Carrillo, state assemblymember from the 51st district (2017–present)[248]
- David Chiu, state assemblymember from the 17th district (2014–present) and former president of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors (2009–2014)[247]
- Bill Dodd, state senator from the 3rd district (2016–present)[249]
- Laura Friedman, state assemblymember from the 43rd district (2016–present)[250]
- Lorena Gonzalez, state assemblymember from the 80th district (2013–present)[250]
- María Elena Durazo, state senator from the 24th district (2018–present)[251]
- Sydney Kamlager-Dove, state senator from the 30th district (2021–2022)[248]
- Eleni Kounalakis, Lieutenant Governor of California (2019–present) and former United States Ambassador to Hungary (2010–2013)[252]
- Ricardo Lara, California Insurance Commissioner (2019–present)[253]
- Fiona Ma, California State Treasurer (2019–present), former member of the California Board of Equalization (2015–2019), and former state assemblymember from the 12th district (2006–2012)[247]
- Fran Pavley, former state senator from the 27th district (2008–2016)[230]
- Richard Pan, state senator from the 6th district (2014–present)[247]
- Robert Rivas, state assemblymember from the 30th district (2018–present)[251]
- Rudy Salas, state assemblymember from the 32nd district (2012–2022)[254]
- Nancy Skinner, state senator from the 9th district (2016–present)[237]
- Tony Thurmond, California State Superintendent of Public Instruction (2019–present)[255]
- Hannah-Beth Jackson, former state senator from the 19th district (2012–2020)[230]
- Betty Yee, California State Controller (2015–2023) and former member of the California Board of Equalization (2004–2015)[247]
- Local officials
- London Breed, Mayor of San Francisco (2018–present)[256]
- Robert Garcia, Mayor of Long Beach (2014–2022)[257]
- Todd Gloria, Mayor of San Diego (2020–present) and former state assemblymember from the 78th district (2016–2020)[258]
- Sam Liccardo, Mayor of San Jose (2015–present)[239]
- Libby Schaaf, Mayor of Oakland (2015–present)[259]
- Antonio Villaraigosa, former Mayor of Los Angeles (2005–2013), former Speaker of the California State Assembly (1998–2000), and 2018 gubernatorial candidate[260]
- Individuals
- Byron Allen, entertainment industry executive[261]
- Mary Carey, adult film actress and candidate for Governor of California in the 2003 recall election[186]
- Jaime Harrison, Chair of the DNC[262]
- Alan F. Horn, entertainment industry executive[261]
- George Lopez, actor and comedian[261]
- Alyssa Milano, actress and activist[263]
- Michael Moore, author, film documentary and activist[263]
- Paula Poundstone, actress, author, and comedian[261]
- Rob Reiner, actor, filmmaker, and activist[261]
- Ann Sarnoff, television executive[261]
- George Takei, actor and activist[261]
- Elijah Wood, actor and producer[263]
- Newspapers and other media
- Bay Area Reporter Editorial Board[264]
- Los Angeles Times Editorial Board[265]
- McClatchy California Editorial Boards[266][267][note 4]
- The Mercury News and East Bay Times Editorial Boards[268]
- Monterey County Weekly Editorial Board[269]
- Napa Valley Register Editorial Board[270]
- The New York Times Editorial Board[271]
- The San Diego Union-Tribune Editorial Board[272]
- San Francisco Chronicle Editorial Board[273]
- Santa Barbara Independent Editorial Board[274]
- Organizations
- American Civil Liberties Union California Action[275]
- Armenian National Committee of America-Western Region[276]
- California Democratic Party[277]
- California Faculty Association[278]
- California Federation of Teachers[279]
- California League of Conservation Voters[280]
- Climate Hawks Vote[281]
- Democratic Governors Association[282]
- Democratic Socialists of America Los Angeles Electoral Committee[283]
- Equality California[284]
- Green Party of California[285]
- Human Rights Campaign[286]
- International Association of Fire Fighters[287]
- Jewish Democratic Council of America[288]
- NARAL Pro-Choice California[289]
- National Union of Healthcare Workers[290]
- Peace and Freedom Party[291]
- Planned Parenthood Affiliates of California[248]
- Service Employees International Union California[292]
- Socialist Equality Party[293]
- United Food and Commercial Workers[294]
- Valley Industry & Commerce Association[295]
For candidates[edit]
- Governors
- Pete Wilson, 36th Governor of California (1991–1999), former U.S. Senator from California (1983–1991), and 29th Mayor of San Diego (1971–1983)[196]
- U.S. Representatives
- Dan Crenshaw, U.S. Representative from Texas's 2nd congressional district (2019–present)[198]
- Burgess Owens, U.S. Representative from Utah's 4th congressional district (2021–present)[203]
- Michelle Steel, U.S. Representative from California's 45th congressional district (2023–present) and California's 48th congressional district (2021–2023), former member of the Orange County Board of Supervisors (2015–2021), and former member of the California State Board of Equalization (2007–2015)[199]
- State legislators
- Laurie Davies, state assemblymember from the 73rd district (2020–present)[204]
- Shannon Grove, state senator from the 16th district (2018–present) and former Minority Leader of the California Senate (2019–2021)[205]
- Gloria Romero, former state senator from the 24th district (2001–2009) and former Democratic Majority Leader of the California Senate (2001–2008)[206]
- Dov Hikind, former state assemblymember from New York's 48th Assembly District (1983–2018) (Democrat)[296]
- Local officials
- Rudy Giuliani, former Mayor of New York City (1994–2001) and former United States Associate Attorney General (1981–1983)[213]
- Clint Eastwood, former mayor of Carmel-by-the-Sea (1986–1988), actor, film director, composer, and producer[208]
- Individuals
- Hugh Hewitt, radio talk show host[297]
- Rose McGowan, former actress and activist[298][215]
- Mike Piazza, former professional baseball player[299]
- Chuck Norris, martial artist, actor, film producer, and screenwriter[300][301]
- Organizations
- American Independent Party[302]
- California College Republicans[303]
- California Rifle and Pistol Association[304][note 5]
- New York Young Republican Club[306]
- Newspapers and other media
- U.S. Representatives
- Darrell Issa, U.S. Representative from California's 48th congressional district (2023–present), California's 50th congressional district (2021–2023), California's 49th congressional district (2003–2019), and California's 48th congressional district (2001–2003); former Director of the USTDA (2019–2021)[200]
- State legislators
- Patricia Bates, state senator from the 36th district (2014–present) and former Minority Leader of the California Senate (2017–2019)[note 6]
- Frank Bigelow, state assemblymember from the 5th district (2012–present)[note 6]
- Jordan Cunningham, state assemblymember from the 35th district (2016–present)[note 6]
- Megan Dahle, state assemblymember from the 1st district (2019–present)[note 6]
- Heath Flora, state assemblymember from the 12th district (2016–present)[note 6]
- Brian Jones, state senator from the 38th district (2018–present)[note 6]
- Tom Lackey, state assemblymember from the 36th district (2014–present)[note 6]
- Devon Mathis, state assemblymember from the 26th district (2014–present)[note 6]
- Melissa Melendez, state senator from the 28th district (2020–present)[note 6]
- Janet Nguyen, state assemblymember from the 72nd district (2020–present)[note 6]
- Jim Nielsen, state senator from the 4th district (2013–present)[note 6]
- Thurston Smith, state assemblymember from the 33rd district (2020–present)[note 6]
- Randy Voepel, state assemblymember from the 71st district (2016–present)[note 6]
- Marie Waldron, state assemblymember from the 75th district (2012–present) and Minority Leader of the California Assembly (2018–present)[note 6]
- Scott Wilk, state senator from the 21st district (2016–present) and Minority Leader of the California Senate (2021–present)[note 6]
- Individuals
- Michael Shellenberger, author and a 2018 gubernatorial candidate[310]
- Newspapers and other media
- The Bakersfield Californian Editorial Board[219]
- Los Angeles Times Editorial Board[265][note 7]
- Organizations
- Local officials
- Mike Feinstein, former mayor of Santa Monica (2000–2002) and candidate for California Secretary of State in 2018[209]
- Organizations
- U.S. Representatives
- Doug Ose, former U.S. Representative for California's 3rd congressional district (1999–2005), candidate for governor in 2018 and 2021[201][202]
- Local officials
- Joel Anderson, member of the San Diego County Board of Supervisors (2021–present) and former state senator from the 38th district (2010–2018)[315]
- Individuals
- Newspapers and other media
- Organizations
- Organizations
- Individuals
- Alyson Kennedy, mineworker and SWP nominee for President in 2016 and 2020[321]
- Organizations
Predictions[edit]
| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| The Cook Political Report[323] | Likely D | September 13, 2021 |
| Inside Elections[324] | Likely D | August 16, 2021 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[325] | Likely D | September 9, 2021 |
Polling[edit]
Newsom recall[edit]
- Aggregate polls
| Source of poll aggregation |
Dates administered |
Dates updated |
Yes on recall | No on recall | Undecided | Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Clear Politics | September 6–13, 2021 | September 14, 2021 | 41.8% | 56.3% | 1.9% | No on recall +14.5 |
| FiveThirtyEight | August 27 – September 14, 2021 | September 14, 2021 | 41.5% | 57.3% | 1.2% | No on recall +15.8 |
| Average | 41.7% | 56.8% | 1.5% | No on recall +15.1 | ||
| Result | 38.12% | 61.88% | – | No on recall +23.76 | ||
- Graphical summary
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[c] |
Margin of error |
Yes on recall |
No on recall |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 CA gubernatorial election | September 14, 2021 | 12,892,578 | – | 38.12% | 61.88% | – |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | September 11–13, 2021 | 1,082 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 45% | 53% | 2% |
| Momentive | August 31 – September 13, 2021 | 3,985 (LV) | ± 1.6% | 41% | 55% | 4% |
| Emerson College | September 10–11, 2021 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 40% | 60% | 1% |
| Data for Progress (D) | September 2–10, 2021 | 2,464 (LV) | ± 2.0% | 43% | 57% | – |
| SurveyUSA | September 7–8, 2021 | 930 (LV) | ± 4.2% | 41% | 54% | 5% |
| Suffolk University | September 6–7, 2021 | 500 (LV) | ± 4.4% | 41% | 58% | 1% |
| Berkeley IGS | August 30 – September 6, 2021 | 7,917 (LV) | ± 2.0% | 38% | 60% | 1% |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | September 2–4, 2021 | 1,079 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 43% | 53% | 4% |
| YouGov | August 30 – September 1, 2021 | 1,618 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 43% | 57% | – |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | August 26–29, 2021 | 1,088 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 44% | 52% | 4% |
| Public Policy Institute of California | August 20–29, 2021 | 1,080 (LV) | ± 4.5% | 39% | 58% | 3% |
| SurveyUSA | August 26–28, 2021 | 816 (LV) | ± 4.4% | 43% | 51% | 6% |
| Gravis Marketing | August 25–27, 2021 | 729 (LV) | ± 3.6% | 45% | 50% | 5% |
| Targoz Market Research | August 23–25, 2021 | 787 (LV) | ± 3.5% | 42% | 52% | 6% |
| Change Research (D) | August 22–25, 2021 | 782 (LV) | ± 3.7% | 42% | 57% | 1% |
| Redfield & Wilton Strategies | August 20–22, 2021 | 1,000 (RV) | ± 3.1% | 41% | 48% | 11%[d] |
| 964 (LV) | ± 3.2% | 43% | 51% | 7% | ||
| YouGov | August 6–12, 2021 | 1,585 (RV) | ± 3.4% | 46% | 54% | – |
| 1,534 (LV) | ± 3.8% | 48% | 52% | – | ||
| SurveyUSA | August 2–4, 2021 | 613 (LV) | ± 5.0% | 51% | 40% | 9% |
| Emerson College | July 30 – August 1, 2021 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 46% | 48% | 6% |
| Core Decision Analytics | July 27–29, 2021 | 804 (RV) | ± 3.5% | 41% | 52% | 7% |
| ~728 (LV) | ± 3.6% | 44% | 51% | 5% | ||
| Berkeley IGS | July 18–24, 2021 | 5,795 (RV) | ± 2.0% | 36% | 51% | 13% |
| 3,266 (LV) | ± 2.5% | 47% | 50% | 3% | ||
| Emerson College | July 19–20, 2021 | 1,085 (RV) | ± 2.9% | 43% | 48% | 9% |
| Change Research (D) | June 11–16, 2021 | 1,085 (RV) | ± 3.0% | 40% | 54% | 6% |
| Moore Information Group (R)[A] | June 1–3, 2021 | 800 (RV) | ± 3.0% | 44% | 50% | 6% |
| 682 (LV) | ± 4.0% | 49% | 46% | 5% | ||
| Tulchin Research (D) | May 21–30, 2021 | 1,500 (RV) | ± 2.5% | 37% | 50% | 13% |
| 1,168 (LV) | ± 2.9% | 38% | 52% | 9% | ||
| Public Policy Institute of California | May 9–18, 2021 | 1,074 (LV) | ± 4.2% | 40% | 57% | 3% |
| Berkeley IGS | April 29 – May 5, 2021 | 10,289 (RV) | ± 2.0% | 36% | 49% | 15% |
| 7,943 (LV) | ± 2.3% | 42% | 50% | 8% | ||
| SurveyUSA | April 30 – May 2, 2021 | 642 (RV) | ± 5.3% | 36% | 47% | 17% |
| McLaughlin & Associates (R)[B] | April 15–19, 2021 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.1% | 45% | 45% | 10% |
| Public Policy Institute of California | March 14–23, 2021 | 1,174 (LV) | ± 3.9% | 40% | 56% | 5% |
| Probolsky Research (R) | March 16–19, 2021 | 900 (RV) | ± 3.3% | 40% | 46% | 14% |
| 900 (LV)[e] | ± 3.3% | 35% | 53% | 13% | ||
| Emerson College | March 12–14, 2021 | 1,045 (RV) | ± 3.0% | 38% | 42% | 20%[f] |
| WPA Intelligence (R)[C] | February 12–14, 2021 | 645 (LV) | ± 3.9% | 47% | 43% | 10% |
| Berkeley IGS | January 23–29, 2021 | 10,357 (RV) | ± 2.0% | 36% | 45% | 20% |
| 7,980 (LV) | ± 2.4% | 36% | 49% | 15% | ||
| Remington Research (R)[D] | March 17–18, 2019 | 1,303 (LV) | ± 2.7% | 31% | 52% | 17% |
Replacement candidates[edit]
The table below contains all candidates who had polled at or above 2% since the filing deadline for the recall, had raised at least $100,000 (excluding loans and including at least $5,000 in the most recent filing period), were a current or former elected official, or were otherwise considered notable in their own right. The graphical summary includes all candidates who met at least one of those criteria and had appeared in at least four separate publicly released polls.
