| Fibronectin type III domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
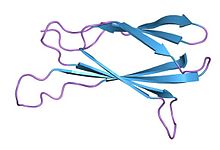 The tenth type III domain of fibronectin | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | fn3 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00041 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0159 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR003961 | ||||||||
| SMART | FN3 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00214 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1ttf / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00063 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 66 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Fibronectin type III domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain that is widely found in animal proteins. The fibronectin protein in which this domain was first identified contains 16 copies of this domain. The domain is about 100 amino acids long and possesses a beta sandwich structure. Of the three fibronectin-type domains, type III is the only one without disulfide bonding present. Fibronectin domains are found in a wide variety of extracellular proteins. They are widely distributed in animal species, but also found sporadically in yeast, plant and bacterial proteins.
Human proteins containing this domain[edit]
ABI3BP; ANKFN1; ASTN2; AXL; BOC; BZRAP1; C20orf75; CDON; CHL1; CMYA5; CNTFR; CNTN1; CNTN2; CNTN3; CNTN4; CNTN5; CNTN6; COL12A1; COL14A1; COL20A1; COL7A1; CRLF1; CRLF3; CSF2RB; CSF3R; DCC; DSCAM; DSCAML1; EBI3; EGFLAM; EPHA1; EPHA10; EPHA2; EPHA3; EPHA4; EPHA5; EPHA6; EPHA7; EPHA8; EPHB1; EPHB2; EPHB3; EPHB4; EPHB6; EPOR; FANK1; FLRT1; FLRT2; FLRT3; FN1; FNDC1; FNDC3A; FNDC3B; FNDC4; FNDC5; FNDC7; FNDC8; FSD1; FSD1L; FSD2; GHR; HCFC1; HCFC2; HUGO; IFNGR2; IGF1R; IGSF22; IGSF9; IGSF9B; IL4R; IL11RA; IL12B; IL12RB1; IL12RB2; IL20RB; IL23R; IL27RA; IL31RA; IL6R; IL6ST; IL7R; INSR; INSRR; ITGB4; KAL1; KALRN; L1CAM; LEPR; LIFR; LRFN2; LRFN3; LRFN4; LRFN5; LRIT1; LRRN1; LRRN3; MERTK; MID1; MID2; MPL; MYBPC1; MYBPC2; MYBPC3; MYBPH; MYBPHL; MYLK; MYOM1; MYOM2; MYOM3; NCAM1; NCAM2; NEO1; NFASC; NOPE; NPHS1; NRCAM; OBSCN; OBSL1; OSMR; PHYHIP; PHYHIPL; PRLR; PRODH2; PTPRB; PTPRC; PTPRD; PTPRF; PTPRG; PTPRH; PTPRJ; PTPRK; PTPRM; PTPRO; PTPRS; PTPRT; PTPRU; PTPRZ1; PTPsigma; PUNC; RIMBP2; ROBO1; ROBO2; ROBO3; ROBO4; ROS1; SDK1; SDK2; SNED1; SORL1; SPEG; TEK; TIE1; TNC; TNN; TNR; TNXB; TRIM36; TRIM42; TRIM46; TRIM67; TRIM9; TTN; TYRO3; UMODL1; USH2A; VASN; VWA1; dJ34F7.1; fmi;
See also[edit]
- Monobodies are engineered (synthetic) antibody mimetics based on a fibronectin type III domain (specifically, the 10th FN3 domain of human fibronectin). Monobodies feature either diversified loops or diversified strands of a flat beta-sheet surface, which serve as interaction epitopes. Monobody binders have been selected a wide variety of target molecules, and have expanded beyond the potential range of binding interfaces observed in both natural and synthetic antibodies.
References[edit]
- Bazan JF (September 1990). "Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (18): 6934–8. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.6934B. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. PMC 54656. PMID 2169613.
- Little E, Bork P, Doolittle RF (December 1994). "Tracing the spread of fibronectin type III domains in bacterial glycohydrolases". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 39 (6): 631–43. Bibcode:1994JMolE..39..631L. doi:10.1007/bf00160409. PMID 7528812. S2CID 11909704.
- Kornblihtt AR, Umezawa K, Vibe-Pedersen K, Baralle FE (July 1985). "Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene". The EMBO Journal. 4 (7): 1755–9. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. PMC 554414. PMID 2992939.