| Dubnium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | [268] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dubnium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d3 7s2[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 11, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid (predicted)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 21.6 g/cm3 (predicted)[5][6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | (+3), (+4), +5[3][7] (parenthesized: prediction) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 139 pm (estimated)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 149 pm (estimated)[8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | synthetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc) (predicted)[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 53850-35-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russia, site of Joint Institute for Nuclear Research | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | independently by the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (1970) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of dubnium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dubnium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Db and atomic number 105. It is highly radioactive: the most stable known isotope, dubnium-268, has a half-life of about 16 hours. This greatly limits extended research on the element.
Dubnium does not occur naturally on Earth and is produced artificially. The Soviet Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) claimed the first discovery of the element in 1968, followed by the American Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory in 1970. Both teams proposed their names for the new element and used them without formal approval. The long-standing dispute was resolved in 1993 by an official investigation of the discovery claims by the Transfermium Working Group, formed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics, resulting in credit for the discovery being officially shared between both teams. The element was formally named dubnium in 1997 after the town of Dubna, the site of the JINR.
Theoretical research establishes dubnium as a member of group 5 in the 6d series of transition metals, placing it under vanadium, niobium, and tantalum. Dubnium should share most properties, such as its valence electron configuration and having a dominant +5 oxidation state, with the other group 5 elements, with a few anomalies due to relativistic effects. A limited investigation of dubnium chemistry has confirmed this.
Introduction[edit]
Synthesis of superheavy nuclei[edit]
A superheavy[a] atomic nucleus is created in a nuclear reaction that combines two other nuclei of unequal size[b] into one; roughly, the more unequal the two nuclei in terms of mass, the greater the possibility that the two react.[20] The material made of the heavier nuclei is made into a target, which is then bombarded by the beam of lighter nuclei. Two nuclei can only fuse into one if they approach each other closely enough; normally, nuclei (all positively charged) repel each other due to electrostatic repulsion. The strong interaction can overcome this repulsion but only within a very short distance from a nucleus; beam nuclei are thus greatly accelerated in order to make such repulsion insignificant compared to the velocity of the beam nucleus.[21] The energy applied to the beam nuclei to accelerate them can cause them to reach speeds as high as one-tenth of the speed of light. However, if too much energy is applied, the beam nucleus can fall apart.[21]
Coming close enough alone is not enough for two nuclei to fuse: when two nuclei approach each other, they usually remain together for approximately 10−20 seconds and then part ways (not necessarily in the same composition as before the reaction) rather than form a single nucleus.[21][22] This happens because during the attempted formation of a single nucleus, electrostatic repulsion tears apart the nucleus that is being formed.[21] Each pair of a target and a beam is characterized by its cross section—the probability that fusion will occur if two nuclei approach one another expressed in terms of the transverse area that the incident particle must hit in order for the fusion to occur.[c] This fusion may occur as a result of the quantum effect in which nuclei can tunnel through electrostatic repulsion. If the two nuclei can stay close for past that phase, multiple nuclear interactions result in redistribution of energy and an energy equilibrium.[21]
| External videos | |
|---|---|
The resulting merger is an excited state[25]—termed a compound nucleus—and thus it is very unstable.[21] To reach a more stable state, the temporary merger may fission without formation of a more stable nucleus.[26] Alternatively, the compound nucleus may eject a few neutrons, which would carry away the excitation energy; if the latter is not sufficient for a neutron expulsion, the merger would produce a gamma ray. This happens in approximately 10−16 seconds after the initial nuclear collision and results in creation of a more stable nucleus.[26] The definition by the IUPAC/IUPAP Joint Working Party (JWP) states that a chemical element can only be recognized as discovered if a nucleus of it has not decayed within 10−14 seconds. This value was chosen as an estimate of how long it takes a nucleus to acquire its outer electrons and thus display its chemical properties.[27][d]
Decay and detection[edit]
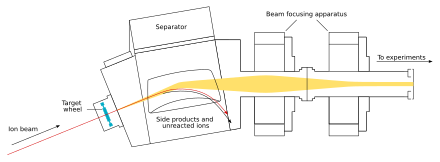
The beam passes through the target and reaches the next chamber, the separator; if a new nucleus is produced, it is carried with this beam.[29] In the separator, the newly produced nucleus is separated from other nuclides (that of the original beam and any other reaction products)[e] and transferred to a surface-barrier detector, which stops the nucleus. The exact location of the upcoming impact on the detector is marked; also marked are its energy and the time of the arrival.[29] The transfer takes about 10−6 seconds; in order to be detected, the nucleus must survive this long.[32] The nucleus is recorded again once its decay is registered, and the location, the energy, and the time of the decay are measured.[29]
Stability of a nucleus is provided by the strong interaction. However, its range is very short; as nuclei become larger, its influence on the outermost nucleons (protons and neutrons) weakens. At the same time, the nucleus is torn apart by electrostatic repulsion between protons, and its range is not limited.[33] Total binding energy provided by the strong interaction increases linearly with the number of nucleons, whereas electrostatic repulsion increases with the square of the atomic number, i.e. the latter grows faster and becomes increasingly important for heavy and superheavy nuclei.[34][35] Superheavy nuclei are thus theoretically predicted[36] and have so far been observed[37] to predominantly decay via decay modes that are caused by such repulsion: alpha decay and spontaneous fission.[f] Almost all alpha emitters have over 210 nucleons,[39] and the lightest nuclide primarily undergoing spontaneous fission has 238.[40] In both decay modes, nuclei are inhibited from decaying by corresponding energy barriers for each mode, but they can be tunnelled through.[34][35]
Alpha particles are commonly produced in radioactive decays because mass of an alpha particle per nucleon is small enough to leave some energy for the alpha particle to be used as kinetic energy to leave the nucleus.[42] Spontaneous fission is caused by electrostatic repulsion tearing the nucleus apart and produces various nuclei in different instances of identical nuclei fissioning.[35] As the atomic number increases, spontaneous fission rapidly becomes more important: spontaneous fission partial half-lives decrease by 23 orders of magnitude from uranium (element 92) to nobelium (element 102),[43] and by 30 orders of magnitude from thorium (element 90) to fermium (element 100).[44] The earlier liquid drop model thus suggested that spontaneous fission would occur nearly instantly due to disappearance of the fission barrier for nuclei with about 280 nucleons.[35][45] The later nuclear shell model suggested that nuclei with about 300 nucleons would form an island of stability in which nuclei will be more resistant to spontaneous fission and will primarily undergo alpha decay with longer half-lives.[35][45] Subsequent discoveries suggested that the predicted island might be further than originally anticipated; they also showed that nuclei intermediate between the long-lived actinides and the predicted island are deformed, and gain additional stability from shell effects.[46] Experiments on lighter superheavy nuclei,[47] as well as those closer to the expected island,[43] have shown greater than previously anticipated stability against spontaneous fission, showing the importance of shell effects on nuclei.[g]
