| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6aR,9aR)-9a-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]furo[3′,2′:4,5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione | |
| Other names
4-Hydroxyaflatoxin B1
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | AFM1 AFM1 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.151 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H12O7 | |
| Molar mass | 328.276 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
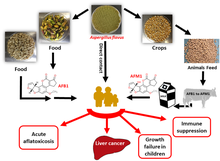
Aflatoxin M1 is a chemical compound of the aflatoxin class, a group of mycotoxins produced by three species of Aspergillus – Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus, and the rare Aspergillus nomius – which contaminate plant and plant products.
Aspergillus flavus produces only B-type aflatoxins. Aflatoxin M1 is the hydroxylated metabolite of aflatoxin B1 and can be found in milk or milk products obtained from livestock that have ingested contaminated feed. The carcinogenic potency of aflatoxin M1 in sensitive species is about one order of magnitude less than that of aflatoxin B1. Aflatoxin M1 is usually considered to be a detoxication by-product of aflatoxin B1. The main sources of aflatoxins in feeds are peanut, meal, maize and cottonseed meal.[1]
Chemical structure[edit]
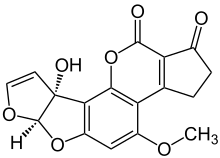
The chemical structure of aflatoxin M1. Aflatoxin M1 is the 4-hydroxy derivative of aflatoxin B1 and is secreted in the milk of mammals that consume aflatoxin B1. Aflatoxin M1 has a relative molecular mass of 328 Da and has the molecular formula C17H12O7.[1]
Sources of exposure[edit]
Aflatoxin M1 may be found in milk, including human milk. In cows, sheep, goats and buffaloes that have consumed feeds contaminated with aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin M1 will be formed as a result of the metabolic process in the livers of ruminants and excreted in their milk. Humans can be exposed to the toxins through consumption of contaminated milk and other foods.[2]
Pathology[edit]
The effect of aflatoxin M1 was much weaker than aflatoxin B1 in producing liver cancer. The limited animal studies carried out to determine toxicity of aflatoxin M1. Aflatoxin M1 has toxic and carcinogenic properties. The toxicity of aflatoxin M1 in ducklings and rats seems to be slightly less than that of aflatoxin B1. The carcinogenicity is probably one to two orders of magnitude less than that of the highly carcinogenic aflatoxin B1.
Bioconversion pathway[edit]
Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1), the principal hydroxylated metabolite of AFB1, is found in the milk (hence the designation M) of mammals fed with contaminated feedstuff. Carry-over of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) as AFM1 in the milk of dairy cows has been established to range from 0.3% to 6.2%.[3] However, AFM1 was also found in lactating mothers' milk.[4] Several studies reported carcinogenic[5] and immunosuppressive effects[6] similar to that of AFB1, on both humans and other animals, even if with a less potent effect. However, AFM1 is the only mycotoxin for which maximum residue limits (MRLs) in milk were established.[7]
Toxicological study[edit]
Several studies have been undertaken of the toxic effects of aflatoxin M1 in laboratory animals. However, in comparison to aflatoxin B1, relatively little is known about the toxicity of aflatoxin M1, primarily because of the difficulty in obtaining sufficient quantities of the pure compound necessary for extensive toxicity testing.[8]
| Species | Sex | Dose | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Trout (fry) up to 12 months[9] |
Male |
8 μg/kg
4-64 μg/kg (120 treated/group) 800 μg/kg |
No tumours (0/110)
Liver tumour response: 0.086 % 50 % tumours at 9 months |
| Fischer rats[10] | Male |
0 μg/kg 0.5 μg/kg 5 μg/kg 50 μg/kg |
Liver cancer 0 % neoplastic nodules 0 % Liver cancer 0 % neoplastic nodules 0 % Liver cancer 0 % neoplastic nodules 0 % Liver cancer 5 % neoplastic nodules 16 % |
| Fischer rats[11] | Male |
1 mg/rat |
Liver cancer 1 of 29 |
Genotoxicity[edit]
The potency of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin M1 in inducing DNA damage and genotoxicity was tested in Drosophila melanogaster. Aflatoxin M1 was found to be a DNA-damaging agent, with an activity about one-third that of aflatoxin B1.[12]
Analytical methods[edit]
