| Millennium |
|---|
| 1st millennium BC |
| Centuries |
| Timelines |
| State leaders |
| Decades |
| Categories: |
|
Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
The 4th century BCE started the first day of 400 BC and ended the last day of 301 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.
This century marked the height of Classical Greek civilization in all of its aspects. By the year 400 BCE Greek philosophy, art, literature and architecture had spread far and wide, with the numerous independent Greek colonies that had sprung up throughout the lands of the eastern Mediterranean.
Arguably the most important series of political events in this period were the conquests of Alexander, bringing about the collapse of the once formidable Persian Empire and spreading Greek culture far into the east. Alexander dreamt of an east/west union, but when his short life ended in 323 BCE, his vast empire was plunged into civil war as his generals each carved out their own separate kingdoms. Thus began the Hellenistic age, a period characterized by a more absolute approach to rule, with Greek kings taking on royal trappings and setting up hereditary successions. While a degree of democracy still existed in some of the remaining independent Greek cities, many scholars see this age as marking the end of classical Greece.
In India, the Maurya Empire was founded in 322 BCE by Chandragupta Maurya who rapidly expanded his power westwards across central and western India, taking advantage of the disruptions of local powers in the wake of the withdrawal westward by the armies of Alexander.
China in the 4th century BCE entered an era of constant warfare known as the Warring States period. The period saw the rapid rise of large states (such as Chu) over smaller ones thanks to technological advancement. Though the period has usually been characterized by historians as being excessively violent compared to the Spring and Autumn period, it was also punctuated by several cultural and social growths through the expansion of several different sects of Confucianism and Taoism, and the formulation of Legalist thought.
The world in the 4th century BC[edit]
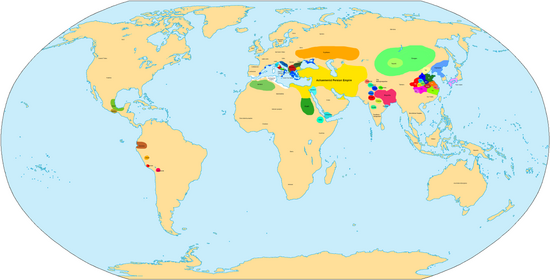


Events[edit]
390s BCE[edit]
- 399 BCE: The Greek philosopher Socrates is sentenced to death by Athenian authorities, condemned for impiety and the corruption of youth. He refuses to flee into exile and dies by drinking hemlock.
- 396 BCE: Marcus Furius Camillus is made dictator by the Romans. Camillus finally destroys the Etruscan city of Veii in southern Etruria.
- 395 BCE: Kalashoka succeeds his father Shishunaga to become king of Magadha. Second Buddhist Council is held during his reign.
- 395 BCE: The "Corinthian War" begins, with Athens, Thebes, Corinth and Argos (with the backing of Persia) against Sparta.
- 392 BCE: A peace conference between the Greek city-states is held in Sparta. Andocides, Athenian orator and politician, goes with three colleagues to negotiate peace with Sparta. The conference is unsuccessful and Athens rejects the terms and exiles the ambassadors.
- 391 BCE: Dionysius I, tyrant of Syracuse, begins an attempt to extend his rule to the Greek cities of southern Italy. He unsuccessfully besieges Rhegium.
- 390 BCE: The Pharaoh of Egypt, Hakor (Akoris), concludes a tripartite alliance with Evagoras, king of Cyprus, and Athens.
380s BCE[edit]
- 389 BCE: Early in the Warring States period, Chu is one of the strongest states in China. The state rose to a new level of power when King Dao of Chu (楚悼王) names the famous reformer Wu Qi as his chancellor.
- 389 BCE: Wu Qi, the prime minister of the State of Chu, enacts his first series of political, municipal, and martial reforms. Wu Qi gains the ire and distrust of Chu officials and aristocratic elite who are against his crusades to sweep up corruption in the state and limit their power.
- 388 BCE: Plato, having left Athens on Socrates' death to visit Megara and possibly Egypt, travels to Syracuse at the invitation of Dionysius I's brother-in-law Dion.