Alpha decays are registered by the emitted alpha particles, and the decay products are easy to determine before the actual decay; if such a decay or a series of consecutive decays produces a known nucleus, the original product of a reaction can be easily determined.[h] (That all decays within a decay chain were indeed related to each other is established by the location of these decays, which must be in the same place.)[29] The known nucleus can be recognized by the specific characteristics of decay it undergoes such as decay energy (or more specifically, the kinetic energy of the emitted particle).[i] Spontaneous fission, however, produces various nuclei as products, so the original nuclide cannot be determined from its daughters.[j]
The information available to physicists aiming to synthesize a superheavy element is thus the information collected at the detectors: location, energy, and time of arrival of a particle to the detector, and those of its decay. The physicists analyze this data and seek to conclude that it was indeed caused by a new element and could not have been caused by a different nuclide than the one claimed. Often, provided data is insufficient for a conclusion that a new element was definitely created and there is no other explanation for the observed effects; errors in interpreting data have been made.[k]Discovery[edit]
Background[edit]
Uranium, element 92, is the heaviest element to occur in significant quantities in nature; heavier elements can only be practically produced by synthesis. The first synthesis of a new element—neptunium, element 93—was achieved in 1940 by a team of researchers in the United States.[58] In the following years, American scientists synthesized the elements up to mendelevium, element 101, which was synthesized in 1955. From element 102, the priority of discoveries was contested between American and Soviet physicists.[59] Their rivalry resulted in a race for new elements and credit for their discoveries, later named the Transfermium Wars.[60]
Reports[edit]

The first report of the discovery of element 105 came from the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Soviet Union, in April 1968. The scientists bombarded 243Am with a beam of 22Ne ions, and reported 9.4 MeV (with a half-life of 0.1–3 seconds) and 9.7 MeV (t1/2 > 0.05 s) alpha activities followed by alpha activities similar to those of either 256103 or 257103. Based on prior theoretical predictions, the two activity lines were assigned to 261105 and 260105, respectively.[62]
- 243
95Am
+ 22
10Ne
→ 265−x105 + x
n
(x = 4, 5)
After observing the alpha decays of element 105, the researchers aimed to observe spontaneous fission (SF) of the element and study the resulting fission fragments. They published a paper in February 1970, reporting multiple examples of two such activities, with half-lives of 14 ms and 2.2±0.5 s. They assigned the former activity to 242mfAm[l] and ascribed the latter activity to an isotope of element 105. They suggested that it was unlikely that this activity could come from a transfer reaction instead of element 105, because the yield ratio for this reaction was significantly lower than that of the 242mfAm-producing transfer reaction, in accordance with theoretical predictions. To establish that this activity was not from a (22Ne,xn) reaction, the researchers bombarded a 243Am target with 18O ions; reactions producing 256103 and 257103 showed very little SF activity (matching the established data), and the reaction producing heavier 258103 and 259103 produced no SF activity at all, in line with theoretical data. The researchers concluded that the activities observed came from SF of element 105.[62]
In April 1970, a team at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (LBL), in Berkeley, California, United States, claimed to have synthesized element 105 by bombarding californium-249 with nitrogen-15 ions, with an alpha activity of 9.1 MeV. To ensure this activity was not from a different reaction, the team attempted other reactions: bombarding 249Cf with 14N, Pb with 15N, and Hg with 15N. They stated no such activity was found in those reactions. The characteristics of the daughter nuclei matched those of 256103, implying that the parent nuclei were of 260105.[62]
- 249
98Cf
+ 15
7N
→ 260105 + 4
n
These results did not confirm the JINR findings regarding the 9.4 MeV or 9.7 MeV alpha decay of 260105, leaving only 261105 as a possibly produced isotope.[62]
JINR then attempted another experiment to create element 105, published in a report in May 1970. They claimed that they had synthesized more nuclei of element 105 and that the experiment confirmed their previous work. According to the paper, the isotope produced by JINR was probably 261105, or possibly 260105.[62] This report included an initial chemical examination: the thermal gradient version of the gas-chromatography method was applied to demonstrate that the chloride of what had formed from the SF activity nearly matched that of niobium pentachloride, rather than hafnium tetrachloride. The team identified a 2.2-second SF activity in a volatile chloride portraying eka-tantalum properties, and inferred that the source of the SF activity must have been element 105.[62]
In June 1970, JINR made improvements on their first experiment, using a purer target and reducing the intensity of transfer reactions by installing a collimator before the catcher. This time, they were able to find 9.1 MeV alpha activities with daughter isotopes identifiable as either 256103 or 257103, implying that the original isotope was either 260105 or 261105.[62]
Naming controversy[edit]
JINR did not propose a name after their first report claiming synthesis of element 105, which would have been the usual practice. This led LBL to believe that JINR did not have enough experimental data to back their claim.[63] After collecting more data, JINR proposed the name bohrium (Bo) in honor of the Danish nuclear physicist Niels Bohr, a founder of the theories of atomic structure and quantum theory;[64] they soon changed their proposal to nielsbohrium (Ns) to avoid confusion with boron.[65] Another proposed name was dubnium.[66][67] When LBL first announced their synthesis of element 105, they proposed that the new element be named hahnium (Ha) after the German chemist Otto Hahn, the "father of nuclear chemistry", thus creating an element naming controversy.[68]
In the early 1970s, both teams reported synthesis of the next element, element 106, but did not suggest names.[69] JINR suggested establishing an international committee to clarify the discovery criteria. This proposal was accepted in 1974 and a neutral joint group formed.[70] Neither team showed interest in resolving the conflict through a third party, so the leading scientists of LBL—Albert Ghiorso and Glenn Seaborg—traveled to Dubna in 1975 and met with the leading scientists of JINR—Georgy Flerov, Yuri Oganessian, and others—to try to resolve the conflict internally and render the neutral joint group unnecessary; after two hours of discussions, this failed.[71] The joint neutral group never assembled to assess the claims, and the conflict remained unresolved.[70] In 1979, IUPAC suggested systematic element names to be used as placeholders until permanent names were established; under it, element 105 would be unnilpentium, from the Latin roots un- and nil- and the Greek root pent- (meaning "one", "zero", and "five", respectively, the digits of the atomic number). Both teams ignored it as they did not wish to weaken their outstanding claims.[72]
In 1981, the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI; Society for Heavy Ion Research) in Darmstadt, Hesse, West Germany, claimed synthesis of element 107; their report came out five years after the first report from JINR but with greater precision, making a more solid claim on discovery.[62] GSI acknowledged JINR's efforts by suggesting the name nielsbohrium for the new element.[70] JINR did not suggest a new name for element 105, stating it was more important to determine its discoverers first.[70]