- Aggregate polls
| Source of poll aggregation |
Dates administered |
Dates updated |
Elder (R) | Paffrath (D) | Faulconer (R) | Cox (R) | Kiley (R) | Jenner (R) | Other/Undecided [g] |
Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Clear Politics | August 20 – Sep 13, 2021 | Sep 13, 2021 | 32.4% | 7.8% | 5.3% | 4.0% | 3.1% | 1.3% | 46.1% | Elder +24.6 |
| FiveThirtyEight | July 18 – Sep 13, 2021 | Sep 13, 2021 | 29.7% | 6.1% | 5.1% | 4.5% | 3.0% | 1.0% | 50.6% | Elder +23.6 |
| Average | 31.1% | 7.0% | 5.2% | 4.3% | 3.1% | 1.2% | 48.4% | Elder +24.1 | ||
| Result | 48.4% | 9.6% | 8.0% | 4.1% | 3.5% | 1.0% | 25.4% | Elder +38.8 | ||
- Graphical summary
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[c] |
Margin of error |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 CA gubernatorial election | Sep 14, 2021 | 7,361,568 | – | 0.5% | 1.3% | 4.1% | 0.9% | 48.4% | 8.0% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 1.0% | 0.9% | 3.5% | 1.2% | 2.9% | 0.4% | 9.6% | 1.2% | 5.3% | 2.5% | 2.3% | 4.6% | – | – |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | Sep 11–13, 2021 | 1,082 (LV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 3% | 1% | 41% | 4% | – | – | 1% | – | 4% | – | 4% | – | 10% | – | 1% | – | – | 9% | 23% | – |
| Emerson College | Sep 10–11, 2021 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 3% | 6% | 30% | 4% | – | – | 2% | – | 4% | – | 3% | 1% | 6% | – | – | – | – | 3% | 6% | 34% |
| Data for Progress (D) | Sep 2–10, 2021 | 2,557 (LV) | ± 2.0% | – | 2% | 7% | – | 22% | 4% | – | – | 1% | – | 3% | – | 4% | – | 6% | – | 5% | – | 3% | 5% | 7% | 29% |
| SurveyUSA | Sep 7–8, 2021 | 597 (LV) | ± 5.5% | – | 4% | 8% | 4% | 29% | 6% | – | – | 2% | – | 3% | 2% | 4% | – | 9% | 1% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 6% | 13% | – |
| Suffolk University | Sep 6–7, 2021 | 233 (LV) | ± 6.4% | 0% | 0% | 4% | 1% | 39% | 5% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 2% | – | 2% | 0% | 5% | 0% | 2% | 1% | – | – | 7% | – |
| Berkeley IGS | Aug 30 – Sep 6, 2021 | 4,707 (LV) | ± 2.6% | – | 1% | 4% | 1% | 38% | 8% | – | 1% | 1% | 1% | 4% | 1% | 2% | – | 10% | 1% | 3% | 2% | 1% | 8% | 16% | – |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | Sep 2–4, 2021 | 1,079 (LV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 3% | – | 32% | 4% | – | – | 1% | – | 4% | – | 3% | – | 13% | – | – | – | – | 11% | 29% | – |
| YouGov | Aug 30 – Sep 1, 2021 | 1,618 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 1% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 24% | 5% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 7% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 4%[h] | – | 39% |
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | Aug 26–29, 2021 | 1,088 (LV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 4% | – | 29% | 4% | – | – | 1% | – | – | – | – | 0% | 22% | – | – | – | – | 9% | 30% | – |
| Public Policy Institute of California | Aug 20–29, 2021 | 1,080 (LV) | ± 4.5% | – | – | 3% | – | 26% | 5% | – | – | 1% | – | 3% | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14% | 24% | 25% |
| SurveyUSA | Aug 26–28, 2021 | 515 (LV) | ± 5.2% | – | 5% | 6% | 2% | 27% | 5% | – | – | 2% | – | 5% | – | 5% | – | 6% | 3% | 5% | 2% | – | 12% | 14% | – |
| Gravis Marketing | Aug 25–27, 2021 | 729 (LV) | ± 3.6% | – | – | 4% | – | 22% | 6% | 1% | 2% | 3% | 3% | 4% | – | – | – | 18% | – | – | – | – | 16% | 21% | – |
| Targoz Market Research | Aug 23–25, 2021 | 787 (LV) | ± 3.5% | – | – | 13% | – | 12% | 7% | – | – | 3% | – | 3% | – | – | 2% | 13% | – | – | – | – | 4% | 20% | 23% |
| Change Research (D) | Aug 22–25, 2021 | 782 (LV) | ± 3.7% | – | 2% | 2% | – | 27% | 3% | – | – | 1% | – | 4% | – | 5% | 1% | 6% | – | 3% | – | 3% | 7% | 15% | 22% |
| YouGov | Aug 6–12, 2021 | 1,534 (LV) | ± 3.8% | – | – | 3% | – | 23% | 3% | 2% | 1% | 2% | – | 3% | – | – | 2% | 13% | – | – | – | – | 5% | 25% | 20% |
| SurveyUSA | Aug 2–4, 2021 | 545 (LV) | ± 5.4% | – | – | 10% | – | 23% | 5% | – | – | 4% | – | 3% | – | – | 4% | 27% | – | – | – | – | 5% | 20% | – |
| Emerson College | Jul 30 – Aug 1, 2021 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 7% | – | 23% | 4% | – | – | 7% | – | 5% | – | – | 0% | 1% | – | – | – | – | 14% | 40% | – |
| Core Decision Analytics | Jul 27–29, 2021 | 803 (RV) | ± 3.5% | 1% | 1% | 4% | 0% | 9% | 3% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 2% | 0% | 1% | 9%[i] | 34% | 22% |
| ~728 (LV) | ± 3.6% | 1% | 1% | 4% | 0% | 10% | 3% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 2% | 0% | 1% | 8%[j] | 32% | 22% | ||
| Berkeley IGS | Jul 18–24, 2021 | 5,795 (RV) | ± 2.0% | 1% | 2% | 7% | 1% | 12% | 8% | 0% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 3% | 0% | 2% | 1% | 5% | – | 2% | 1% | 2% | 1%[k] | 44% | – |
| 3,266 (LV) | ± 2.5% | 0% | 1% | 10% | 1% | 18% | 10% | 0% | 1% | 3% | 1% | 5% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 3% | – | 1% | 0% | 2% | 1%[l] | 40% | – | ||
| Emerson College | Jul 19–20, 2021 | 1,085 (RV) | ± 2.9% | – | – | 6% | – | 16% | 6% | – | – | 4% | – | 4% | – | – | 0% | 2% | – | – | – | – | 8% | 53% | – |
| Moore Information Group (R)[A] | Jun 1–3, 2021 | 800 (RV) | ± 3.0% | – | – | 22% | – | – | 11% | – | – | 6% | – | – | – | – | 4% | – | – | – | – | – | 18% | 39% | – |
| 682 (LV) | ± 4.0% | – | – | 24% | – | – | 12% | – | – | 6% | – | – | – | – | 4% | – | – | – | – | – | 17% | 37% | – | ||
| SurveyUSA | Apr 30 – May 2, 2021 | 642 (RV) | ± 5.3% | – | – | 9% | – | – | 3% | – | – | 5% | – | – | – | – | 2% | – | – | – | – | – | 17%[m] | 26% | 38% |
- Full-field ballot including potential Democratic candidates
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[c] |
Margin of error |
John Cox (R) |
Kevin de León (D) |
Kevin Faulconer (R) |
Caitlyn Jenner (R) |
Doug Ose (R) |
Tom Steyer (D) |
Antonio Villaraigosa (D) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moore Information Group (R)[A] | Jun 1–3, 2021 | 800 (RV) | ± 3.0% | 16% | 4% | 7% | 4% | 2% | 5% | 9% | 14% | 38% |
| 682 (LV) | ± 4.0% | 18% | 4% | 8% | 4% | 2% | 5% | 8% | 13% | 37% |
- Antonio Villaraigosa vs. Kevin Faulconer
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[c] |
Margin of error |
Antonio Villaraigosa (D) |
Kevin Faulconer (R) |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPA Intelligence (R)[C] | Feb 12–14, 2021 | 645 (LV) | ± 3.9% | 28% | 31% | 41% |
Results[edit]
The recall election result was officially certified on October 22, 2021.[326] Newsom had survived the recall with similar results as his first run for governor. No on recall votes exceeded that of what the votes Newsom received in 2018 by 200,000 votes and had a similar vote percentage as well. No on recall had also won nearly all counties that Newsom had, save for Merced County that voted for the recall by 4 points.
Substantially fewer voters voted on the second question regarding replacement candidates than had voted on the first question regarding whether Newsom should be recalled.
