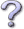Introduction
Selected article -Charles Robert Darwin FRS FRGS FLS FZS JP (/ˈdɑːrwɪn/ DAR-win; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh; instead, he helped to investigate marine invertebrates. His studies at the University of Cambridge's Christ's College from 1828 to 1831 encouraged his passion for natural science. His five-year voyage on HMS Beagle from 1831 to 1836 established Darwin as an eminent geologist, whose observations and theories supported Charles Lyell's concept of gradual geological change. Publication of his journal of the voyage made Darwin famous as a popular author. (Full article...)General images -The following are images from various evolutionary biology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected picture - The passenger pigeon, one of several species of extinct birds, was hunted to extinction over the course of a few decades. Did you know... -
CategoriesRelated portalsTasks you can do
Related topicsWikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with biology: A complete list of scientific WikiProjects can be found here. See also Wikispecies, a Wikimedia project dedicated to classification of biological species. Associated WikimediaDiscover Wikipedia using portals
Purge server cache |
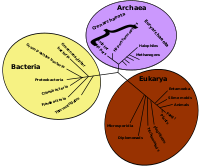





![Image 5A covalent adduct between the metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene, the major mutagen in tobacco smoke, and DNA (from Mutation)](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png/87px-Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png)