In 1985, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) formed a Transfermium Working Group (TWG) to assess discoveries and establish final names for the controversial elements.[62] The party held meetings with delegates from the three competing institutes; in 1990, they established criteria on recognition of an element, and in 1991, they finished the work on assessing discoveries and disbanded. These results were published in 1993. According to the report, the first definitely successful experiment was the April 1970 LBL experiment, closely followed by the June 1970 JINR experiment, so credit for the discovery of the element should be shared between the two teams.[62]
LBL said that the input from JINR was overrated in the review. They claimed JINR was only able to unambiguously demonstrate the synthesis of element 105 a year after they did. JINR and GSI endorsed the report.[70]
In 1994, IUPAC published a recommendation on naming the disputed elements. For element 105, they proposed joliotium (Jl) after the French physicist Frédéric Joliot-Curie, a contributor to the development of nuclear physics and chemistry; this name was originally proposed by the Soviet team for element 102, which by then had long been called nobelium.[73] This recommendation was criticized by the American scientists for several reasons. Firstly, their suggestions were scrambled: the names rutherfordium and hahnium, originally suggested by Berkeley for elements 104 and 105, were respectively reassigned to elements 106 and 108. Secondly, elements 104 and 105 were given names favored by JINR, despite earlier recognition of LBL as an equal co-discoverer for both of them. Thirdly and most importantly, IUPAC rejected the name seaborgium for element 106, having just approved a rule that an element could not be named after a living person, even though the 1993 report had given the LBL team the sole credit for its discovery.[74]
In 1995, IUPAC abandoned the controversial rule and established a committee of national representatives aimed at finding a compromise. They suggested seaborgium for element 106 in exchange for the removal of all the other American proposals, except for the established name lawrencium for element 103. The equally entrenched name nobelium for element 102 was replaced by flerovium after Georgy Flerov, following the recognition by the 1993 report that that element had been first synthesized in Dubna. This was rejected by American scientists and the decision was retracted.[75][3] The name flerovium was later used for element 114.[76]
In 1996, IUPAC held another meeting, reconsidered all names in hand, and accepted another set of recommendations; it was approved and published in 1997.[77] Element 105 was named dubnium (Db), after Dubna in Russia, the location of the JINR; the American suggestions were used for elements 102, 103, 104, and 106. The name dubnium had been used for element 104 in the previous IUPAC recommendation. The American scientists "reluctantly" approved this decision.[78] IUPAC pointed out that the Berkeley laboratory had already been recognized several times, in the naming of berkelium, californium, and americium, and that the acceptance of the names rutherfordium and seaborgium for elements 104 and 106 should be offset by recognizing JINR's contributions to the discovery of elements 104, 105, and 106.[79]
Even after 1997, LBL still sometimes used the name hahnium for element 105 in their own material, doing so as recently as 2014.[80][81][82][83] However, the problem was resolved in the literature as Jens Volker Kratz, editor of Radiochimica Acta, refused to accept papers not using the 1997 IUPAC nomenclature.[84]
Isotopes[edit]

Dubnium, having an atomic number of 105, is a superheavy element; like all elements with such high atomic numbers, it is very unstable. The longest-lasting known isotope of dubnium, 268Db, has a half-life of around a day.[86] No stable isotopes have been seen, and a 2012 calculation by JINR suggested that the half-lives of all dubnium isotopes would not significantly exceed a day.[85][m] Dubnium can only be obtained by artificial production.[n]
The short half-life of dubnium limits experimentation. This is exacerbated by the fact that the most stable isotopes are the hardest to synthesize.[89] Elements with a lower atomic number have stable isotopes with a lower neutron–proton ratio than those with higher atomic number, meaning that the target and beam nuclei that could be employed to create the superheavy element have fewer neutrons than needed to form these most stable isotopes. (Different techniques based on rapid neutron capture and transfer reactions are being considered as of the 2010s, but those based on the collision of a large and small nucleus still dominate research in the area.)[90][91]
Only a few atoms of 268Db can be produced in each experiment, and thus the measured lifetimes vary significantly during the process. As of 2022, following additional experiments performed at the JINR's Superheavy Element Factory (which started operations in 2019), the half-life of 268Db is measured to be 16+6
−4 hours.[13] The second most stable isotope, 270Db, has been produced in even smaller quantities: three atoms in total, with lifetimes of 33.4 h,[92] 1.3 h, and 1.6 h.[93] These two are the heaviest isotopes of dubnium to date, and both were produced as a result of decay of the heavier nuclei 288Mc and 294Ts rather than directly, because the experiments that yielded them were originally designed in Dubna for 48Ca beams.[94] For its mass, 48Ca has by far the greatest neutron excess of all practically stable nuclei, both quantitative and relative,[86] which correspondingly helps synthesize superheavy nuclei with more neutrons, but this gain is compensated by the decreased likelihood of fusion for high atomic numbers.[95]
Predicted properties[edit]
According to the periodic law, dubnium should belong to group 5, with vanadium, niobium, and tantalum. Several studies have investigated the properties of element 105 and found that they generally agreed with the predictions of the periodic law. Significant deviations may nevertheless occur, due to relativistic effects,[o] which dramatically change physical properties on both atomic and macroscopic scales. These properties have remained challenging to measure for several reasons: the difficulties of production of superheavy atoms, the low rates of production, which only allows for microscopic scales, requirements for a radiochemistry laboratory to test the atoms, short half-lives of those atoms, and the presence of many unwanted activities apart from those of synthesis of superheavy atoms. So far, studies have only been performed on single atoms.[3]
Atomic and physical[edit]

A direct relativistic effect is that as the atomic numbers of elements increase, the innermost electrons begin to revolve faster around the nucleus as a result of an increase of electromagnetic attraction between an electron and a nucleus. Similar effects have been found for the outermost s orbitals (and p1/2 ones, though in dubnium they are not occupied): for example, the 7s orbital contracts by 25% in size and is stabilized by 2.6 eV.[3]
A more indirect effect is that the contracted s and p1/2 orbitals shield the charge of the nucleus more effectively, leaving less for the outer d and f electrons, which therefore move in larger orbitals. Dubnium is greatly affected by this: unlike the previous group 5 members, its 7s electrons are slightly more difficult to extract than its 6d electrons.[3]

Another effect is the spin–orbit interaction, particularly spin–orbit splitting, which splits the 6d subshell—the azimuthal quantum number ℓ of a d shell is 2—into two subshells, with four of the ten orbitals having their ℓ lowered to 3/2 and six raised to 5/2. All ten energy levels are raised; four of them are lower than the other six. (The three 6d electrons normally occupy the lowest energy levels, 6d3/2.)[3]
A singly ionized atom of dubnium (Db+) should lose a 6d electron compared to a neutral atom; the doubly (Db2+) or triply (Db3+) ionized atoms of dubnium should eliminate 7s electrons, unlike its lighter homologs. Despite the changes, dubnium is still expected to have five valence electrons. As the 6d orbitals of dubnium are more destabilized than the 5d ones of tantalum, and Db3+ is expected to have two 6d, rather than 7s, electrons remaining, the resulting +3 oxidation state is expected to be unstable and even rarer than that of tantalum. The ionization potential of dubnium in its maximum +5 oxidation state should be slightly lower than that of tantalum and the ionic radius of dubnium should increase compared to tantalum; this has a significant effect on dubnium's chemistry.[3]