- 387 BCE: Under the threat of Spartan intervention, Thebes disbands its league, and Argos and Corinth end their shared government. Corinth, deprived of its strong ally, is incorporated back into Sparta's Peloponnesian League. After eight years of fighting, the Corinthian War is at an end.
- 387 BCE: Plato founds the Platonic Academy in Athens, where he teaches Aristotle until 347 BC.
- 387 BCE: Romans are defeated by the Gauls under Brennus in the Battle of the Allia who then go on to occupy the city of Rome. After the Gauls leave again the Romans begin the rebuilding of their city.
- 386 BCE: Freed from Spartan attacks by the Peace of Antalcidas of the previous year, Persia turns to quieting Cyprus and Egypt. Owing to the skill of King Evagoras of Cyprus and of Egypt's Greek mercenary general Chabrias, these wars drag on for the rest of the decade.
- 386 BCE: The Chinese city of Handan is founded by the State of Zhao.
- 385 BCE: Plato forms his Academy, teaching mathematics, astronomy and other sciences as well as philosophy. It is dedicated to the Attic hero Academus. Philanthropists bear all costs; students pay no fees.
- 384 BCE: Lysias, the Athenian orator, on the occasion of the Olympiad, rebukes the Greeks for allowing themselves to be dominated by the Syracusan tyrant Dionysius I and by the barbarian Persians.
- 384 BCE: The Greeks found the colony of Pharos at the site of today's Stari Grad on the island of Hvar, defeating Iadasinoi warriors brought in for its defense.
- 383 BC: The 19 year lunar cycle is introduced into the Babylonian calendar.
- 383 BC: The second Buddhist council is convened by king Kalasoka and held at Vaisali.
- 381 BC: Sparta increases its hold on central Greece by reestablishing the city of Plataea, which Sparta formerly destroyed in 427 BC.
- 381 BC: Wu Qi is assassinated at the funeral of King Diao of Chu, although his assassins are executed shortly after by the newly enthroned King Su of Chu.
- 380 BC: Persia forces the Athenians to withdraw their general Chabrias from Egypt. Chabrias has been successfully supporting the Egyptian Pharaohs in maintaining their independence from the Persian Empire.
- 380 BC: Cleombrotus I succeeds his brother Agesipolis I as king of Sparta.
370s BC[edit]
- 376 BC: The states of Han, Wei and Zhao deposed Duke Jing of Jin and divided the last remaining Jin territory between themselves, which marked the final end of the Jin state.
360s BC[edit]
350s BC[edit]
- 356 BC: Shang Yang implemented his first set of reforms in Qin.
340s BC[edit]
- 344 BC: Duke Hui of Wei is the first to claim the royal title of king (Chinese: 王) for himself, proclaiming themselves fully independent kingdoms.
- 344 BC: The rulers of Qi and Wei mutually recognized each other as "kings": King Wei of Qi and King Hui of Wei, in effect declaring their independence from the Zhou court.
- 343 BC: State of Qi wins the Battle of Maling over Wei that takes place in Maling, currently Dazhangjia Town, Shen County, Henan Province, during the Warring States period. After the death of Pang Juan, Prince Shen was captured by Qi. The power of the state of Wei decreased considerably after this battle.
330s BC[edit]
- 338 BC: King Huiwen becomes ruler of Qin.
- 331 BC: Alexander the Great Wins the Battle of Gaugamela, effectively ending Persian hegemony. He would spend much of the 330s conquering the remnants of the Achaemenid Empire.
- 331 BC: Chu rises to its peak in 334 BC, when it conquers Yue to its east on the Pacific coast.
320s BC[edit]
- 326 BC: Battle of the Hydaspes is fought between Alexander the Great and King Porus on the banks of Jhelum river. The battle resulted in Macedonian victory.
- 323 BC: In Babylon, Alexander the Great dies, ten days after being taken ill after a prolonged banquet and drinking bout.