One surprise in the results of the replacement candidate vote was the fourth-place finish of little-known contender Brandon M. Ross.[327]
| 2021 California gubernatorial recall election (question 1)[328][329][330] | |||
| Choice | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No on recall | 7,944,092 | 61.88 | |
| Yes on recall | 4,894,473 | 38.12 | |
| Blank and invalid votes | 54,013 | – | |
| Total votes | 12,892,578 | 100 | |
| Registered voters and turnout | 22,057,154 | 58.45% | |

- 20–30%
- 30–40%
- 40–50%
- 50–60%
- 60–70%
- 20–30%
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Larry Elder | 3,563,867 | 48.4% | |
| Democratic | Kevin Paffrath | 706,778 | 9.6% | |
| Republican | Kevin Faulconer | 590,346 | 8.0% | |
| Democratic | Brandon M. Ross | 392,029 | 5.3% | |
| Republican | John Cox | 305,095 | 4.1% | |
| Republican | Kevin Kiley | 255,490 | 3.5% | |
| Democratic | Jacqueline McGowan | 214,242 | 2.9% | |
| Democratic | Joel Ventresca | 186,345 | 2.5% | |
| Democratic | Daniel Watts | 167,355 | 2.3% | |
| Democratic | Holly L. Baade | 92,218 | 1.3% | |
| Democratic | Patrick Kilpatrick | 86,617 | 1.2% | |
| Democratic | Armando "Mando" Perez-Serrato | 85,061 | 1.2% | |
| Republican | Caitlyn Jenner | 75,215 | 1.0% | |
| Democratic | John R. Drake | 68,545 | 0.9% | |
| Green | Dan Kapelovitz | 64,375 | 0.9% | |
| Libertarian | Jeff Hewitt | 50,378 | 0.7% | |
| Republican | Ted Gaines | 47,937 | 0.7% | |
| No party preference | Angelyne | 35,900 | 0.5% | |
| No party preference | David Moore[note 9] | 31,224 | 0.4% | |
| Republican | Anthony Trimino | 28,101 | 0.4% | |
| Republican | Doug Ose | 26,204 | 0.4% | |
| No party preference | Michael Loebs[note 10] | 25,468 | 0.3% | |
| Green | Heather Collins | 24,260 | 0.3% | |
| No party preference | Major Singh | 21,394 | 0.3% | |
| Republican | David Lozano | 19,945 | 0.3% | |
| Republican | Denver Stoner | 19,588 | 0.3% | |
| Republican | Sam Gallucci | 18,134 | 0.2% | |
| Republican | Steve Chavez Lodge | 17,435 | 0.2% | |
| Republican | Jenny Rae Le Roux | 16,032 | 0.2% | |
| Republican | David Alexander Bramante | 11,501 | 0.2% | |
| Republican | Diego Martinez | 10,860 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Robert C. Newman II | 10,602 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Sarah Stephens | 10,583 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | Dennis Richter[note 11] | 10,468 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Major Williams (write-in) | 8,965 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | Denis Lucey | 8,182 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | James G. Hanink[note 12] | 7,193 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Daniel Mercuri | 7,110 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Chauncey "Slim" Killens | 6,879 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Leo S. Zacky | 6,099 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | Kevin Kaul | 5,600 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | David Hillberg | 4,435 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | Adam Papagan | 4,021 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Rhonda Furin | 3,964 | 0.1% | |
| Republican | Nickolas Wildstar | 3,811 | 0.1% | |
| No party preference | Jeremiah "Jeremy" Marciniak | 2,894 | 0.0% | |
| Republican | Joe M. Symmon | 2,397 | 0.0% | |
| No party preference | Miki Habryn (write-in) | 137 | 0.0% | |
| Democratic | Roxanne (write-in) | 116 | 0.0% | |
| Democratic | Stacy Smith (write-in) | 81 | 0.0% | |
| No party preference | Vivek B. Mohan (write-in) | 68 | 0.0% | |
| American Independent | Thuy E. Hugens (write-in) | 19 | 0.0% | |
| No party preference | Vince Lundgren (write-in) | 5 | 0.0% | |
| Total valid votes | 7,361,568 | 100 | ||
| Invalid or blank votes | 5,531,010 | 42.90% | ||
| Turnout | 12,892,578 | 58.45% | ||
| Registered electors | 22,057,154 | |||
By county[edit]
On recall question[edit]
Here are the results of the recall election by county. Khaki represents counties won by No. Light blue represents counties won by Yes.[329]
| County | No | Yes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | # | % | # | |
| Alameda | 81.2% | 465,901 | 18.8% | 108,081 |
| Alpine | 61.1% | 354 | 38.9% | 225 |
| Amador | 35.0% | 6,957 | 65.0% | 12,895 |
| Butte | 45.6% | 36,128 | 54.4% | 43,129 |
| Calaveras | 35.5% | 8,320 | 64.5% | 15,133 |
| Colusa | 33.4% | 2,027 | 66.6% | 4,037 |
| Contra Costa | 71.4% | 324,747 | 28.6% | 130,058 |
| Del Norte | 40.1% | 3,505 | 59.9% | 5,243 |
| El Dorado | 40.6% | 39,907 | 59.4% | 58,393 |
| Fresno | 48.7% | 126,488 | 51.3% | 133,309 |
| Glenn | 28.2% | 2,485 | 71.8% | 6,331 |
| Humboldt | 64.0% | 33,164 | 36.0% | 18,621 |
| Imperial | 59.4% | 19,288 | 40.6% | 13,177 |
| Inyo | 45.9% | 3,502 | 54.1% | 4,134 |
| Kern | 38.2% | 81,030 | 61.8% | 131,061 |
| Kings | 36.3% | 11,242 | 63.7% | 19,710 |
| Lake | 51.0% | 11,367 | 49.0% | 10,923 |
| Lassen | 15.8% | 1,604 | 84.2% | 8,538 |
| Los Angeles | 70.8% | 2,077,859 | 29.2% | 855,940 |
| Madera | 38.8% | 16,233 | 61.2% | 25,638 |
| Marin | 81.7% | 108,599 | 18.3% | 24,273 |
| Mariposa | 38.6% | 3,376 | 61.4% | 5,378 |
| Mendocino | 64.7% | 22,093 | 35.3% | 12,075 |
| Merced | 48.0% | 27,867 | 52.0% | 30,210 |
| Modoc | 22.0% | 730 | 78.0% | 2,593 |
| Mono | 55.5% | 2,805 | 44.5% | 2,245 |
| Monterey | 67.9% | 80,664 | 32.1% | 38,169 |
| Napa | 67.6% | 38,948 | 32.4% | 18,681 |
| Nevada | 54.0% | 29,851 | 46.0% | 25,426 |
| Orange | 51.7% | 586,457 | 48.3% | 547,685 |
| Placer | 42.6% | 85,677 | 57.4% | 115,411 |
| Plumas | 36.8% | 3,408 | 63.2% | 5,842 |
| Riverside | 49.5% | 355,630 | 50.5% | 362,958 |
| Sacramento | 59.9% | 329,952 | 40.1% | 220,498 |
| San Benito | 57.8% | 12,718 | 42.2% | 9,276 |
| San Bernardino | 50.2% | 288,877 | 49.8% | 286,364 |
| San Diego | 57.2% | 674,670 | 42.8% | 505,081 |
| San Francisco | 86.1% | 292,744 | 13.9% | 47,193 |
| San Joaquin | 52.6% | 105,405 | 47.4% | 94,877 |
| San Luis Obispo | 52.8% | 68,429 | 47.2% | 61,203 |
| San Mateo | 77.9% | 227,368 | 22.1% | 64,390 |
| Santa Barbara | 61.8% | 94,219 | 38.2% | 58,149 |
| Santa Clara | 73.7% | 468,851 | 26.3% | 166,995 |
| Santa Cruz | 78.1% | 90,874 | 21.9% | 25,454 |
| Shasta | 30.4% | 22,592 | 69.6% | 51,608 |
| Sierra | 36.6% | 616 | 63.4% | 1,065 |
| Siskiyou | 38.1% | 6,961 | 61.9% | 11,295 |
| Solano | 62.7% | 97,935 | 37.3% | 58,372 |
| Sonoma | 73.7% | 160,602 | 26.3% | 57,419 |
| Stanislaus | 45.5% | 69,247 | 54.5% | 82,911 |
| Sutter | 36.2% | 11,593 | 63.8% | 20,458 |
| Tehama | 27.6% | 6,386 | 72.4% | 16,770 |
| Trinity | 43.8% | 2,106 | 56.2% | 2,699 |
| Tulare | 38.9% | 41,009 | 61.1% | 64,372 |
| Tuolumne | 38.4% | 9,850 | 61.6% | 15,832 |
| Ventura | 57.2% | 182,470 | 42.8% | 136,610 |
| Yolo | 67.9% | 52,444 | 32.1% | 24,769 |
| Yuba | 34.2% | 7,961 | 65.8% | 15,291 |
| Totals | 61.88% | 7,944,092 | 38.12% | 4,894,473 |
On replacement candidates[edit]
Here are the results of the election by county for replacement candidates. Red represents counties won by Elder. Blue represents a county won by Paffrath.
| County | Elder | Paffrath | Faulconer | Ross | Others | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | # | |
| Alameda | 26.83% | 68,410 | 18.65% | 47,543 | 7.36% | 18,755 | 6.69% | 17,067 | 40.48% | 103,203 |
| Alpine | 48.01% | 157 | 7.65% | 25 | 3.98% | 13 | 4.89% | 16 | 35.47% | 116 |
| Amador | 60.68% | 8,862 | 3.20% | 467 | 7.30% | 1,066 | 2.09% | 305 | 26.74% | 3,905 |
| Butte | 52.41% | 28,705 | 6.48% | 3,547 | 3.80% | 2,083 | 3.43% | 1,876 | 33.88% | 18,555 |
| Calaveras | 62.61% | 10,660 | 2.93% | 499 | 6.33% | 1,077 | 1.81% | 309 | 26.32% | 4,481 |
| Colusa | 54.48% | 2,574 | 3.45% | 163 | 4.08% | 193 | 2.33% | 110 | 35.66% | 1,685 |
| Contra Costa | 37.99% | 91,262 | 12.78% | 30,696 | 7.15% | 17,165 | 8.08% | 19,407 | 34.00% | 81,670 |
| Del Norte | 64.23% | 4,094 | 4.14% | 264 | 2.68% | 171 | 3.36% | 214 | 25.59% | 1,631 |
| El Dorado | 53.01% | 37,507 | 4.76% | 3,368 | 7.30% | 5,162 | 2.77% | 1,959 | 32.16% | 22,753 |
| Fresno | 59.85% | 103,060 | 5.55% | 9,551 | 7.27% | 12,514 | 3.14% | 5,411 | 24.20% | 41,669 |
| Glenn | 58.60% | 4,202 | 2.86% | 205 | 2.23% | 160 | 2.15% | 154 | 34.17% | 2,450 |
| Humboldt | 45.58% | 13,483 | 8.55% | 2,528 | 3.87% | 1,145 | 5.11% | 1,511 | 36.89% | 10,911 |
| Imperial | 50.25% | 9,564 | 5.73% | 1,091 | 4.17% | 793 | 8.15% | 1,551 | 31.70% | 6,033 |
| Inyo | 63.05% | 3,275 | 4.95% | 257 | 6.55% | 340 | 3.31% | 172 | 22.14% | 1,150 |
| Kern | 67.79% | 99,969 | 4.87% | 7,188 | 4.50% | 6,634 | 1.41% | 2,076 | 21.43% | 31,609 |
| Kings | 66.81% | 15,577 | 4.25% | 991 | 5.17% | 1,205 | 2.04% | 476 | 21.73% | 5,067 |
| Lake | 52.23% | 7,259 | 4.77% | 663 | 3.54% | 492 | 3.42% | 475 | 36.04% | 5,008 |
| Lassen | 69.58% | 6,293 | 1.43% | 129 | 2.58% | 233 | 1.25% | 113 | 25.17% | 2,276 |
| Los Angeles | 43.59% | 648,067 | 10.22% | 151,944 | 8.29% | 123,331 | 7.93% | 117,961 | 29.97% | 445,562 |
| Madera | 65.13% | 19,530 | 3.12% | 936 | 6.52% | 1,954 | 2.20% | 660 | 23.04% | 6,908 |
| Marin | 29.88% | 15,901 | 16.57% | 8,817 | 12.06% | 6,417 | 11.65% | 6,198 | 29.85% | 15,887 |
| Mariposa | 63.14% | 4,086 | 4.99% | 323 | 5.97% | 386 | 2.50% | 162 | 23.40% | 1,514 |
| Mendocino | 42.40% | 7,799 | 7.51% | 1,382 | 4.75% | 873 | 4.08% | 750 | 41.26% | 7,589 |
| Merced | 61.54% | 21,830 | 4.30% | 1,525 | 3.75% | 1,329 | 2.24% | 796 | 28.17% | 9,993 |
| Modoc | 62.01% | 1,753 | 1.84% | 52 | 2.12% | 60 | 1.27% | 36 | 32.76% | 926 |
| Mono | 53.40% | 1,690 | 8.78% | 278 | 7.74% | 245 | 3.70% | 117 | 26.38% | 835 |
| Monterey | 44.39% | 27,841 | 11.37% | 7,130 | 4.92% | 3,088 | 5.35% | 3,354 | 33.98% | 21,312 |
| Napa | 43.02% | 12,613 | 9.73% | 2,853 | 7.17% | 2,101 | 6.28% | 1,841 | 33.80% | 9,909 |
| Nevada | 47.97% | 16,546 | 6.93% | 2,390 | 8.24% | 2,841 | 3.33% | 1,149 | 33.53% | 11,564 |
| Orange | 57.37% | 423,224 | 8.09% | 59,694 | 7.74% | 57,109 | 3.61% | 26,599 | 23.19% | 171,030 |
| Placer | 52.02% | 73,309 | 5.11% | 7,207 | 7.53% | 10,613 | 2.92% | 4,110 | 32.42% | 45,681 |
| Plumas | 57.46% | 3,918 | 3.37% | 230 | 6.22% | 424 | 2.11% | 144 | 30.84% | 2,103 |
| Riverside | 60.70% | 283,217 | 6.01% | 28,046 | 5.83% | 27,214 | 3.94% | 18,379 | 23.52% | 109,740 |
| Sacramento | 45.93% | 147,776 | 8.89% | 28,585 | 8.88% | 28,579 | 5.21% | 16,772 | 31.09% | 100,010 |
| San Benito | 49.03% | 6,848 | 9.21% | 1,287 | 3.32% | 464 | 4.57% | 638 | 33.87% | 4,731 |
| San Bernardino | 61.59% | 225,674 | 5.47% | 20,042 | 5.27% | 19,296 | 3.85% | 14,119 | 23.82% | 87,295 |
| San Diego | 46.58% | 355,417 | 10.76% | 82,089 | 14.96% | 114,155 | 4.10% | 31,289 | 23.59% | 180,009 |
| San Francisco | 20.95% | 26,285 | 21.07% | 26,434 | 11.41% | 14,317 | 6.69% | 8,387 | 39.87% | 50,015 |
| San Joaquin | 54.16% | 68,230 | 5.59% | 7,047 | 6.26% | 7,889 | 5.60% | 7,058 | 28.38% | 35,756 |
| San Luis Obispo | 53.68% | 45,298 | 10.90% | 9,195 | 6.64% | 5,607 | 2.92% | 2,460 | 25.87% | 21,829 |
| San Mateo | 30.82% | 41,162 | 17.43% | 23,271 | 8.87% | 11,845 | 7.62% | 10,179 | 35.26% | 47,091 |
| Santa Barbara | 49.04% | 43,582 | 10.51% | 9,344 | 6.66% | 5,921 | 4.09% | 3,633 | 29.69% | 26,389 |
| Santa Clara | 32.79% | 105,590 | 17.86% | 57,503 | 7.50% | 24,166 | 6.70% | 21,568 | 35.15% | 113,197 |
| Santa Cruz | 31.49% | 17,494 | 17.21% | 9,562 | 5.33% | 2,960 | 7.42% | 4,123 | 38.55% | 21,420 |
| Shasta | 60.09% | 36,022 | 3.21% | 1,922 | 2.72% | 1,631 | 2.65% | 1,586 | 31.34% | 18,788 |
| Sierra | 56.70% | 698 | 2.84% | 35 | 7.47% | 92 | 1.22% | 15 | 31.76% | 391 |
| Siskiyou | 60.89% | 8,127 | 3.30% | 441 | 2.99% | 399 | 3.08% | 411 | 29.74% | 3,970 |
| Solano | 47.18% | 40,387 | 6.79% | 5,813 | 6.23% | 5,336 | 8.33% | 7,132 | 31.47% | 26,935 |
| Sonoma | 37.42% | 38,131 | 12.69% | 12,936 | 6.69% | 6,821 | 7.75% | 7,903 | 35.44% | 36,119 |
| Stanislaus | 57.99% | 58,812 | 4.02% | 4,075 | 6.74% | 6,835 | 5.45% | 5,526 | 25.80% | 26,171 |
| Sutter | 52.54% | 12,440 | 3.63% | 859 | 5.21% | 1,233 | 2.53% | 598 | 36.10% | 8,546 |
| Tehama | 61.90% | 11,529 | 2.83% | 527 | 2.42% | 451 | 1.65% | 307 | 31.20% | 5,812 |
| Trinity | 53.38% | 1,770 | 3.41% | 113 | 2.59% | 86 | 2.20% | 73 | 38.42% | 1,274 |
| Tulare | 67.64% | 51,152 | 3.85% | 2,912 | 5.61% | 4,241 | 2.46% | 1,859 | 20.45% | 15,464 |
| Tuolumne | 62.58% | 11,374 | 3.32% | 603 | 5.60% | 1,017 | 2.41% | 438 | 26.09% | 4,742 |
| Ventura | 56.44% | 108,043 | 7.79% | 14,908 | 7.51% | 14,372 | 3.76% | 7,201 | 24.50% | 46,909 |
| Yolo | 37.19% | 15,911 | 10.40% | 4,450 | 10.74% | 4,596 | 6.83% | 2,921 | 34.83% | 14,900 |
| Yuba | 54.86% | 9,878 | 4.68% | 843 | 4.73% | 851 | 2.08% | 375 | 33.65% | 6,060 |
| Totals | 48.41% | 3,563,867 | 9.60% | 706,778 | 8.02% | 590,346 | 5.33% | 392,029 | 28.64% | 2,108,548 |
By congressional district[edit]
On recall question[edit]
Khaki represents congressional districts won by No. Light blue represents congressional districts won by Yes.[336] All districts with incumbent Democratic representatives voted for No except one, and all districts with incumbent Republican representatives voted for Yes except two.