Atoms of dubnium in the solid state should arrange themselves in a body-centered cubic configuration, like the previous group 5 elements.[4] The predicted density of dubnium is 21.6 g/cm3.[5]
Chemical[edit]

Computational chemistry is simplest in gas-phase chemistry, in which interactions between molecules may be ignored as negligible. Multiple authors[3] have researched dubnium pentachloride; calculations show it to be consistent with the periodic laws by exhibiting the properties of a compound of a group 5 element. For example, the molecular orbital levels indicate that dubnium uses three 6d electron levels as expected. Compared to its tantalum analog, dubnium pentachloride is expected to show increased covalent character: a decrease in the effective charge on an atom and an increase in the overlap population (between orbitals of dubnium and chlorine).[3]
Calculations of solution chemistry indicate that the maximum oxidation state of dubnium, +5, will be more stable than those of niobium and tantalum and the +3 and +4 states will be less stable. The tendency towards hydrolysis of cations with the highest oxidation state should continue to decrease within group 5 but is still expected to be quite rapid. Complexation of dubnium is expected to follow group 5 trends in its richness. Calculations for hydroxo-chlorido- complexes have shown a reversal in the trends of complex formation and extraction of group 5 elements, with dubnium being more prone to do so than tantalum.[3]
Experimental chemistry[edit]
Experimental results of the chemistry of dubnium date back to 1974 and 1976. JINR researchers used a thermochromatographic system and concluded that the volatility of dubnium bromide was less than that of niobium bromide and about the same as that of hafnium bromide. It is not certain that the detected fission products confirmed that the parent was indeed element 105. These results may imply that dubnium behaves more like hafnium than niobium.[3]
The next studies on the chemistry of dubnium were conducted in 1988, in Berkeley. They examined whether the most stable oxidation state of dubnium in aqueous solution was +5. Dubnium was fumed twice and washed with concentrated nitric acid; sorption of dubnium on glass cover slips was then compared with that of the group 5 elements niobium and tantalum and the group 4 elements zirconium and hafnium produced under similar conditions. The group 5 elements are known to sorb on glass surfaces; the group 4 elements do not. Dubnium was confirmed as a group 5 member. Surprisingly, the behavior on extraction from mixed nitric and hydrofluoric acid solution into methyl isobutyl ketone differed between dubnium, tantalum, and niobium. Dubnium did not extract and its behavior resembled niobium more closely than tantalum, indicating that complexing behavior could not be predicted purely from simple extrapolations of trends within a group in the periodic table.[3]
This prompted further exploration of the chemical behavior of complexes of dubnium. Various labs jointly conducted thousands of repetitive chromatographic experiments between 1988 and 1993. All group 5 elements and protactinium were extracted from concentrated hydrochloric acid; after mixing with lower concentrations of hydrogen chloride, small amounts of hydrogen fluoride were added to start selective re-extraction. Dubnium showed behavior different from that of tantalum but similar to that of niobium and its pseudohomolog protactinium at concentrations of hydrogen chloride below 12 moles per liter. This similarity to the two elements suggested that the formed complex was either DbOX−
4 or [Db(OH)
2X
4]−
. After extraction experiments of dubnium from hydrogen bromide into diisobutyl carbinol (2,6-dimethylheptan-4-ol), a specific extractant for protactinium, with subsequent elutions with the hydrogen chloride/hydrogen fluoride mix as well as hydrogen chloride, dubnium was found to be less prone to extraction than either protactinium or niobium. This was explained as an increasing tendency to form non‐extractable complexes of multiple negative charges. Further experiments in 1992 confirmed the stability of the +5 state: Db(V) was shown to be extractable from cation‐exchange columns with α‐hydroxyisobutyrate, like the group 5 elements and protactinium; Db(III) and Db(IV) were not. In 1998 and 1999, new predictions suggested that dubnium would extract nearly as well as niobium and better than tantalum from halide solutions, which was later confirmed.[3]
The first isothermal gas chromatography experiments were performed in 1992 with 262Db (half-life 35 seconds). The volatilities for niobium and tantalum were similar within error limits, but dubnium appeared to be significantly less volatile. It was postulated that traces of oxygen in the system might have led to formation of DbOBr
3, which was predicted to be less volatile than DbBr
5. Later experiments in 1996 showed that group 5 chlorides were more volatile than the corresponding bromides, with the exception of tantalum, presumably due to formation of TaOCl
3. Later volatility studies of chlorides of dubnium and niobium as a function of controlled partial pressures of oxygen showed that formation of oxychlorides and general volatility are dependent on concentrations of oxygen. The oxychlorides were shown to be less volatile than the chlorides.[3]
In 2004–05, researchers from Dubna and Livermore identified a new dubnium isotope, 268Db, as a fivefold alpha decay product of the newly created element 115. This new isotope proved to be long-lived enough to allow further chemical experimentation, with a half-life of over a day. In the 2004 experiment, a thin layer with dubnium was removed from the surface of the target and dissolved in aqua regia with tracers and a lanthanum carrier, from which various +3, +4, and +5 species were precipitated on adding ammonium hydroxide. The precipitate was washed and dissolved in hydrochloric acid, where it converted to nitrate form and was then dried on a film and counted. Mostly containing a +5 species, which was immediately assigned to dubnium, it also had a +4 species; based on that result, the team decided that additional chemical separation was needed. In 2005, the experiment was repeated, with the final product being hydroxide rather than nitrate precipitate, which was processed further in both Livermore (based on reverse phase chromatography) and Dubna (based on anion exchange chromatography). The +5 species was effectively isolated; dubnium appeared three times in tantalum-only fractions and never in niobium-only fractions. It was noted that these experiments were insufficient to draw conclusions about the general chemical profile of dubnium.[96]
In 2009, at the JAEA tandem accelerator in Japan, dubnium was processed in nitric and hydrofluoric acid solution, at concentrations where niobium forms NbOF−
4 and tantalum forms TaF−
6. Dubnium's behavior was close to that of niobium but not tantalum; it was thus deduced that dubnium formed DbOF−
4. From the available information, it was concluded that dubnium often behaved like niobium, sometimes like protactinium, but rarely like tantalum.[97]
In 2021, the volatile heavy group 5 oxychlorides MOCl3 (M = Nb, Ta, Db) were experimentally studied at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The trend in volatilities was found to be NbOCl3 > TaOCl3 ≥ DbOCl3, so that dubnium behaves in line with periodic trends.[98]
Notes[edit]
- ^ In nuclear physics, an element is called heavy if its atomic number is high; lead (element 82) is one example of such a heavy element. The term "superheavy elements" typically refers to elements with atomic number greater than 103 (although there are other definitions, such as atomic number greater than 100[15] or 112;[16] sometimes, the term is presented an equivalent to the term "transactinide", which puts an upper limit before the beginning of the hypothetical superactinide series).[17] Terms "heavy isotopes" (of a given element) and "heavy nuclei" mean what could be understood in the common language—isotopes of high mass (for the given element) and nuclei of high mass, respectively.