Many methods have become available for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. In particular, solid-phase correction and immunoaffinity chromatography cartridges offer good possibilities for efficient clean up. Both thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are adequate techniques to separate and determine aflatoxin M1 in extracts of milk. Enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA) is more popular, due to ease of use and properties which are conducive to rapid screening and semi-quantitative determination.[13][8] Aflatoxins determinations are usually expensive and employ environmentally unfriendly procedures, thus, the search for new materials and technologies, that are both ecologically safe and inexpensive its rice husk as an adsorbent method.[14]
Regulation[edit]
According to a recent review conducted by the Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) on behalf of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) approximately 60 countries have set specific limits for aflatoxin M1. The European Union countries generally apply a maximum level of 0.05 μg/kg milk. Some countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America also propose this level. In contrast, the USA as well as some European and several Asian countries accept a maximum level of 0.5 μg/kg aflatoxin M1 in milk, which is also the harmonized Mercosur limit applied in Latin America. The 0.5 μg/kg limit for aflatoxin M1. Thus, the maximum permitted level of aflatoxin M1 in milk in the EU is among the lowest in the world, and is based on the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle. Considering the carry-over into milk and the established adverse effects on animal health, approximately 45 countries have set specific levels for aflatoxin B1 in feed for dairy animals. To support compliance with the maximum levels in milk intended for human consumption, stringent maximum levels were also set in the EU for feed stuffs which might be consumed by dairy cows. A limit of 0.005 mg/kg feed for dairy cattle is applied in the EU countries and in the new member states as well as in Europe Union countries, but only in few countries outside Europe. This level is below the no-effect level in target animals.[citation needed]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Safety evaluation of certain mycotoxinsin food (PDF). Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations. 2001. ISBN 92-4-166047-3.
- ^ "Food Safety Focus". Aflatoxins in Milk. 67 (2012). Feb 2012. Retrieved 20 October 2018.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Veldman, A.; Meijs, J.; Borggreve, G.; Heeres-van der Tol, J. Carry-over of aflatoxin from cows’ food to milk.Anim. Sci. 1992, 55, 163–168
- ^ Jafari, T.; Fallah, A.A.; Kheiri, S.; Fadaei, A.; Amini, S.A. Aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk in Shahrekord, Iran and association with dietary factors. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2017, 10, 128–136
- ^ Cullen, J.M.; Ruebner, B.H.; Hsieh, L.S.; Hyde, D.M.; Hsieh, D.P. Carcinogenicity of Dietary Aflatoxin M1 in Male Fischer Rats Compared to Aflatoxin B1
- ^ Luongo, D.; Russo, R.; Balestrieri, A.; Marzocco, S.; Bergamo, P.; Severino, L. (2013). In vitro study of AFB1 and AFM1 effects on human lymphoblastoid Jurkat T-cell model. J. Immunotoxicol., 11, 353–358.
- ^ Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. (2018). "Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development". Toxins. 10 (6): 214. doi:10.3390/toxins10060214. PMC 6024316. PMID 29794965.
- ^ a b van Egmond, H.P. (1994). Aflatoxins in milk. In: Eaton, D.L. & Groopman, J.D., eds. The Toxicology of Aflatoxin: Human Health, Veterinary, and Agricultural Significance. San Diego, CA, Academic Press, pp. 365–381.
- ^ Aflatoxins (IARC monographs on the identification of carcinogenic hazards to humans) (PDF). June 2018. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ Cullen, J.M., Reubner, B.H., Hsieh, L.S., Hyde, D.M. & Hsieh, D.S.P. (1987). Carcinogenicity of dietary aflatoxin M1 in male Fisher rats compare to aflatoxin B1. Cancer Res., 47, 1913–1917.
- ^ Wogan, G. N.; Paglialunga, S. (14 November 1973). "Carcinogenicity of synthetic aflatoxin M1 in rats" (PDF). Food and Cosmetics Toxicology. 12 (14 November 1973): 381–384. doi:10.1016/0015-6264(74)90012-1. PMID 4374416. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- ^ Shibahara, T., Ogawa, H.I., Ryo, H. & Fujikawa, K. (1995). DNA-damaging potency and genotoxicity of aflatoxin M1 in somatic cells in vivo of Drosophila melanogaster. Mutagenesis, 10, 161–164.
- ^ Li, Songli; Min, Li; Wang, Gang; Li, Dagang; Zheng, Nan; Wang, Jiaqi (28 April 2018). "Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk from Manufacturers of Infant Milk Powder in China". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 15 (5): 879. doi:10.3390/ijerph15050879. PMC 5981918. PMID 29710778.
- ^ Scaglioni, Priscila Tessmer; Badiale-Furlong, Eliana (15 May 2016). "Rice husk as an adsorbent: A new analytical approach to determine aflatoxins in milk". Talanta. 152 (5): 423–431. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.042. PMID 26992538.