| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
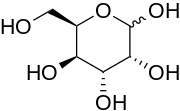
| IUPAC name
D-Gulose
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3R,4R,5R,6R)-6-(Hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,3,4,5-tetraol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.156 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Gulose is an aldohexose sugar. It is a monosaccharide that is very rare in nature, but has been found in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes.[2] It also exists as a syrup with a sweet taste. It is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol. Neither the d- nor l-forms are fermentable by yeast.
D-Gulose is a C-3 epimer of D-galactose and a C-5 epimer of L-mannose.[3]
References[edit]
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4490
- ^ Swain, M., Brisson, J. R., Sprott, G. D., Cooper, F. P. and Patel, G. B. (1997). "Identification of β-L-gulose as the sugar moiety of the main polar lipid Thermoplasma acidophilum". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1345 (1): 56–64. doi:10.1016/s0005-2760(96)00163-4. PMID 9084501.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zhang, Qingju; et al. (2016). "On the Reactivity of Gulose and Guluronic Acid Building Blocks in the Context of Alginate Assembly". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2016 (14): 2393–2397. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201600336.