- ^ In 2009, a team at the JINR led by Oganessian published results of their attempt to create hassium in a symmetric 136Xe + 136Xe reaction. They failed to observe a single atom in such a reaction, putting the upper limit on the cross section, the measure of probability of a nuclear reaction, as 2.5 pb.[18] In comparison, the reaction that resulted in hassium discovery, 208Pb + 58Fe, had a cross section of ~20 pb (more specifically, 19+19
-11 pb), as estimated by the discoverers.[19] - ^ The amount of energy applied to the beam particle to accelerate it can also influence the value of cross section. For example, in the 28
14Si
+ 1
0n
→ 28
13Al
+ 1
1p
reaction, cross section changes smoothly from 370 mb at 12.3 MeV to 160 mb at 18.3 MeV, with a broad peak at 13.5 MeV with the maximum value of 380 mb.[23] - ^ This figure also marks the generally accepted upper limit for lifetime of a compound nucleus.[28]
- ^ This separation is based on that the resulting nuclei move past the target more slowly then the unreacted beam nuclei. The separator contains electric and magnetic fields whose effects on a moving particle cancel out for a specific velocity of a particle.[30] Such separation can also be aided by a time-of-flight measurement and a recoil energy measurement; a combination of the two may allow to estimate the mass of a nucleus.[31]
- ^ Not all decay modes are caused by electrostatic repulsion. For example, beta decay is caused by the weak interaction.[38]
- ^ It was already known by the 1960s that ground states of nuclei differed in energy and shape as well as that certain magic numbers of nucleons corresponded to greater stability of a nucleus. However, it was assumed that there was no nuclear structure in superheavy nuclei as they were too deformed to form one.[43]
- ^ Since mass of a nucleus is not measured directly but is rather calculated from that of another nucleus, such measurement is called indirect. Direct measurements are also possible, but for the most part they have remained unavailable for superheavy nuclei.[48] The first direct measurement of mass of a superheavy nucleus was reported in 2018 at LBNL.[49] Mass was determined from the location of a nucleus after the transfer (the location helps determine its trajectory, which is linked to the mass-to-charge ratio of the nucleus, since the transfer was done in presence of a magnet).[50]
- ^ If the decay occurred in a vacuum, then since total momentum of an isolated system before and after the decay must be preserved, the daughter nucleus would also receive a small velocity. The ratio of the two velocities, and accordingly the ratio of the kinetic energies, would thus be inverse to the ratio of the two masses. The decay energy equals the sum of the known kinetic energy of the alpha particle and that of the daughter nucleus (an exact fraction of the former).[39] The calculations hold for an experiment as well, but the difference is that the nucleus does not move after the decay because it is tied to the detector.
- ^ Spontaneous fission was discovered by Soviet physicist Georgy Flerov,[51] a leading scientist at JINR, and thus it was a "hobbyhorse" for the facility.[52] In contrast, the LBL scientists believed fission information was not sufficient for a claim of synthesis of an element. They believed spontaneous fission had not been studied enough to use it for identification of a new element, since there was a difficulty of establishing that a compound nucleus had only ejected neutrons and not charged particles like protons or alpha particles.[28] They thus preferred to link new isotopes to the already known ones by successive alpha decays.[51]
- ^ For instance, element 102 was mistakenly identified in 1957 at the Nobel Institute of Physics in Stockholm, Stockholm County, Sweden.[53] There were no earlier definitive claims of creation of this element, and the element was assigned a name by its Swedish, American, and British discoverers, nobelium. It was later shown that the identification was incorrect.[54] The following year, RL was unable to reproduce the Swedish results and announced instead their synthesis of the element; that claim was also disproved later.[54] JINR insisted that they were the first to create the element and suggested a name of their own for the new element, joliotium;[55] the Soviet name was also not accepted (JINR later referred to the naming of the element 102 as "hasty").[56] This name was proposed to IUPAC in a written response to their ruling on priority of discovery claims of elements, signed 29 September 1992.[56] The name "nobelium" remained unchanged on account of its widespread usage.[57]
- ^ This notation signifies that the nucleus is a nuclear isomer that decays via spontaneous fission.
- ^ The current experimental value is 16+6
−4 hours for 268Db, but the statistical law of large numbers, on which the determination of half-lives relies, cannot be directly applied due to a very limited number of experiments (decays). The range of uncertainty is an indication that the half-life period lies within this range with 95% probability. - ^ The modern theory of the atomic nucleus does not suggest a long-lived isotope of dubnium, but claims were made in the past that unknown isotopes of superheavy elements existed primordially on the Earth: for example, such a claim was raised for 267108 of a half-life of 400 to 500 million years in 1963[87] or 292122 of a half-life of over 100 million years in 2009;[88] neither claim gained acceptance.
- ^ Relativistic effects arise when an object moves at velocities comparable to the speed of light; in heavy atoms, the quickly moving objects are electrons.