On replacement candidates[edit]
Elder swept all congressional districts except two, losing to Paffrath in 12th and 13th districts: the latter was the best performance for both Paffrath and Newsom.[337] Conversely, Elder's best result was in the 23rd district, which supported recalling Newsom the most.
| District | Elder | Paffrath | Faulconer | Ross | Representative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 57.07% | 4.44% | 4.17% | 2.68% | Doug LaMalfa |
| 2nd | 38.5% | 12.19% | 7.57% | 7.83% | Jared Huffman |
| 3rd | 49.32% | 6.04% | 6.69% | 5.76% | John Garamendi |
| 4th | 55.02% | 4.67% | 7.28% | 2.74% | Tom McClintock |
| 5th | 39.35% | 11.14% | 5.96% | 7.18% | Mike Thompson |
| 6th | 38.75% | 11.26% | 9.75% | 6.26% | Doris Matsui |
| 7th | 49.11% | 7.71% | 8.67% | 4.86% | Ami Bera |
| 8th | 66.79% | 4.45% | 4.71% | 2.5% | Jay Obernolte |
| 9th | 52.46% | 6.28% | 5.63% | 6.47% | Jerry McNerney |
| 10th | 57.57% | 4.38% | 6.46% | 5.75% | Josh Harder |
| 11th | 35.14% | 14.07% | 8.39% | 7.66% | Mark DeSaulnier |
| 12th | 19.82% | 21.65% | 11.7% | 6.8% | Nancy Pelosi |
| 13th | 14.65% | 24.49% | 8.31% | 7.47% | Barbara Lee |
| 14th | 31.02% | 16.88% | 8.3% | 7.52% | Jackie Speier |
| 15th | 36.62% | 14.15% | 6.81% | 6.4% | Eric Swalwell |
| 16th | 56.51% | 5.49% | 4.97% | 3.15% | Jim Costa |
| 17th | 30.95% | 17.39% | 6.96% | 6.92% | Ro Khanna |
| 18th | 31.53% | 20.14% | 9.63% | 6.86% | Anna Eshoo |
| 19th | 35.79% | 15.05% | 5.75% | 6.33% | Zoe Lofgren |
| 20th | 40.06% | 13.24% | 4.85% | 6.0% | Jimmy Panetta |
| 21st | 62.06% | 5.29% | 4.49% | 2.61% | David Valadao |
| 22nd | 64.59% | 4.72% | 7.5% | 2.73% | Devin Nunes |
| 23rd | 68.27% | 4.44% | 4.78% | 1.61% | Kevin McCarthy |
| 24th | 51.41% | 10.69% | 6.66% | 3.51% | Salud Carbajal |
| 25th | 60.07% | 5.92% | 6.16% | 3.45% | Mike Garcia |
| 26th | 54.97% | 8.22% | 7.83% | 4.07% | Julia Brownley |
| 27th | 45.39% | 9.48% | 10.45% | 7.51% | Judy Chu |
| 28th | 39.36% | 12.99% | 9.72% | 6.99% | Adam Schiff |
| 29th | 37.1% | 10.46% | 5.67% | 7.41% | Tony Cárdenas |
| 30th | 46.13% | 10.44% | 9.53% | 6.81% | Brad Sherman |
| 31st | 58.83% | 5.92% | 5.92% | 4.09% | Pete Aguilar |
| 32nd | 49.47% | 7.18% | 5.95% | 9.05% | Grace Napolitano |
| 33rd | 46.93% | 11.43% | 13.37% | 5.52% | Ted Lieu |
| 34th | 24.59% | 13.66% | 8.25% | 11.51% | Jimmy Gomez |
| 35th | 52.46% | 7.17% | 4.82% | 6.73% | Norma Torres |
| 36th | 57.48% | 6.46% | 5.66% | 6.1% | Raul Ruiz |
| 37th | 26.32% | 15.24% | 11.14% | 15.27% | Karen Bass |
| 38th | 50.43% | 7.12% | 5.28% | 12.94% | Linda Sánchez |
| 39th | 58.04% | 7.15% | 7.28% | 6.78% | Young Kim |
| 40th | 34.86% | 9.86% | 3.89% | 13.74% | Lucille Roybal-Allard |
| 41st | 55.31% | 7.02% | 5.26% | 4.22% | Mark Takano |
| 42nd | 65.62% | 5.16% | 6.01% | 2.52% | Ken Calvert |
| 43rd | 39.44% | 11.72% | 6.84% | 5.68% | Maxine Waters |
| 44th | 35.85% | 10.45% | 3.9% | 6.17% | Nanette Barragán |
| 45th | 57.5% | 9.09% | 8.08% | 3.52% | Katie Porter |
| 46th | 44.63% | 10.25% | 5.73% | 4.35% | Lou Correa |
| 47th | 48.67% | 9.92% | 7.56% | 3.72% | Alan Lowenthal |
| 48th | 60.31% | 7.34% | 8.58% | 2.77% | Michelle Steel |
| 49th | 54.14% | 9.15% | 12.51% | 3.44% | Mike Levin |
| 50th | 58.89% | 6.27% | 11.37% | 2.74% | Darrell Issa |
| 51st | 40.35% | 12.05% | 10.79% | 5.36% | Juan Vargas |
| 52nd | 41.9% | 12.53% | 19.15% | 4.73% | Scott Peters |
| 53rd | 40.3% | 13.01% | 15.1% | 4.84% | Sara Jacobs |
Aftermath[edit]
Turnout and participation[edit]
The number of valid votes cast on the recall question (question 1) was vastly greater than the number cast on the replacement question (question 2). The Newsom campaign's official message to voters had been to vote "no" on the recall and to ignore the replacement question.[338][339]
Commentary after election[edit]
In an October 2021 interview with Chuck Todd at the Milken Institute Global Conference, Newsom commented on the personal impact of the recall, saying "it's hard", and that it was the result of "personal stupidity", which "took a life of its own" and was "weaponized" by opponents, and, "I mean, we colored it in. I took responsibility."[340]
Recall candidate Larry Elder's support for the Trump administration, being unpopular among California's electorate, as well as his status as a front-runner and likely gubernatorial replacement if the recall was successful, were reported to have helped Newsom defeat it.[341][342] Mid-summer polling conducted two months prior to election day suggested a close race.[341][342] Newsom ultimately defeated the recall with a margin of roughly 24 percent after mobilizing Democrats to vote with a message that framed the race as a referendum on him versus Elder and their pandemic policy proposals.[343] Newsom's campaigning had also invoked Elder's connections to the inner circle of former President Donald Trump,[341][342] as well as his history of provocative right-wing rhetoric as a radio talk show host.[344] Exit polling suggested the result fell along partisan lines, with 94 percent of self-reported Democrats saying they voted against the recall and 89 percent of self-reported Republicans saying they voted to remove Newsom from office.[343]
The recall was widely invoked following the victory of Republican Glenn Youngkin two months later in the 2021 Virginia gubernatorial election (where Democrat Joe Biden had won in 2020 by 10 points); Virginia's race featured similar campaigning on education, the pandemic, and former President Trump.[345][346][347]
See also[edit]
- 1921 North Dakota gubernatorial recall election
- 2003 California gubernatorial recall election
- 2012 Wisconsin gubernatorial recall election
- 2021 United States gubernatorial elections
- 2022 California gubernatorial election
Notes[edit]
General polling notes[edit]
- ^ All individuals listed below are Republicans, except the ones labeled with a different party affiliation.
- ^ All individuals listed below are Democrats, except the ones labeled with a different party affiliation.
- ^ a b c d Key:
A – all adults
RV – registered voters
LV – likely voters
V – unclear - ^ Includes "won't vote" with 3%
- ^ Weighted by vote propensity
- ^ Includes "would not vote" with 6%
- ^ Calculated by taking the difference of 100% and all other candidates combined.