- 323 BC: The Partition of Babylon sets out the division of the territories conquered by Alexander the Great between his generals. The partition is a result of a compromise, essentially brokered by Eumenes, following a conflict of opinion between the party of Meleager, who wishes to give full power to Philip III, and the party of Perdiccas, who wishes to wait for the birth of the heir of Alexander and his wife, Roxana to give him the throne under the control of a regent.
- 322 BC: Chandragupta Maurya overthrows Dhana Nanda and becomes King of Magadha. Establishment of Maurya dynasty.
310s BC[edit]
- 316 BC: Qin conquers Shu and Ba.
- 314 BC: Upon the ascension of King Nan, East Zhou becomes an independent state. The king comes to reside in what becomes known as West Zhou.[1]
- 311 BC: King Hui of Qin dies, follows by prime minister Zhang Yi one year later. The new monarch, King Wu, reigns only four years before dying without legitimate heirs.
300s BC[edit]
- 309 BC: Ptolemy personally commands a fleet that captures the coastal regions of Lycia and Caria from Antigonus.
- 309 BC: Cassander, who has held Roxana, widow of Alexander the Great, in prison for a number of years, has her put to death along with her young son Alexander, the nominal King Alexander IV of Macedon.
- 309 BC: Soon after the State of Qin has conquered the State of Shu (in modern-day Sichuan province), they employ the Shu engineer Bi Ling to create the Guanxian irrigation system, which will eventually provide for over five million people in an area of 40 to 50 square miles (130 km2), still in use today.
- 308 BC: Ptolemy crosses from Asia Minor into Greece, where he takes possession of Corinth, Sicyon and Megara.[2]
- 308 BC: Ptolemy makes peace with Cassander[2]
- 308 BC: Cleopatra of Macedon is assassinated by the order of Antigonus[2]
- 307 BC: Ptolemy founds the Museum and Library of Alexandria with the help of Demetrius Phalereus. Like Alexander the Great, Ptolemy has studied under Aristotle and staffs the museum with some 100 professors paid by the state.
- 307 BC: The city of Segesta in Sicily is destroyed by Agathocles.
- 307 BC: The Chinese King Wuling of Zhao reforms the military of the State of Zhao by putting more emphasis on cavalry over charioteers.
- 304 BC: The tyrant Agathocles takes on the title of King of Sicily. He extends his influence into southern Italy and the Adriatic.
- 304 BC: The Mauryan emperor Chandragupta defeats Seleucos I as he tries to invade India. Seleucid Empire's Eastern Satrapies ceded to Mauryan Empire.
- 301 BC: The southern part of Syria is occupied by Ptolemy.
Significant people[edit]








Politics[edit]
- Alexander the Great, king of Macedon
- Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Macedonian diadoch
- Antipater, Macedonian statesman
- Appius Claudius Caecus, Roman statesman
- Atropates, Persian nobleman that founded an independent kingdom
- Bessus, Persian satrap of Bactria
- Cassander, King of Macedon
- Chandragupta Maurya, Founder of the "Mauryan Dynasty"
- Craterus, Macedonian diadoch
- Darius III, king of the Achaemenid Empire
- Demetrius Poliocretes, King of Macedon
- Demosthenes, Athenian statesman and orator
- Dhana Nanda, last emperor of the Nanda dynasty
- Duke Xiao of Qin, ruler of Qin
- Epaminondas, Theban statesman
- King Wuling of Zhao, ruler of Zhao
- Lysimachus, Macedonian diadoch and king of Thrace
- Mahapadma Nanda, founding emperor of the Nanda dynasty
- Manius Curius Dentatus, Roman statesman
- Nakhthorheb, last native Pharaoh of Egypt
- Pelopidas, Theban statesman
- Perdiccas, Macedonian diadoch
- Philip II, King of Macedon
- Ptolemy I Soter, Macedonian diadoch and king of Egypt
- Porus, King of the Pauravas, in the Indian Subcontinent
- Seleucus I Nicator, Macedonian diadoh and founder of the Seleucid Empire
- Shang Yang, Chinese statesman
- Su Qin, Chinese politician and strategist
Military leaders[edit]
- Hephaestion, Macedonian general
- Pang Juan, Chinese general
- Parmenion, Macedonian general
- Tian Ji, Chinese general
- Zhang Yi, Chinese strategist
Visual arts[edit]
- Apelles, Greek painter
- Cephisodotus the Elder, Greek sculptor
- Leochares, Greek sculptor
- Lysippos, Greek sculptor
- Praxiteles, Greek sculptor
- Scopas, Greek sculptor and architect
Literature[edit]
- Demetrius of Phalerum, Greek rhetorician
- Isocrates, Greek rhetorician and writer
- Menander, Greek playwright
- Onesicritus, Greek historical writer
- Qu Yuan, Chinese poet
- Simonides of Ceos, Greek lyric poet
- Xenophon, Greek historian and writer
Science and philosophy[edit]
- Anaximenes of Lampsacus, Greek rhetorician and historian.