References[edit]
- ^ "dubnium". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ "dubnium". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on December 18, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Hoffman, D. C.; Lee, D. M.; Pershina, V. (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". In Morss, L.R.; Edelstein, N. M.; Fuger, Jean (eds.). The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (3rd ed.). Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 1652–1752. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ a b c Östlin, A.; Vitos, L. (2011). "First-principles calculation of the structural stability of 6d transition metals". Physical Review B. 84 (11). Bibcode:2011PhRvB..84k3104O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.84.113104.
- ^ a b Gyanchandani, Jyoti; Sikka, S. K. (May 10, 2011). "Physical properties of the 6 d -series elements from density functional theory: Close similarity to lighter transition metals". Physical Review B. 83 (17): 172101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.172101.
- ^ Kratz; Lieser (2013). Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications (3rd ed.). p. 631.
- ^ Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Retrieved October 4, 2013.
- ^ "Dubnium". Royal Chemical Society. Retrieved October 9, 2017.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ Münzenberg, G.; Gupta, M. (2011). "Production and Identification of Transactinide Elements". Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry. Springer. p. 877. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-0720-2_19.
- ^ a b Six New Isotopes of the Superheavy Elements Discovered. Berkeley Lab. News center. October 26, 2010
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Utyonkov, V. K.; Kovrizhnykh, N. D.; et al. (2022). "New isotope 286Mc produced in the 243Am+48Ca reaction". Physical Review C. 106 (064306). doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.106.064306.
- ^ a b c Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Utyonkov, V. K.; Kovrizhnykh, N. D.; et al. (September 29, 2022). "First experiment at the Super Heavy Element Factory: High cross section of 288Mc in the243Am+48Ca reaction and identification of the new isotope 264Lr". Physical Review C. 106 (3): L031301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.106.L031301. S2CID 252628992.
- ^ Khuyagbaatar, J.; Yakushev, A.; Düllmann, Ch. E.; et al. (2014). "48Ca+249Bk Fusion Reaction Leading to Element Z=117: Long-Lived α-Decaying 270Db and Discovery of 266Lr". Physical Review Letters. 112 (17): 172501. Bibcode:2014PhRvL.112q2501K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.172501. hdl:1885/148814. PMID 24836239. S2CID 5949620.
- ^ Krämer, K. (2016). "Explainer: superheavy elements". Chemistry World. Retrieved March 15, 2020.
- ^ "Discovery of Elements 113 and 115". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Archived from the original on September 11, 2015. Retrieved March 15, 2020.
- ^ Eliav, E.; Kaldor, U.; Borschevsky, A. (2018). "Electronic Structure of the Transactinide Atoms". In Scott, R. A. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–16. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibc2632. ISBN 978-1-119-95143-8. S2CID 127060181.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Dmitriev, S. N.; Yeremin, A. V.; et al. (2009). "Attempt to produce the isotopes of element 108 in the fusion reaction 136Xe + 136Xe". Physical Review C. 79 (2): 024608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.79.024608. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Münzenberg, G.; Armbruster, P.; Folger, H.; et al. (1984). "The identification of element 108" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Physik A. 317 (2): 235–236. Bibcode:1984ZPhyA.317..235M. doi:10.1007/BF01421260. S2CID 123288075. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 7, 2015. Retrieved October 20, 2012.
- ^ Subramanian, S. (August 28, 2019). "Making New Elements Doesn't Pay. Just Ask This Berkeley Scientist". Bloomberg Businessweek. Retrieved January 18, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f Ivanov, D. (2019). "Сверхтяжелые шаги в неизвестное" [Superheavy steps into the unknown]. nplus1.ru (in Russian). Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ Hinde, D. (2017). "Something new and superheavy at the periodic table". The Conversation. Retrieved January 30, 2020.
- ^ Kern, B. D.; Thompson, W. E.; Ferguson, J. M. (1959). "Cross sections for some (n, p) and (n, α) reactions". Nuclear Physics. 10: 226–234. Bibcode:1959NucPh..10..226K. doi:10.1016/0029-5582(59)90211-1.
- ^ Wakhle, A.; Simenel, C.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (2015). Simenel, C.; Gomes, P. R. S.; Hinde, D. J.; et al. (eds.). "Comparing Experimental and Theoretical Quasifission Mass Angle Distributions". European Physical Journal Web of Conferences. 86: 00061. Bibcode:2015EPJWC..8600061W. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20158600061. hdl:1885/148847. ISSN 2100-014X.
- ^ "Nuclear Reactions" (PDF). pp. 7–8. Retrieved January 27, 2020. Published as Loveland, W. D.; Morrissey, D. J.; Seaborg, G. T. (2005). "Nuclear Reactions". Modern Nuclear Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 249–297. doi:10.1002/0471768626.ch10. ISBN 978-0-471-76862-3.
- ^ a b Krása, A. (2010). "Neutron Sources for ADS". Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering. Czech Technical University in Prague: 4–8. S2CID 28796927.
- ^ Wapstra, A. H. (1991). "Criteria that must be satisfied for the discovery of a new chemical element to be recognized" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 63 (6): 883. doi:10.1351/pac199163060879. ISSN 1365-3075. S2CID 95737691.
- ^ a b Hyde, E. K.; Hoffman, D. C.; Keller, O. L. (1987). "A History and Analysis of the Discovery of Elements 104 and 105". Radiochimica Acta. 42 (2): 67–68. doi:10.1524/ract.1987.42.2.57. ISSN 2193-3405. S2CID 99193729.
- ^ a b c d Chemistry World (2016). "How to Make Superheavy Elements and Finish the Periodic Table [Video]". Scientific American. Retrieved January 27, 2020.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 334.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, p. 335.
- ^ Zagrebaev, Karpov & Greiner 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432.
- ^ a b Pauli, N. (2019). "Alpha decay" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved February 16, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Pauli, N. (2019). "Nuclear fission" (PDF). Introductory Nuclear, Atomic and Molecular Physics (Nuclear Physics Part). Université libre de Bruxelles. Retrieved February 16, 2020.
- ^ Staszczak, A.; Baran, A.; Nazarewicz, W. (2013). "Spontaneous fission modes and lifetimes of superheavy elements in the nuclear density functional theory". Physical Review C. 87 (2): 024320–1. arXiv:1208.1215. Bibcode:2013PhRvC..87b4320S. doi:10.1103/physrevc.87.024320. ISSN 0556-2813.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, pp. 030001-129–030001-138.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 439.
- ^ a b Beiser 2003, p. 433.
- ^ Audi et al. 2017, p. 030001-125.
- ^ Aksenov, N. V.; Steinegger, P.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; et al. (2017). "On the volatility of nihonium (Nh, Z = 113)". The European Physical Journal A. 53 (7): 158. Bibcode:2017EPJA...53..158A. doi:10.1140/epja/i2017-12348-8. ISSN 1434-6001. S2CID 125849923.