- ^ Stoner, Loebs, Trimino, and Moore with 1%; Lozano, Collins, Newman, Lodge, Richter, Martinez, Gallucci, Symmon, Furin, Le Roux, Stephens, Hillberg, Kaul, Hanink, Papagan, Marciniak, Lucey, Killens, Wildstar, Singh, Zacky, Bramante, and Mercuri with 0%
- ^ Bramante, Gallucci, Lodge, Lozano, Lucey, Marciniak, Stoner, Trimino, and Wildstar with 1%; Collins, Furin, Hanink, Hillberg, Kaul, Killens, Le Roux, Loebs, Martinez, Mercuri, Moore, Newman, Papagan, Richter, Singh, Stephens, Symmon, and Zacky with 0%
- ^ Bramante, Lodge, Lozano, Lucey, Marciniak, Stoner, Trimino, and Wildstar with 1%; Collins, Furin, Gallucci, Hanink, Hillberg, Kaul, Killens, Le Roux, Loebs, Martinez, Mercuri, Moore, Newman, Papagan, Richter, Singh, Stephens, Symmon, and Zacky with 0%
- ^ Singh with 1%; Collins, Gallucci, Hanink, Loebs, Mercuri, Moore, Lodge, Lozano, Lucey, Bramante, Leroux, Martinez, Stoner, Newman, Richter, Stephens, Trimino, Zacky, Killens, and Wildstar with 0%
- ^ Singh with 1%; Gallucci, Collins, Lodge, Mercuri, Hanink, Moore, Richter, Killens, Leroux, Loebs, Martinez, and Trimino with 0%
- ^ Grenell with 5%; Cernovich, Mercuri, Moorlach, and Williams with 3%
Polling sponsor notes[edit]
Other[edit]
- ^ Due to legislation introduced by state Democratic lawmakers in 2017 to delay or prevent the recall of Democratic State Senator Josh Newman[46]
- ^ The law also imposed a similar disclosure requirement on presidential candidates, primarily aimed at forcing Donald Trump to release his most recent tax returns when he ran in 2020. The disclosure requirement for presidential candidates was struck down by the courts.[137]
- ^ a b Southern California News Group has a single central editorial board for all of its newspapers, which include Daily Breeze, Inland Valley Daily Bulletin, Press-Telegram, Los Angeles Daily News, Orange County Register, Pasadena Star-News, Redlands Daily Facts, The Press-Enterprise, The San Bernardino Sun, San Gabriel Valley Tribune, and Whittier Daily News.[221]
- ^ McClatchy issued a joint endorsement by the editorial boards for its California newspapers, which include The Sacramento Bee, The Fresno Bee, Merced Sun-Star, The Modesto Bee, The San Luis Obispo Tribune, and The Beaufort Gazette.[citation needed]
- ^ The California Rifle and Pistol Association is the official California branch of the National Rifle Association.[305]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o The press release announcing the endorsement was made before the recall was announced, so the press release only references the 2022 campaign for governor.[308] The endorsements have been reported, with less details, in mainstream media outlets.[309]
- ^ a b c Endorser also gave a "no" endorsement on the recall question
- ^ As a political organizer, Heatlie directed the successful effort to collect recall petition signatures from voters, which ultimately led to the recall election.[318]
- ^ Moore was listed on the ballot as a "no party preference" because the Socialist Equality Party did not have ballot access in the State of California at the time the ballot was printed.[293]
- ^ Loebs was listed on the ballot as a "no party preference" because the California National Party did not have ballot access in the State of California at the time the ballot was printed.[331]
- ^ Richter was listed on the ballot as a "no party preference" because the Socialist Workers Party did not have ballot access in the State of California at the time the ballot was printed.[322]
- ^ Hanink was listed on the ballot as "no party preference" and listed in the official Voter Information Guide as "no qualified party preference" because the party with which Hanink was registered, the American Solidarity Party, did not have ballot access at the time the ballot was printed. The party is attempting to qualify for ballot access in time for the 2022 California primaries.[332][333][334][335]
References[edit]
- ^ "Recall Question – Statewide Results". September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 14, 2021.
- ^ "California Recall Newsom Recall Vote". September 15, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ Korte, Lara (July 1, 2021). "Gavin Newsom recall election date set: California voters to cast ballots in September". The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved July 1, 2021.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (July 1, 2021). "It's a date: Newsom recall election set for Sept. 14". CalMatters.
- ^ a b Blood, Michael R. (September 15, 2021). "GOP's Elder concedes California recall, hints: 'Stay tuned'". Associated Press. Archived from the original on September 15, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ a b Prokop, Andrew (August 23, 2021). "How California's bizarre recall system could elect a Republican governor". Vox.
- ^ Olmsted, Kathryn (August 18, 2021). "Why Deep Blue California Could Elect a Bright Red Governor". The New York Times. Archived from the original on August 18, 2021.
- ^ a b Navarro, Aaron (February 1, 2021). "Recall threats are common in California. But the latest one against Gavin Newsom might get further than most". CBS News. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ^ a b Lozano, Alicia Victoria (December 20, 2020). "California governor faces recall effort amid pandemic, dining at famed French Laundry". NBC News. Retrieved May 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "Recall History in California (1913 to Present)". California Secretary of State.
- ^ Abruzzese, Sarah (February 19, 2021). "Gavin Newsom and the Coronavirus-Driven California Recall Effort". US News.
- ^ a b Brownstein, Ronald (May 13, 2021). "The Trouble With the Gavin Newsom Recall". The Atlantic. Retrieved May 26, 2021.
- ^ "PETITION FOR RECALL" (PDF). rescuecalifornia.org.
- ^ Cillizza, Chris (December 15, 2020). "How it all went so wrong for Gavin Newsom". CNN. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ a b "Gavin Newsom recall, Governor of California (2019–2021)". Ballotpedia. Retrieved May 9, 2021.
- ^ "PETITION FOR RECALL" (PDF). takecaback.org.
- ^ a b Marinucci, Carla (December 16, 2020). "Long shot Newsom recall drive gets serious in California". Politico. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved April 15, 2021.
- ^ a b c d ORRIN E. HEATLIE and CALIFORNIA PATRIOT COALITION – RECALL GOVERNOR GAVIN NEWSOM v. ALEX PADILLA (SUPERIOR COURT OF CALIFORNIA November 6, 2020), Text.
- ^ a b c "Official Recall Petition". recallgavin2020.com. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 3, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (February 19, 2021). "Newsom recall drive faces tight finish based on latest California data". Politico. Archived from the original on February 20, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ Tapp, Tom (February 19, 2021). "Gavin Newsom Recall Effort Delivers 1M Signatures To California Elections Officials". Deadline. Archived from the original on February 20, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2021.
- ^ a b Ronayne, Kathleen (April 1, 2021). "Meet Orrin Heatlie, the ex-cop leading the push to recall California Gov. Gavin Newsom". The Desert Sun.
[Heatlie] worked on the recall effort led by Erin Cruz, an unsuccessful candidate for U.S. House and Senate. Heatlie joined Cruz's group after seeing Newsom's immigration video and was made moderator of a Facebook group, using it to make contacts and assess the operation's flaws.
- ^ Siders, David (March 19, 2021). "The Three Men Who Could Take Down Gavin Newsom". Politico. Retrieved November 20, 2021.
- ^ "Recall of Governor Gavin Newsom, Filed by Orrin E. Heatlie: Extension of Time to Circulate Petitions and Revised Calendar of Events". memorandum No. 20251 of November 17, 2020 (PDF). Secretary of State of California.
- ^ Stone, Ken (November 6, 2020). "Newsom Recall Drive Gets New Life: Signature Deadline Delayed to March 17". Times of San Diego. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ Korte, Lara (March 15, 2021). "'Lost in the shuffle.' Did Democrats miss a chance to block a Newsom recall election?". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Luna, Taryn (November 18, 2020). "Photos raise doubts about Newsom's claim that dinner with lobbyist was outdoors amid COVID-19 surge". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (November 18, 2020). "Doctors' lobby execs joined Newsom at maskless dinner". CalMatters.
- ^ Nieves, Alexander (December 14, 2020). "Newsom's dinner party venue 'indoor' under new state guidelines". Politico. Archived from the original on February 4, 2021. Retrieved April 27, 2021.
- ^ "'I made a bad mistake': Newsom apologizes for attending French Laundry dinner party". KTLA. November 16, 2020.
- ^ a b Fuller, Thomas (November 18, 2020). "For California Governor the Coronavirus Message Is Do as I Say, Not as I Dine". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 19, 2020.
- ^ Melugin, Bill; Insheiwat, Shelly (November 18, 2020). "FOX 11 obtains exclusive photos of Gov. Newsom at French restaurant allegedly not following COVID-19 protocols". KTTV. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ Bikales, James (November 20, 2020). "How risky was that Napa party Gavin Newsom attended?". CalMatters.
- ^ Koseff, Alexei (November 17, 2020). "Newsom on French Laundry dinner party: 'I made a bad mistake'". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved November 18, 2020.
- ^ Sources that reference Newsom's attendance at The French Laundry as a contributor to the recall petition:
- Marinucci, Carla (November 25, 2020). "French Laundry snafu reignites longshot Newsom recall drive". Politico. Archived from the original on December 6, 2020. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- Victoria Lozano, Alicia (December 20, 2020). "Recall effort against California governor an attempt to 'destabilize the political system,' analysts say". NBC News. Archived from the original on January 10, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- Roos, Meghan (December 31, 2020). "Gavin Newsom Under Renewed Fire Over French Laundry Lobbyist as Recall Bid Gains Steam". Newsweek. Archived from the original on January 1, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- Siders, David; Marinucci, Carla (January 11, 2021). "'It's all fallen apart': Newsom scrambles to save California – and his career". Politico. Archived from the original on January 11, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- Pogue, James (February 3, 2021). "Gavin Newsom Is Blowing It". The New Republic. Archived from the original on February 5, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ a b Blood, Michael R. (March 17, 2021). "EXPLAINER: Why is California Gov. Newsom facing a recall?". ABC News.
- ^ Hoeven, Emily (August 4, 2021). "How much will California's EDD scandal cost Newsom in the recall election?". CalMatters.
- ^ a b Korte, Lara (March 29, 2021). "The origin of the Newsom recall had nothing to do with COVID-19. Here's why it began". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Harris, Mary (May 3, 2021). "Are Californians Still Mad at Gavin Newsom?". Slate Magazine.
- ^ a b Mason, Melanie; Mehta, Seema (September 16, 2021). "After recall flop, struggling California Republicans once again fighting over future". The Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Isenstadt, Alex (February 11, 2021). "National Republicans dive into Newsom recall push". Politico. Archived from the original on February 12, 2021. Retrieved February 15, 2021.
- ^ a b Tapp, Tom (January 15, 2021). "California Governor Gavin Newsom Refuses To Address Recall Effort, Called "California Coup," During Press Conference". Deadline. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ a b Marinucci, Carla (January 13, 2021). "California Democrats try to tie Newsom recall movement to Capitol attack". Politico. Archived from the original on January 13, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ Nichols, Chris (January 13, 2021). "No, Efforts To Recall California Gov. Newsom Are Not 'A Coup'". Cap Radio. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ Axelrod, Tal (March 18, 2021). "Newsom recall organizers submit 2.1 million signatures". The Hill. Archived from the original on March 19, 2021. Retrieved March 19, 2021.
- ^ Rakich, Nathaniel (May 4, 2021). "California Voters Should Start Preparing For A Recall Election". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Myers, John (April 26, 2021). "The exact date of the Newsom recall election is still unclear. Here's why". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (May 4, 2021). "There Are Enough Signatures To Trigger A Recall Of Gov. Gavin Newsom. Here's What You Need To Know". Cap Radio.
- ^ "Newsom to Face Recall Election Later This Year After Only 43 Petition Signatures Withdrawn". KGO-TV. June 23, 2021. Retrieved July 1, 2021 – via KABC-TV.
- ^ Koseff, Alexei (April 26, 2021). "Newsom recall has enough signatures to make ballot, California says". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved April 26, 2021.
- ^ Weber, Shirley (July 1, 2021). "Letter to Lt. Governor from SOS" (PDF). Office of the Secretary of State of California. Retrieved July 1, 2021.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (July 1, 2021). "It's a date: Newsom recall election set for Sept. 14". CalMatters. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Mays, Mackenzie (March 19, 2021). "Newsom's 'Zoom school' experience was in the past, office confirms". Politico Pro.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (March 12, 2021). "Newsom relied on Dodgers, donor-driven foundation for splashy state speech". Politico Pro.
- ^ Korte, Lara. "Fact check: Are Gavin Newsom's kids 'living through Zoom school'?". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b Hong, Joe (July 28, 2021). "Newsom recall: GOP challengers see parents as 'consumers'". CalMatters.
- ^ Kopan, Tal (July 21, 2021). "Kamala Harris says she will campaign for Gavin Newsom in recall fight". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (August 12, 2021). "Biden comes to Newsom's recall defense as White House mulls larger role". Politico.
- ^ Bollag, Sophia; Karte, Lara. "Kamala Harris to miss Gavin Newsom's recall defense rally after deadly Kabul bombings". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b Faith E. Pinho; Seema Mehta; Julia Wick; Robin Estrin (September 13, 2021). "In final campaign push with Newsom, Biden says 'eyes of the nation' are on California recall". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Holland, Steve (September 14, 2021). "Biden campaigns with California governor on eve of Republican-backed recall election". Reuters.
- ^ a b c d Ronayne, Kathleen; Blood, Michael R. (September 3, 2021). "Gov. Newsom calls GOP rivals 'anti-vax,' but are they?". Associated Press.
- ^ Martichoux, Alix (February 2, 2021). "Why do people want to recall Gov. Gavin Newsom? We explain". KGO-TV.
- ^ Bollag, Sophia (August 1, 2021). "Did Gavin Newsom do anything wrong? It wasn't just the French Laundry that led to the recall". Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (May 14, 2021). "3 things to know about Gov. Newsom's spending proposal". KXTV.
- ^ Mason, Melanie (May 15, 2021). "Gusher of federal stimulus funds a gift for governors like Gavin Newsom". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Gleason, Patrick (July 30, 2021). "Blue State Taxpayers To Receive A Reprieve". Forbes.
- ^ a b Skelton, George (May 20, 2021). "Column: Newsom is admonished for his big-spending budget by Sacramento's legislative analyst". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Myers, John (May 17, 2021). "Even with huge California surplus, Newsom's budget relies on reserves, analyst says". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "Analyst criticizes Newsom's spending plan as 'shortsighted'". KTXL. Associated Press. May 18, 2021.
- ^ Hoeven, Emily (July 14, 2021). "'Not sustainable': Jerry Brown bursts Newsom's budget bubble". CalMatters.
- ^ Tavlian, Alex (July 12, 2021). "Newsom's recall spending spree prompts a word of warning – from Jerry Brown". The Sun.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (May 10, 2021). "Facing A Recall And A Massive Surplus, Gov. Newsom Proposes More Stimulus Checks". NPR.