- Antisthenes, Greek philosopher
- Archytas, Greek philosopher
- Aristippus, Greek philosopher
- Aristotle, Greek philosopher
- Callisthenes, Greek historian
- Chanakya, Indian economist and political advisor
- Crates of Thebes, Greek philosopher
- Diogenes of Sinope, Greek philosopher
- Epicurus, Greek philosopher
- Mencius, Chinese philosopher
- Panini, Indian philosopher and writer
- Plato, Greek philosopher
- Pyrrho, Greek philosopher
- Socrates, Greek Philosopher
- Speusippus, Greek philosopher
- Sun Bin, Chinese author and military strategist
- Theophrastus, Greek philosopher
- Wu Qi, Chinese military strategist and philosopher
- Xenocrates, Greek philosopher
- Xenophon, Greek philosopher, writer and historian
- Zeno of Citium, Greek philosopher
- Zhuangzi, Chinese philosopher
Health professionals[edit]
- Agnodice, female Athenian physician and midwife
Inventions, discoveries, introductions[edit]

- Oldest Brahmi script dates from this period. Brāhmī is the ancestor of Brahmic scripts, used in much of India and Southeast Asia.
- Romans build their first aqueduct.
- Chinese use the handheld trigger crossbow for the first time.
- The first crossbow, the gastraphetes, is invented at Syracuse. (pre-421 BC)
- Donkey-powered mills or 'Pompeiian Mills' were first used in Greece and Italy.[3]
- In Greece, Aristotle proposes the division of the known sciences.
- Torque with lion's-head terminals, from Susa (modern Shush, Iran) was made. It is now in Musée du Louvre, Paris.
- Daric, a coin first minted under Darius I of Persia is made. It is now kept in Heberden Coin Room, Ashmolean Museum, Oxford.
- Second half of the 4th century BC – Tomb II, so called Tomb of Philip II of Macedon, Vergina, Macedonia is made.
- Starting in the year 309 BC, the later Chinese historian Sima Qian (145 BC–90 BC) wrote that the Qin-employed engineer Bi Ling of the newly conquered State of Shu in Sichuan had the shoulder of a mountain cut through, making the 'Separated Hill' that abated the Mo River, and excavated two canals in the plain of Chengdu. The significance of this was phenomenal, as it allowed the new Guardian irrigation system to populate an area of some 40 by 50 miles (60 × 80 km) with over five million people, still in use today (Needham, Science and Civilization in China, Volume 4, Part 3, 288).
- The Chinese astronomer Gan De divides the celestial sphere into 365¼ degrees, and the tropical year into 365¼ days at a time when most astronomers used the Babylon division of the celestial sphere as 360 degrees (Deng, Yinke. [2005] (2005). Chinese Ancient Inventions. ISBN 7-5085-0837-8).
- First formal system by Pāṇini in Mahajanapada, ancient India and written in Sanskrit.
Sovereign states[edit]
See: List of political entities in the 4th century BC.
References[edit]
External links[edit]
 Media related to 4th century BC at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 4th century BC at Wikimedia Commons