- ^ Beiser 2003, p. 432–433.
- ^ a b c Oganessian, Yu. (2012). "Nuclei in the "Island of Stability" of Superheavy Elements". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 337 (1): 012005-1–012005-6. Bibcode:2012JPhCS.337a2005O. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/337/1/012005. ISSN 1742-6596.
- ^ Moller, P.; Nix, J. R. (1994). Fission properties of the heaviest elements (PDF). Dai 2 Kai Hadoron Tataikei no Simulation Symposium, Tokai-mura, Ibaraki, Japan. University of North Texas. Retrieved February 16, 2020.
- ^ a b Oganessian, Yu. Ts. (2004). "Superheavy elements". Physics World. 17 (7): 25–29. doi:10.1088/2058-7058/17/7/31. Retrieved February 16, 2020.
- ^ Schädel, M. (2015). "Chemistry of the superheavy elements". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 373 (2037): 20140191. Bibcode:2015RSPTA.37340191S. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0191. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 25666065.
- ^ Hulet, E. K. (1989). Biomodal spontaneous fission. 50th Anniversary of Nuclear Fission, Leningrad, USSR. Bibcode:1989nufi.rept...16H.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Rykaczewski, K. P. (2015). "A beachhead on the island of stability". Physics Today. 68 (8): 32–38. Bibcode:2015PhT....68h..32O. doi:10.1063/PT.3.2880. ISSN 0031-9228. OSTI 1337838. S2CID 119531411.
- ^ Grant, A. (2018). "Weighing the heaviest elements". Physics Today. doi:10.1063/PT.6.1.20181113a. S2CID 239775403.
- ^ Howes, L. (2019). "Exploring the superheavy elements at the end of the periodic table". Chemical & Engineering News. Retrieved January 27, 2020.
- ^ a b Robinson, A. E. (2019). "The Transfermium Wars: Scientific Brawling and Name-Calling during the Cold War". Distillations. Retrieved February 22, 2020.
- ^ "Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Сиборгий (экавольфрам)" [Popular library of chemical elements. Seaborgium (eka-tungsten)]. n-t.ru (in Russian). Retrieved January 7, 2020. Reprinted from "Экавольфрам" [Eka-tungsten]. Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Серебро – Нильсборий и далее [Popular library of chemical elements. Silver through nielsbohrium and beyond] (in Russian). Nauka. 1977.
- ^ "Nobelium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table". Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved March 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Kragh 2018, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Kragh 2018, p. 40.
- ^ a b Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (1993). "Responses on the report 'Discovery of the Transfermium elements' followed by reply to the responses by Transfermium Working Group" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1815–1824. doi:10.1351/pac199365081815. S2CID 95069384. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 25, 2013. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (1997). "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1997)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 69 (12): 2471–2474. doi:10.1351/pac199769122471.
- ^ Choppin, G. R.; Liljenzin, J.-O.; Rydberg, J. (2002). Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 416. ISBN 978-0-7506-7463-8.
- ^ Hoffman, D. C. (1996). The Transuranium Elements: From Neptunium and Plutonium to Element 112 (PDF) (Report). Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2017. Retrieved October 10, 2017.
- ^ Karol, P. (1994). "The Transfermium Wars". Chemical & Engineering News. 74 (22): 2–3. doi:10.1021/cen-v072n044.p002.
- ^ Zvara, I. J. (2003). "Dubnium". Chemical and Engineering News. 81 (36): 182. doi:10.1021/cen-v081n036.p182. Archived from the original on December 31, 2017. Retrieved October 9, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Barber, R. C.; Greenwood, N. N.; Hrynkiewicz, A. Z.; et al. (1993). "Discovery of the Transfermium elements" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1757. doi:10.1351/pac199365081757. S2CID 195819585. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 20, 2016. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ "Dubnium | chemical element". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on March 25, 2018. Retrieved March 25, 2018.
- ^ Städtler, Ingrid; Niemann, Hans (1971). Symbolik und Fachausdruecke. Mathematik, Physik, Chemie (in German). Germany: Verlag Enzyklopädie. p. 83.
- ^ Industries atomiques et spatiales, Volume 16 (in French). Switzerland. 1972. pp. 30–31. Archived from the original on December 23, 2022. Retrieved September 8, 2022.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Radiochemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry. 1972. ISBN 9780851862545.
- ^ Suomen kemistilehti. Suomalaisten Kemistien Seura. 1971.
- ^ Fontani, M.; Costa, M.; Orna, M. V. (2014). The Lost Elements: The Periodic Table's Shadow Side. Oxford University Press. p. 386. ISBN 978-0-19-938335-1. Archived from the original on February 27, 2018.
- ^ Hoffmann, K. (1987). Можно ли сделать золото? Мошенники, обманщики и ученые в истории химических элементов [Can one make gold? Swindlers, deceivers and scientists from the history of the chemical elements] (in Russian). Nauka. pp. 180–181. Translation from Hoffmann, K. (1979). Kann man Gold machen? Gauner, Gaukler und Gelehrte. Aus der Geschichte der chemischen Elemente [Can one make gold? Swindlers, deceivers and scientists. From the history of the chemical elements] (in German). Urania.
- ^ a b c d e Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (1993). "Responses on the report 'Discovery of the Transfermium elements' followed by reply to the responses by Transfermium Working Group" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 65 (8): 1815–1824. doi:10.1351/pac199365081815. S2CID 95069384. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 25, 2013. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ Robinson, A. (2017). "An Attempt to Solve the Controversies Over Elements 104 and 105: A Meeting in Russia, 23 September 1975". Bulletin of the American Physical Society. 62 (1): B10.003. Bibcode:2017APS..APRB10003R. Archived from the original on September 22, 2017. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
- ^ Öhrström, L.; Holden, N. E. (2016). "The Three-letter Element Symbols". Chemistry International. 38 (2). doi:10.1515/ci-2016-0204.
- ^ "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1994)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 66 (12): 2419–2421. 1994. doi:10.1351/pac199466122419. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 22, 2017. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ Yarris, L. (1994). "Naming of element 106 disputed by international committee". Archived from the original on July 1, 2016. Retrieved September 7, 2016.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, pp. 389–394
- ^ Loss, R. D.; Corish, J. (2012). "Names and symbols of the elements with atomic numbers 114 and 116 (IUPAC Recommendations 2012)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 84 (7): 1669–1672. doi:10.1351/PAC-REC-11-12-03. S2CID 96830750. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 3, 2017. Retrieved April 21, 2018.