- ^ Flores, Jessica (July 1, 2021). "Here's when California's new round of $600 of stimulus checks are coming". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ Howland, Lena (July 13, 2021). "No, the relief package signed by Governor Newsom will not provide 'immediate' relief". KXTV.
- ^ McGreevy, Patrick (August 31, 2021). "State stimulus checks arrive in Californians' bank accounts ahead of recall election". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 31, 2021.
- ^ Hart, Angela (May 6, 2021). "Salesforce, Google, Facebook. How Big Tech Undermines California's Public Health System". KHN.org.
- ^ a b Bollag, Sophia (June 18, 2021). "Curb nonprofit donations? Republicans running in Newsom recall say it would reduce conflicts". The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b Pedroja, Cammy (June 4, 2021). "Gavin Newsom Says Corporate Donations to His Wife's Nonprofit Caused No Conflict of Interest". Newsweek. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Keene, Houston (March 15, 2021). "California's Newsom blames 'anti-mask and anti-vax extremists' for recall effort, vows to fight". Fox News. Archived from the original on March 15, 2021. Retrieved March 15, 2021.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla (March 15, 2021). "Warren, Sanders join Newsom to fight 'extremist' GOP recall". Politico. Archived from the original on March 15, 2021. Retrieved March 15, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B.; Marinucci, Carla; Yamamura, Kevin (March 24, 2021). "Newsom swats away Democratic challengers. Will his party live to regret it?". Politico Pro. Archived from the original on March 26, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ Willon, Phil (May 11, 2021). "Opposition to Newsom recall grows as Caitlyn Jenner, GOP generate little support, poll finds". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla (March 31, 2021). "Arnold Schwarzenegger has a warning for Gavin Newsom". Politico.
- ^ Lozano, Alicia Victoria (April 7, 2021). "'A Different Time': Why the Recall Effort Against California Gov. Newsom Isn't History Repeating". NBC News. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ^ Phil Willon (March 16, 2021). "Gavin Newsom and Democrats are dragging Donald Trump into the recall fight". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Myers, John (March 15, 2021). "Essential Politics: Making California's recall about Trump". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Ting, Eric (September 8, 2021). "Trump, without evidence, already claiming Gavin Newsom recall election is 'rigged'". SFGate. Retrieved September 8, 2021.
- ^ Green, Matthew (May 17, 2021). "When Can You Stop Wearing a Mask in California? State Says June 15". KQED.
- ^ Ting, Eric (May 14, 2021). "UCSF expert: California, San Francisco should 'immediately' lift mask mandates for vaccinated". SFGate.
- ^ Ting, Eric (May 17, 2021). "How heavily did recall politics weigh on Gavin Newsom's mask decision?". SFGate.
- ^ "Newsom Recall: Democrats Again Seeking To Alter California's Recall Laws". KPIX-TV. June 27, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (July 2, 2021). "New, Earlier Date Puts GOP At A Disadvantage In California Recall Election". NPR.
- ^ "Newsom can't tie recall election to GOP in voter guide, lawsuit says". KTLA. Associated Press. August 2, 2021.
- ^ Dolan, Maura (August 5, 2021). "Court ruling is final: Newsom may blame recall on 'Republicans and Trump supporters'". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (August 4, 2021). "Newsom can reference Trump in argument against recall, judge says". Politico.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (July 24, 2021). "California Republican Party creates recall endorsement path". Politico.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (August 7, 2021). "California GOP won't endorse a candidate in Newsom recall". Politico.
- ^ Mehta, Seema (August 7, 2021). "State GOP votes not to endorse a candidate in the recall race". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Myers, John; Mehta, Seema (August 9, 2021). "Newsom wants voters to ignore the recall ballot's second question. They don't have to". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ a b c d Cassidy, Christina A.; Brumback, Kate (September 3, 2021). "Experts call for rigorous audit to protect California recall". Associated Press. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ^ a b Seitz-Wald, Alex (September 13, 2021). "As Newsom leads California recall polls, Larry Elder pushes baseless fraud claims". NBC News. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Dale, Daniel. "Republicans are laying the groundwork to lie that the California recall was stolen". CNN.
- ^ "Randomized Alphabet :: California Secretary of State". California Secretary of State.
- ^ Blood, Michael R. (March 17, 2021). "Recall of State Officials". Associated Press. Archived from the original on April 6, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ "Article II, Section 13". Constitution of California. June 8, 1976.
- ^ "Article II, Clause B, Section 14". Constitution of California. June 8, 1976.
- ^ a b Blankley, Bethany (January 5, 2021). "Newsom recall reaches 60 percent of goal over holiday with two months to deadline". Washington Examiner. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Article II, Clause A, Section 15 of the Constitution of California (November 8, 1994)
- ^ a b c Wilson, Reid (March 19, 2021). "What's next in the California recall". The Hill. Archived from the original on March 19, 2021. Retrieved March 19, 2021.
- ^ Article II, Clause B, Section 15 of the Constitution of California (November 8, 1994)
- ^ "Procedures for Recalling State and Local Officials" (PDF). California Secretary of State. January 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 1, 2021.
- ^ Haskell, Josh (July 22, 2021). "Newsom recall effort: California's ballot could confuse voters. Here's what you need to know". KABC-TV.
- ^ Karlamangla, Soumya (September 3, 2021). "Why Newsom Is Telling California Voters to Leave Half the Ballot Blank". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021.
- ^ "California Gubernatorial Recall Election – Frequently Asked Questions". California Secretary of State. Archived from the original on September 10, 2021. Retrieved September 11, 2021.
- ^ "California Adopts Vote-by-Mail System for All Future Elections". KQED.
- ^ a b "California recall price tag could hit $300 million. Some say it was a waste of money". Los Angeles Times. September 16, 2021.
- ^ "SB-117 Elections". California Legislative Information. August 24, 2017.
- ^ Nuttle, Matthew (June 23, 2021). "Newsom recall is a go after only 43 people remove their signatures from effort". KXTV.
- ^ Ronayne, Kathleen (June 27, 2021). "California Democrats again seek to alter recall laws". Associated Press.
- ^ Hoeven, Emily (June 11, 2021). "In switch, lawmakers accelerate Newsom recall election". CalMatters.
- ^ Korte, Lara (June 28, 2021). "UPDATE: California Democrats change election rules ahead of Gavin Newsom recall". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (July 2, 2021). "New, Earlier Date Puts GOP At A Disadvantage In California Recall Election". NPR.
- ^ "Official Voter Information Guide | California Secretary of State". voterguide.sos.ca.gov.
- ^ a b "Cost for California recall that could oust Newsom: $215 million". KRON-TV. Associated Press. June 10, 2020.
- ^ a b c Myers, John (June 17, 2021). "Elections officials alarmed by Democrats' plans to change Newsom recall rules". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "Don't hold Newsom recall before mid-September, California county clerks urge". KTLA. Associated Press. June 15, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Ting, Eric (June 11, 2021). "Republicans rage after Dems move up Newsom recall timeline". SFGate.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (July 18, 2021). "California Recall: What To Know About The Effort To Remove Gavin Newsom". Cap Radio.
- ^ a b Myers, John (April 26, 2021). "Essential Politics: A $400-million Newsom recall election?". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Sierra, Stephanie (September 15, 2021). "California Recall: Election price tag 'could be' more than $300M, secretary of state says, as experts call for reform". KGO-TV. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ chief, John Myers John Myers leads the Los Angeles Times' coverage of state government as Sacramento bureau; analysis, writes a weekly newsletter on California politics along with regular news (February 4, 2022). "California recall election cost $200 million, top elections official says". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "SB-151 Elections". California Legislative Information. October 8, 2019.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (July 12, 2021). "Newsom can't label himself a Democrat on recall ballot". Politico Pro.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (June 30, 2021). "Gov. Newsom Sues Secretary Of State To Get Party Affiliation On Recall Ballot". Cap Radio.
- ^ Korte, Lara. "Gavin Newsom loses court fight to be listed as a Democrat on recall ballot". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Cahill, Nick (November 21, 2019). "California High Court Strikes Down Candidate Tax Return Law". Court House News. Retrieved October 13, 2021.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (May 17, 2021). "Newsom releases tax return, but will recall candidates?". CalMatters.
- ^ a b Rosenhall, Laurel (June 30, 2021). "Will tax return rule scare off Newsom recall candidates?". CalMatters. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Deruy, Emily (July 19, 2021). "You can see tax returns for all 41 recall candidates, but not Gov. Newsom's". The Mercury News.
- ^ a b Koseff, Alexei (July 21, 2021). "California recall ballot expands after judge tosses tax requirement". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ Sheeler, Andrew (July 22, 2021). "Recall ballot takes shape + Meet our new reporter + Garment workers push for better pay". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel; Kamal, Sameea (July 20, 2021). "Six things to know about the Newsom recall candidates' tax returns". CalMatters.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (July 22, 2021). "Judge puts Larry Elder on recall ballot, throws out tax return requirement". KFMB-TV.
- ^ Chemerinsky, Erwin; Edlin, Aaron S. (August 11, 2021). "There Is a Problem With California's Recall. It's Unconstitutional". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021.
- ^ White, Randol (August 14, 2021). "Interview: Legal Scholar Says Newsom Recall Is Unconstitutional". Cap Radio.
- ^ Cooke, Charles C. W. (August 12, 2021). "If California's Recall Is Illegal, So Was Jon Ossoff's Election in Georgia". National Review.
- ^ Dolan, Maura (August 22, 2021). "California recall reality: Newsom could be replaced by candidate with far fewer votes". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Miller, Cheryl (August 18, 2021). "Once Disbarred, Civil Rights Attorney Now Fights to Stop the Newsom Recall". law.com.
- ^ Sheeler, Andrew. "Is the California recall election unconstitutional? A new lawsuit makes the case". The Tribune.
- ^ a b White, Jeremy B.; Kahn, Debra (August 16, 2021). "Federal lawsuit challenges California recall as unconstitutional". Politico.
- ^ Ting, Eric (August 27, 2021). "Lawsuit hoping to stop Gavin Newsom recall election fails". SFGate.
- ^ a b Nixon, Nicole (August 27, 2021). "California's Recall Process Is Constitutional, Federal Judge Rules". Cap Radio.
- ^ a b Christopher, Ben (March 8, 2021). "How California's recall rules could spell trouble for Gavin Newsom". CalMatters.
- ^ a b c Walters, Dan (April 14, 2021). "Bills would hamstring future California recalls". CalMatters.
- ^ "California bill that would let recall targets see who signed petition clears Senate committee". KTLA. Associated Press. April 12, 2021.
- ^ Ronayne, Kathleen (April 20, 2021). "Bill to reveal names of recall signers won't move ahead". Associated Press.
- ^ Nixon, Nicole (April 12, 2021). "Newsom Recall Organizers Oppose Bill To Let Future Recall Targets Access Signature Lists". Cap Radio.
- ^ "California bill seeking to reveal names of recall petition signers won't move ahead". KTLA. April 21, 2021.
- ^ "Bill History". California Legislative Information.
- ^ "As California Votes, It Rethinks Its Tradition of Direct Democracy - The New York Times". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ "California Democrats Begin Push to Change State's Recall Election Rules". Times of San Diego. September 20, 2021.
- ^ Bollag, Sophia. "Gavin Newsom can raise unlimited money in a recall. Candidates to replace him can't". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ Bote, Joshua (June 30, 2021). "Larry Ellison is apparently a real big fan of Caitlyn Jenner". SFGate.
- ^ Gardiner, Dustin; Sumida, Nami (June 29, 2021). "Biggest donors funding the California recall campaign of Gov. Newsom". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Gardiner, Dustin (June 25, 2021). "Hollywood celebrity donors pile into California governor Newsom recall election". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (July 6, 2021). "Former Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer gives Newsom $200K to defeat recall". Politico.
- ^ a b White, Jeremy B. (June 3, 2021). "Newsom counting on labor union army to tank the California recall". Politico Pro.
- ^ Gardiner, Dustin (March 3, 2021). "Recall bankrolled by mega-donors, national Republicans — and retirees". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ Christopher, Ben (May 26, 2021). "Who's funding the Newsom recall campaigns?". CalMatters.
- ^ Mehta, Seema; Moore, Maloy (August 4, 2021). "Newsom and his allies raise tens of millions more than recall backers and GOP candidates". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Rosenhall, Laurel (October 4, 2021). "What's at stake for Newsom's biggest recall campaign donors" – via calmatters.org.
- ^ a b c d e f "Recall Notice to Candidates" (PDF). California Secretary of State. July 17, 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 18, 2021. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "California Gubernatorial Recall Election – September 14, 2021". California Secretary of State. Archived from the original on July 20, 2021. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ a b Rosenhall, Laurel (July 21, 2021). "Judge puts Larry Elder on recall ballot, throws out tax return requirement". CalMatters.
- ^ "CERTIFIED LIST OF WRITE-IN CANDIDATES SEPTEMBER 14, 2021, CALIFORNIA GUBERNATORIAL RECALL ELECTION" (PDF). California Secretary of State. September 3, 2021. Retrieved September 4, 2021.