- ^ Bera, J. K. (1999). "Names of the Heavier Elements". Resonance. 4 (3): 53–61. doi:10.1007/BF02838724. S2CID 121862853.
- ^ Hoffman, Ghiorso & Seaborg 2000, pp. 369–399
- ^ "Names and symbols of transfermium elements (IUPAC Recommendations 1997)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 69 (12): 2471–2474. 1997. doi:10.1351/pac199769122471.
- ^ "Periodic Table of the Elements". lbl.gov. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. 1999. Archived from the original on April 21, 2021. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ^ Wilk, P. A. (2001). Properties of Group Five and Group Seven transactinium elements (PhD). University of California, Berkeley. doi:10.2172/785268. OSTI 785268. Archived from the original on October 31, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ^ Buhler, Brendan (2014). "Branding the Elements: Berkeley Stakes its Claims on the Periodic Table". alumni.berkeley.edu. Cal Alumni Association. Archived from the original on October 31, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
Poor element 105 has had five different names—Berkeley partisans still call it hahnium.
- ^ @BerkeleyLab (January 8, 2014). "#16elements from Berkeley Lab: mendelevium, nobelium, lawrencium, rutherfordium, hahnium, seaborgium" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Armbruster, Peter; Münzenberg, Gottfried (2012). "An experimental paradigm opening the world of superheavy elements". The European Physical Journal H. 37 (2): 237–309. Bibcode:2012EPJH...37..237A. doi:10.1140/epjh/e2012-20046-7. S2CID 123446987. Archived from the original on December 6, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ^ a b Karpov, A. V.; Zagrebaev, V. I.; Palenzuela, Y. M.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Superheavy Nuclei: Decay and Stability". In Greiner, W. (ed.). Exciting Interdisciplinary Physics. FIAS Interdisciplinary Science Series. Springer International Publishing. pp. 69–79. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-00047-3_6. ISBN 978-3-319-00046-6.
- ^ a b Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; et al. (2012). "The NUBASE2012 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 36 (12): 1157–1286. Bibcode:2012ChPhC..36....1A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/36/12/001. S2CID 123457161. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2016.
- ^ Emsley, J. (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements (New ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 215–217. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- ^ Marinov, A.; Rodushkin, I.; Kolb, D.; et al. (2010). "Evidence for a long-lived superheavy nucleus with atomic mass number A=292 and atomic number Z=~122 in natural Th". International Journal of Modern Physics E. 19 (1): 131–140. arXiv:0804.3869. Bibcode:2010IJMPE..19..131M. doi:10.1142/S0218301310014662. S2CID 117956340.
- ^ Karpov, A. V.; Zagrebaev, V. I.; Palenzuela, Y. M.; et al. (2013). "Superheavy Nuclei: Decay and Stability". Exciting Interdisciplinary Physics. FIAS Interdisciplinary Science Series. p. 69. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-00047-3_6. ISBN 978-3-319-00046-6.
- ^ Botvina, Al.; Mishustin, I.; Zagrebaev, V.; et al. (2010). "Possibility of synthesizing superheavy elements in nuclear explosions". International Journal of Modern Physics E. 19 (10): 2063–2075. arXiv:1006.4738. Bibcode:2010IJMPE..19.2063B. doi:10.1142/S0218301310016521. S2CID 55807186.
- ^ Wuenschel, S.; Hagel, K.; Barbui, M.; et al. (2018). "An experimental survey of the production of alpha decaying heavy elements in the reactions of 238U +232Th at 7.5-6.1 MeV/nucleon". Physical Review C. 97 (6): 064602. arXiv:1802.03091. Bibcode:2018PhRvC..97f4602W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.064602. S2CID 67767157.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Bailey, P. D.; et al. (2010). "Synthesis of a New Element with Atomic Number Z=117". Physical Review Letters. 104 (14): 142502. Bibcode:2010PhRvL.104n2502O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.142502. PMID 20481935. Archived from the original on December 19, 2016.
- ^ Khuyagbaatar, J.; Yakushev, A.; Düllmann, Ch. E.; et al. (2014). "48Ca + 249Bk Fusion Reaction Leading to Element Z = 117: Long-Lived α-Decaying 270Db and Discovery of 266Lr" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 112 (17): 172501. Bibcode:2014PhRvL.112q2501K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.172501. hdl:1885/148814. PMID 24836239. S2CID 5949620. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 17, 2017.
- ^ Wills, S.; Berger, L. (2011). "Science Magazine Podcast. Transcript, 9 September 2011" (PDF). Science. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 18, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Sobiczewski, A.; Ter-Akopian, G. M. (2017). "Superheavy nuclei: from prediction to discovery". Physica Scripta. 92 (2): 023003. Bibcode:2017PhyS...92b3003O. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/aa53c1. S2CID 125713877.
- ^ Stoyer, N. J.; Landrum, J. H.; Wilk, P. A.; et al. (2006). Chemical Identification of a Long-Lived Isotope of Dubnium, a Descendant of Element 115 (PDF) (Report). IX International Conference on Nucleus Nucleus Collisions. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 31, 2017. Retrieved October 9, 2017.
- ^ Nagame, Y.; Kratz, J. V.; Schädel, M. (2016). "Chemical properties of rutherfordium (Rf) and dubnium (Db) in the aqueous phase" (PDF). EPJ Web of Conferences. 131: 07007. Bibcode:2016EPJWC.13107007N. doi:10.1051/epjconf/201613107007. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 28, 2019.
- ^ Chiera, Nadine M.; Sato, Tetsuya K.; Eichler, Robert; et al. (2021). "Chemical Characterization of a Volatile Dubnium Compound, DbOCl3". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 60 (33): 17871–17874. doi:10.1002/anie.202102808. PMC 8456785. PMID 33978998.
Bibliography[edit]
- Audi, G.; Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; et al. (2017). "The NUBASE2016 evaluation of nuclear properties". Chinese Physics C. 41 (3): 030001. Bibcode:2017ChPhC..41c0001A. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/41/3/030001.
- Beiser, A. (2003). Concepts of modern physics (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-244848-1. OCLC 48965418.
- Hoffman, D. C.; Ghiorso, A.; Seaborg, G. T. (2000). The Transuranium People: The Inside Story. World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-78-326244-1.
- Kragh, H. (2018). From Transuranic to Superheavy Elements: A Story of Dispute and Creation. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-75813-8.
- Zagrebaev, V.; Karpov, A.; Greiner, W. (2013). "Future of superheavy element research: Which nuclei could be synthesized within the next few years?". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 420 (1): 012001. arXiv:1207.5700. Bibcode:2013JPhCS.420a2001Z. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/420/1/012001. ISSN 1742-6588. S2CID 55434734.