- ^ Byrnes, Jesse (April 17, 2021). "California Democrats weigh their recall options". The Hill. Retrieved April 18, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Rosenhall, Laurel; Kamal, Sameea (July 18, 2021). "Who's running in Newsom recall? Politicians, activists, Californians of all stripes". CalMatters. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ Phillips, Morgan (January 30, 2021). "John Cox says he'll challenge California's Newsom if recall effort succeeds". Fox News. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 1, 2021.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla (February 1, 2021). "Former San Diego mayor to officially launch GOP challenge to Newsom". Politico. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 1, 2021.
- ^ Chu, Hau (April 23, 2021). "Caitlyn Jenner announces plans to run for governor of California". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ "CAMPAIGN FINANCE: Candidates & Elected Officials". California Secretary of State. 2021. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ Markay, Lachlan; Treene, Alayna; Swan, Jonathan (April 23, 2021). "Caitlyn Jenner files paperwork to run for governor of California". Axios. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
- ^ Roos, Meghan (July 6, 2021). "California Lawmaker Kevin Kiley Enters Race to Recall Gavin Newsom". Newsweek.
- ^ Jackson, Jon (May 17, 2021). "Kevin Paffrath, "Meet Kevin" YouTuber, becomes 26th candidate to announce challenge to Newsom". Newsweek.
- ^ a b Marinucci, Carla (April 27, 2021). "California braces for another 'clown car' of recall candidates". Politico Pro. Archived from the original on May 5, 2021. Retrieved May 5, 2021.
- ^ Fracassa, Dominic (June 12, 2019). "It's official: Six challengers aim to unseat SF Mayor London Breed in November - SFChronicle.com". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b Lloyd, Jonathan (July 23, 2021). "Here Are the Five California Recall Election Candidates Who Will Debate Aug. 4 at Richard Nixon Presidential Library". KNBC.
- ^ Jennewein, Chris (July 24, 2021). "Larry Elder Won't Debate Other Calif. Republicans in 'Circular Firing Squad'". Times of San Diego.
- ^ Roos, Meghan (July 26, 2021). "Larry Elder to Attend Fundraiser Instead of First GOP California Recall Debate". Newsweek.
- ^ Meeks, Alexandra; Stracqualursi, Veronica (August 18, 2021). "California GOP recall candidate served with subpoena during debate". CNN.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (August 17, 2020). "Republican rivals attack recall frontrunner Elder in California debate". Politico.
- ^ Flores, Hilda (August 26, 2021). "Recap: KCRA 3 and San Francisco Chronicle gubernatorial recall debate". kcra.com.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (July 15, 2021). "Trump associate Richard Grenell will not run in California recall". Politico.
- ^ a b Demsas, Jerusalem (April 26, 2021). "The effort to recall California Gov. Gavin Newsom, explained". Vox.
- ^ a b Arellano, Gustavo (September 4, 2021). "Column: Larry Elder is the most Latino candidate in California's recall. It won't help him". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Lara Korte; David Lightman (April 22, 2021). "Some of the biggest names in the California GOP are staying quiet on recalling Gavin Newsom". Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b Palmer, Ewan (September 9, 2021). "Video of Larry Elder being egged by woman in gorilla mask viewed 3.5 million times". Newsweek.
- ^ a b D'Urso, William (August 17, 2021). "Orange County GOP chair endorses Larry Elder for governor". Spectrum News 1.
- ^ a b "California GOP Still Struggling To Find Governor Recall Strategy". CBS SF Bay Area. Associated Press. July 22, 2021.
- ^ a b Korte, Lara (August 24, 2021). "Doug Ose endorses Kevin Kiley in California recall race after suspending his own campaign". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b Blood, Michael R. (March 16, 2021). "Former GOP Rep. Doug Ose enters California recall election". Associated Press. Archived from the original on March 17, 2021. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b Owens, Burgess (September 7, 2021). "Rep. Burgess Owens: California Newsom recall, Larry Elder and the liberal media's return to Jim Crow". Fox News.
- ^ a b Korte, Lara (July 16, 2021). "Larry Elder talks politics on the radio. Can he get votes in the California recall election?". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b Roos, Meghan (July 26, 2021). "Larry Elder to Attend Fundraiser Instead of First GOP California Recall Debate". Newsweek.
- ^ a b Colton, Emma (August 25, 2021). "Former California Democratic Senate leader endorses Larry Elder in campaign against Gov. Newsom". Fox News. Retrieved August 25, 2021.
- ^ Verbin, Dan (July 16, 2021). "Larry Elder says he would replace Dianne Feinstein with a Republican if he wins California recall election". ArutzSheva7.
- ^ a b Mittelstadt, Natalia (August 10, 2021). "Clint Eastwood endorses Larry Elder in California recall election". Just The News.
- ^ a b "Dismissing Voter Choice No Way to Win Recall Election". LA Progressive. August 21, 2021.
- ^ Kamal, Sameea (August 12, 2021). "Meet Kevin Kiley". CalMatters.
- ^ Schleifer, Theodore (January 25, 2021). "Some Silicon Valley donors' next political fight? Trying to oust California's governor". Vox.
- ^ Peterson, Becky (May 8, 2021). "Silicon Valley VCs are at war with the 'far left radicals' running California". Business Insider.
- ^ a b Slisco, Alia (August 7, 2021). "Gavin Newsom Says Recall Frontrunner Larry Elder Doesn't 'Believe in' Minimum Wage". Newsweek.
- ^ Bollag, Sophia (September 12, 2021). "Larry Elder levels accusation against Gavin Newsom's wife two days before recall election". The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ a b Blood, Michael R.; Garcia, Eugene (September 12, 2021). "Allegations fly as recall vote looms for California's Newsom". Associated Press. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Krause, Amanda (December 18, 2020). "Kat Von D says she bought a second home as an escape from California's high taxes, 'terrible policies,' and 'tyrannical government'". Insider.}
- ^ Coupal, Jon (August 1, 2021). "Recall Gov. Newsom, and keep the process". Daily Breeze.
- ^ Robson, Mimi (August 14, 2021). "Newsom is wrong to describe the recall as just a Republican effort". Orange County Register.
- ^ a b "Our View: Vote YES on recall; elect Faulconer to replace Newsom". The Bakersfield Californian. August 15, 2021. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ a b c Amato, Madalyn (August 19, 2021). "Here's how Democrats, Republicans and others say you should vote in the California recall". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ a b c Richardson, Valerie (August 16, 2021). "Larry Elder wins Southern California News Group's backing in Gavin Newsom recall election". The Washington Times. Archived from the original on August 21, 2021. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ a b White, Jeremy B. (February 9, 2021). "White House declares opposition to Newsom recall". Politico. Archived from the original on February 10, 2021. Retrieved February 10, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (September 8, 2021). "Obama to star in Newsom ads in recall's final week". Politico.
- ^ a b c d e f Mai-Duc, Christine (March 15, 2021). "Gavin Newsom Recall: National Democrats Rally Behind California Governor". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ Garofoli, Joe (May 3, 2021). "California Democrats stay on message in opposing Newsom recall". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ Ibssa, Lalee; Shah, Zohreen (September 5, 2021). "Big-name Democrats join Gavin Newsom's fight to remain California governor: 'It's democracy that's at stake'". ABC News. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ Bernstein, Sharon (March 16, 2021). "Democrats, progressives fight California governor recall". Reuters. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ Klein, Charlotte (September 8, 2021). "An Army of Democrats is Mobilizing to Save Gavin Newsom". Vanity Fair. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "Newsom, Elders swarm Southern California before recall vote". Los Angeles Times. September 7, 2021.
- ^ a b c Wilson, Kathleen (September 8, 2021). "Candidates campaign in Ventura County as election nears; Democratic figures back Newsom". Ventura County Star. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Garofoli, Joe (May 3, 2021). "California Democrats stay on message in opposing Newsom recall". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved June 4, 2021.
- ^ Hodgson, Mike (September 6, 2021). "Congressman Salud Carbajal offers updates on issues affecting 24th District". Santa Maria Times. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "Gov. Newsom implores Asian American community to vote in recall election". spectrumnews1.com.
- ^ Lemon, Jason (September 9, 2021). "Where Gavin Newsom Stands in Polls 5 Days Ahead of California Recall Election". Newsweek. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ "Should California adopt a stricter recall election law? Bay Area Rep. Mark DeSaulnier weighs in". California News Times. February 18, 2021. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ John Bowden (May 2, 2021). "Harris, Pelosi backing Newsom amid recall effort". The Hill.
- ^ a b Deruy, Emily (September 11, 2021). "California Recall: Newsom urges supporters, 'Polls don't vote. People vote'". The Mercury News.
- ^ Deese, Kathleen (September 13, 2021). "Newsom hits at Texas abortion law, criticizing recall effort". Yahoo News. Retrieved September 15, 2021 – via Washington Examiner.
- ^ a b Kreutz, Liz (August 16, 2021). "Gov. Newsom ratchets up attacks on opponents in San Jose campaign stop". KGO-TV.
- ^ "Biden speaks in Long Beach, offers late push for Newsom". September 14, 2021.
- ^ Wallace, Eytan; Malone, Connor (September 11, 2021). "Republicans, Democrats hold get-out-and-vote drives ahead of Tuesday's governor recall election". KTXL. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Reyes, Jesus (September 7, 2021). "Rep. Raul Ruiz casts his ballot in the recall election". kesq.com.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla; White, Jeremy B.; Dadey, Camryn. "Final frenzy — will women save NEWSOM?". POLITICO.
- ^ Wright, Sarah. "Recall campaign heats up in San Mateo County". Half Moon Bay Review. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ "Stop the Republican Recall of Governor Gavin Newsom with Congresswoman Sara Jacobs 路 Sara Jacobs for Congress". Mobilize.us. Archived from the original on September 14, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ Suter, Leanne (September 5, 2021). "California recall election: Newsom continues 'Vote No' campaign with weekend tour across SoCal". KABC-TV. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "California API Members Denounce Recall Newsom Effort". KSRO. March 11, 2021. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 15, 2021.
- ^ a b c Richards, Brandon (August 2, 2021). "Joint Release: Reproductive Freedom Advocates Sound Alarm on Extremist Recall Attempt". plannedparenthoodaction.org.
- ^ "Why Sen. Bill Dodd is spending big to keep Gov. Newsom in office". September 2021.
- ^ a b White, Jeremy B. (April 2, 2021). "His polls are sinking. Democrats are mobilizing. The Newsom recall just got real". Politico. Retrieved February 4, 2021.
- ^ a b Bojórquez, Kim (April 8, 2021). "Democratic Latino leaders denounce Newsom recall after poll finds 'slippage' in support". sacbee.com. The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ Barrabi, Thomas (February 11, 2021). "California Lt. Gov. Kounalakis slams Newsom recall effort, says 'shameful' for any Dem to run to replace him". Fox News. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ "Kamala Harris comes to Newsom's rescue, whether he needs it or not". September 8, 2021.
- ^ "Local Democrats urge 'no' vote in recall election". www.bakersfield.com. The Bakersfield Californian. Retrieved August 18, 2021.
- ^ Korte, Lara (August 27, 2021). "California recall candidate Larry Elder says 'systemic racism is a lie.' Here's why". The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- ^ Andrews, Justin (September 7, 2021). "Gov. Gavin Newsom Appears at Recall Election Campaign Rally in SF". Yahoo News.
- ^ "Biden set to visit Long Beach Monday for rally against Newsom recall". September 12, 2021.
- ^ Watson, Nia (August 15, 2021). "Gov. Newsom holds 'Vote No' campaign rally ahead of recall election". KGTV.
- ^ "Labor, Community Leaders Urge 'No' Vote On Newsom Recall At Oakland Rally". KPIX-TV. August 25, 2021. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Mehta, Seemta; Wick, Julia (July 17, 2021). "As list of recall candidates takes shape, Jenner's in Australia for a TV show". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Tapp, Tom (August 18, 2021). "George Lopez Endorses Embattled Gavin Newsom As California Governor Struggles Among Latinos". Deadline. Retrieved August 18, 2021.
- ^ "In final campaign push with Newsom, Biden says 'eyes of the nation' are on California recall". Los Angeles Times. September 13, 2021.
- ^ a b c "Hollywood Reacts to Gavin Newsom's Win in California Gubernatorial Recall Election". The Hollywood Reporter. September 14, 2021.
- ^ "Editorial: Vote no on Newsom recall". www.ebar.com. The Bay Area Reporter / B.A.R. Inc. August 11, 2021. Retrieved August 16, 2021.
- ^ a b "Editorial: Wake up, California! Removing Gavin Newsom would be a disaster". Los Angeles Times. August 13, 2021. Retrieved August 13, 2021.
- ^ "Voters should reject Newsom Recall, Fresno Bee urges". The Fresno Bee. August 8, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021 – via PressReader.
- ^ "Vote 'no' on the recall, and fill out the entire California ballot. Here's why that's important". www.sacbee.com. The Sacramento Bee. August 14, 2021. Retrieved August 18, 2021.
- ^ "Editorial: California voters should reject the Newsom recall". The Mercury News. July 17, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ "Our endorsement in the effort to oust Newsom: Vote no, and let the governor finish the job". Monterey County Weekly. September 2, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ "Our View: You must vote in the California Recall election". Napa Valley Register. August 7, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ "California's Recall Election Is Broken". The New York Times. September 9, 2021. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ "Opinion: Recall Newsom? Vote no on this ridiculous and ridiculously expensive election, then fix the recall process". San Diego Union-Tribune. August 13, 2021. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ^ "Endorsement: There is absolutely no justification for removing Gavin Newsom. Vote NO on the recall". Chronicle Editorial Board. San Francisco Chronicle. August 21, 2021.
- ^ "Vote No on California Recall of Governor". Santa Barbara Independent. August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ "Coalition of ACLU California chapters announce opposition to Newsom recall". The Antelope Valley Times. July 29, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ "ANCA-WR Supports Gov. Newsom in the September 14 Recall Election". ANCA Western Region. August 25, 2021. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ "California Democratic Party Commits $250,000 to Stop the Republican Recall Campaign | CDP". www.cadem.org. California Democratic Party. March 15, 2021. Archived from the original on June 4, 2021. Retrieved June 4, 2021.
- ^ "CFA: NO on Wasteful Recall". www.calfac.org. California Faculty Association. July 22, 2021.
- ^ "What does CFT says about the recall? No, No, No!". CFT. CFT – A Union of Educators and Classified Professionals. May 25, 2021.
- ^ "Protect Our Future – Vote NO on the Recall". California League of Conservation Voters. August 26, 2021. Archived from the original on August 28, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ "Gavin Newsom". Climate Hawks Vote.
- ^ "DGA Statement on California Recall Campaign". www.democraticgovernors.org. Democratic Governors Association. March 15, 2021. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ^ "Statement on Gubernatorial Recall Election". DSA Los Angeles. August 12, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ "Election Center". eqca.org.
- ^ "GPCA Opposes Recall – Endorses Dan Kapelovitz". Green Party CA.
- ^ Brookshire, Richard (August 23, 2021). "Human Rights Campaign Urges Californians To Vote No On Recall Question". www.hrc.org. Human Rights Campaign.
- ^ Zavala, Ashley (May 5, 2021). "Firefighters join Gov. Newsom to speak out against recall effort". www.kron4.com. KRON-TV. Retrieved June 4, 2021.
- ^ "STOP THE GOP RECALL IN CALIFORNIA". Jewish Democratic Council of America. August 25, 2021.
- ^ "NARAL Pro-Choice California: A Vote to Recall Governor Newsom is a Vote Against Reproductive Freedom". NARAL Pro-Choice California. August 24, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (February 4, 2021). "His polls are sinking. Democrats are mobilizing. The Newsom recall just got real". Politico. Retrieved April 25, 2021.
- ^ "PEACE & FREEDOM PARTY OPPOSES RECALL OF NEWSOM". peaceandfreedom.us. Peace and Freedom Party. March 31, 2021.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla; Tzul, Richard (May 28, 2021). "10 dead after MASS SHOOTING in San Jose — NEWSOM: 'The hell's wrong with us?' — JENNER hits East Coast media — MANDATORY water restrictions on the way?". Politico. Retrieved May 31, 2021.
- ^ a b c Socialist Equality Party (July 23, 2021). "David Moore to run as the Socialist Equality Party candidate in the California gubernatorial recall election". World Socialist Web Site. Retrieved August 22, 2021.
- ^ "Major California labor unions back Gov. Newsom in likely recall". KTLA. Associated Press. June 1, 2021. Retrieved June 4, 2021.
- ^ White, Jeremy B.; Marinucci, Carla; Tzul, Richard (June 25, 2021). "CA backlash to TECH push — PELOSI announces JAN. 6 committee — NEWSOM wildfire defense — KAMALA staff departures". Politico. Retrieved July 24, 2021.
- ^ Dan Verbin (July 16, 2021). "Dov Hikind endorses Larry Elder for CA governor, calls him the 'ultimate mensch'". ArutzSheva7.
- ^ D'Urso, William (August 25, 2021). "Orange County GOP chair endorses Larry Elder for governor". spectrumnews1.com. Retrieved August 26, 2021.
- ^ Roos, Meghan (September 10, 2021). "Rose McGowan Alleges Gavin Newsom's Wife Tried to Bribe Her Before Harvey Weinstein Scandal Broke". Newsweek.
- ^ Gentile, Luke (September 15, 2021). "Dodgers legend Mike Piazza calls on Californians to elect Larry Elder". Yahoo! News. Retrieved September 16, 2021 – via The Washington Examiner.
- ^ Albough, Greg (July 22, 2021). "Conservative Powerhouse Restored To California Governor's Recall Race". Citizens Journal.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (August 6, 2021). "Larry Elder surges to GOP fundraising lead, but Newsom still lapping recall field". Politico.
- ^ "Voter Information Guide and Sample Ballot" (PDF). San Bernardino County Elections. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 10, 2021. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ California College Republicans [@cacollegegop] (August 2, 2021). "#BreakingNews: CCR Unanimously Endorses @larryelder for Governor of California. #RecallGavinNewsom #cagop CC: @JeremyBWhite @cmarinucci" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "Let's talk about the recall". YouTube. CRPA TV.
- ^ "Membership". California Rifle and Pistol Association.
- ^ "Endorsement: Larry Elder for California Governor". nyyrc.com. New York Young Republican Club. September 13, 2021. Retrieved June 1, 2022.
- ^ "Our View – Newsom Set Stage for Recall". Santa Clarita Valley Signal. September 4, 2021. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ "Majority of GOP State Legislators Rally Behind Faulconer for Governor". Kevin Faulconer for Governor. Archived from the original on February 5, 2021. Retrieved July 27, 2021.
- ^ Staggs, Brooke (June 10, 2021). "Republican Kevin Faulconer brings governor campaign to Orange County". Orange County Register.
- ^ Tavlian, Alex (August 25, 2021). "Down the stretch come endorsement: Elder, Kiley, Faulconer tout new backers". The Sun.
- ^ Carroll, Brian. "Dr. James G. Hanink for Governor 2021". Crowdpac. Retrieved August 27, 2021.
- ^ "American Solidarity Party". American Solidarity Party of California. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ^ "Jeff Hewit Announces his run for Governor on the Libertarian Party Ticket". Libertarian Party of California. May 22, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ "Green Party of California endorses Dan Kapelovitz". Green Party US.
- ^ Kamal, Sameea (August 12, 2021). "Meet Kevin Kiley". [permanent dead link]
- ^ Hoeven, Emily (July 7, 2021). "Another challenger jumps into Newsom recall race". CalMatters.
- ^ Ronayne, Kathleen (April 1, 2021). "Former California cop leads GOP dream of Newsom recall". Associated Press.
- ^ Ronayne, Kathleen (April 1, 2021). "Meet Orrin Heatlie, the ex-cop leading the push to recall California Gov. Gavin Newsom". The Desert Sun.
- ^ White, Jeremy B. (July 27, 2021). "A radio host, a YouTuber and a guy with a bear. Meet California's top recall contenders". Politico.
- ^ Loebs, Michael (April 19, 2021). "CNP Endorses Michael Loebs for Governor". California National Party.
- ^ "SWP running for governor in California special election – The Militant". The Militant. Retrieved August 22, 2021.
- ^ a b Stone, Betsey (May 31, 2021). "SWP running for governor in California special election". The Militant. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- ^ "2022 Governor Race Ratings for September 13, 2021". The Cook Political Report. Archived from the original on December 10, 2021. Retrieved December 9, 2021.
- ^ "Gubernatorial Ratings". Inside Elections. Retrieved December 9, 2021.
- ^ Marinucci, Carla (September 9, 2021). "The California Recall: Newsom's Position Has Improved Down the Stretch". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved September 9, 2021.
- ^ "California Gubernatorial Recall Election - Statement of Vote, September 14, 2021". Secretary of State California.
- ^ Christopher, Ben (September 19, 2021). "And the winner in the California recall is? None of the above". Pleasanton Weekly. Retrieved March 22, 2024.
- ^ a b Andre, Michael; et al. (September 14, 2021). "California Recall Election Results". The New York Times. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ a b "California Gubernatorial Recall Election Results". Election Results.
- ^ a b Weber, Shirley (October 22, 2021). "STATEMENT OF VOTE, SEPTEMBER 14, 2021 CALIFORNIA GUBERNATORIAL RECALL ELECTION" (PDF). Office of the California Secretary of State. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Ting, Eric (June 21, 2021). "This SFSU Calif. secessionist is Newsom's most fascinating recall foe". SF Gate. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Spielmann, Cristobal; Backer-Peral, Veronica (May 6, 2021). "Former LMU professor runs for governor in recall election". Los Angeles Loyolan. Retrieved July 12, 2021.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 18, 2021). "California Secretary of State Makes a Tiny Concession to Unqualified Parties in the Official Voter Information Guide". Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 22, 2021.
- ^ Black, SaVannah. "Political Body: American Solidarity Party" (PDF). California Secretary of State. Retrieved July 20, 2021.
- ^ Weber, Shirley. "California Gubernatorial Recall Election Official Voter Information Guide" (PDF). California Secretary of State. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ "Counties by Congressional Districts for Recall Question" (PDF).
- ^ "Counties by Congressional Districts for Recall Election Gubernatorial Replacement Candidates" (PDF).
- ^ Christopher, Ben (September 18, 2021). "'Nobody' Beat GOP Frontrunner Larry Elder by Wide Margin in California Recall". Times of San Diego. Retrieved September 19, 2021.
- ^ Gardiner, Dustin (September 15, 2021). "Larry Elder leads replacement field, but nearly half of recall voters skipped second question". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved September 19, 2021.
- ^ Todd, Chuck; Murray, Mark; Kamisar, Ben; Sarlin, Benjy (October 22, 2021). "Gavin Newsom reflects on the recall, discusses upcoming challenges". NBC News.
- ^ a b c Bollag, Sophia (August 23, 2021). "Larry Elder is leader among California recall candidates. That might help Gavin Newsom". The Sacramento Bee.
- ^ a b c Reston, Maeve (September 14, 2021). "How Larry Elder has helped Gavin Newsom in California's recall election - CNNPolitics". Cnn.com. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- ^ a b Rosenhall, Laurel (September 16, 2021). "A partisan recall puts California Republican Party in disarray". CalMatters. Retrieved October 28, 2021.
- ^ "Column: Larry Elder joining the recall race was the best thing that could've happened to Newsom". Los Angeles Times. September 13, 2021.
- ^ Kilgore, Ed (November 3, 2021). "MAGA Without the Madness Wins". Intelligencer.
- ^ Prokop, Andrew (November 3, 2021). "What Glenn Youngkin's Virginia win means for Democrats". Vox.
- ^ Godfrey, Elaine; Berman, Russell (November 2, 2021). "If Democrats Can Lose in Virginia, They Can Lose Almost Anywhere". The Atlantic.
External links[edit]
- California recall procedures guide
- Complete list of recall election attempts in California – Secretary of State of California
- Candidates for the 2021 California gubernatorial recall election, official listing
Anti-recall campaign[edit]
- Stop the Republican Recall (Archived September 14, 2021, at the Wayback Machine), the official retention campaign for Gavin Newsom
Recall campaign[edit]
- Recall Gavin 2020 (Archived September 14, 2021, at the Wayback Machine), the official recall Gavin Newsom campaign
Official candidate campaign websites[edit]
- Angelyne (I) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- David Bramante (R) for Governor
- John Cox (R) for Governor Archived June 14, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- John Drake (D) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Larry Elder (R) for Governor
- Kevin Faulconer (R) for Governor Archived July 23, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Rhonda Furin (R) for Governor
- Ted Gaines (R) for Governor
- Sam Gallucci (R) for Governor Archived May 13, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- James Hanink (I) for Governor
- Jeff Hewitt (L) for Governor
- Caitlyn Jenner (R) for Governor
- Dan Kapelovitz (G) for Governor
- Kevin Kaul (I) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Kevin Kiley (R) for Governor
- Jenny Rae Le Roux (R) for Governor
- Michael Loebs (I) for Governor Archived May 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- David Lozano (R) for Governor
- Diego Martinez (R) for Governor
- Daniel Mercuri (R) for Governor
- Doug Ose (R) for Governor
- Kevin Paffrath (D) for Governor
- Adam Papagan (I) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Armando Perez-Serrato (D) for Governor
- Brandon Ross (D) for Governor
- Major Singh (I) for Governor
- Sarah Stephens (R) for Governor
- Joe Symmon (R) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Anthony Trimino (R) for Governor
- Joel Ventresca (D) for Governor
- Daniel Watts (D) for Governor Archived July 24, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Nickolas Wildstar (R) for Governor
- Major Williams (R, Write-in) for Governor Archived April 29, 2021, at the Wayback Machine