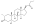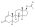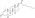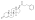 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Durabolin, others |
| Other names | • NPP • Nandrolone phenpropionate • 19-Nortestosterone phenylpropionate • Nandrolone hydrocinnamate • 19-Nortestosterone 17β-phenylpropionate • NSC-23162 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester; Progestogen |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | • Oral: 0.3–2.9% (pigs)[1] • Intramuscular: high[2] |
| Metabolism | Blood (hydrolysis), liver (reduction)[7][5] |
| Metabolites | • Nandrolone[3] • 5α-Dihydronandrolone[3] • 19-Norandrosterone[4] • 19-Noretiocholanolone[4] • Conjugates[5] |
| Elimination half-life | • Intramuscular: 2.7 days[6] • Nandrolone: <4.3 hours[7] |
| Duration of action | • Intramuscular: 5–7 days[3][6] |
| Excretion | Urine[7] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.502 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H34O3 |
| Molar mass | 406.566 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
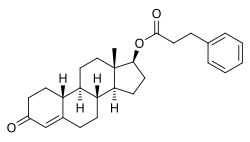
Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP), or nandrolone phenpropionate, sold under the brand name Durabolin among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which has been used primarily in the treatment of breast cancer and osteoporosis in women.[8][9][10][11][3] It is given by injection into muscle once every week.[3] Although it was widely used in the past, the drug has mostly been discontinued and hence is now mostly no longer available.[3][11]
Side effects of NPP include symptoms of masculinization like acne, increased hair growth, voice changes, and increased sexual desire.[3] The drug is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[3][12] It has strong anabolic effects and weak androgenic effects, which give it a mild side effect profile and make it especially suitable for use in women and children.[3][12][13] NPP is a nandrolone ester and a long-lasting prodrug of nandrolone in the body.[3]
NPP was first described in 1957 and was introduced for medical use in 1959.[3] It was the first nandrolone ester to be introduced, followed by nandrolone decanoate in 1962, and has been one of the most widely used nandrolone esters.[3][14] However, in more recent times, the drug has been largely superseded by nandrolone decanoate, which is longer-acting and more convenient to use.[3][11] In addition to its medical use, NPP is used to improve physique and performance.[3] The drug is a controlled substance in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit.[3]
Medical uses[edit]
NPP has been used mainly in the treatment of advanced breast cancer in women and as an adjunct therapy for the treatment of senile or postmenopausal osteoporosis in women.[3] Historically, it has also had a variety of other uses.[3] Because of its reduced androgenic effects, the drug has not generally been used in androgen replacement therapy for androgen deficiency in men and has instead been used for solely for anabolic indications.[2][15] However, nandrolone esters have more recently been proposed for the treatment of androgen deficiency in men due to favorable properties including their high ratio of anabolic to androgenic effects and consequent much lower risk of prostate enlargement, prostate cancer, and scalp hair loss relative to testosterone.[16][17]
| Route | Medication | Form | Dosage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 30–200 mg/day | |
| Fluoxymesterone | Tablet | 10–40 mg 3x/day | ||
| Calusterone | Tablet | 40–80 mg 4x/day | ||
| Normethandrone | Tablet | 40 mg/day | ||
| Buccal | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 25–100 mg/day | |
| Injection (IM or SC) | Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 3x/week | |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Mixed testosterone esters | Oil solution | 250 mg 1x/week | ||
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | 100 mg 3x/week | ||
| Androstanolone (DHT) | Aqueous suspension | 300 mg 3x/week | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | Oil solution | 100 mg 1–3x/week | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | 400 mg 3x/week | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 1x/1–3 weeks | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg/week | ||
| Note: Dosages are not necessarily equivalent. Sources: See template. | ||||
Available forms[edit]
NPP is or has been available 25 mg/mL and 50 mg/mL formulations in oil solution for intramuscular injection.[3]
Non-medical uses[edit]
NPP is used for physique- and performance-enhancing purposes by competitive athletes, bodybuilders, and powerlifters.[3] Nandrolone esters have been said to be the most popular AAS used by bodybuilders and in sports.[3][18] This is in part due to the high ratio of anabolic to androgenic effect of nandrolone and its weak propensity for androgenic and estrogenic side effects.[3]
Side effects[edit]
The most common side effects of NPP consist of virilization (masculinization) in women, including symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (increased body/facial hair growth), hoarseness of the voice, and voice deepening.[3] However, relative to most other AAS, NPP has a greatly reduced propensity for virilization and such side effects are relatively uncommon at recommended dosages.[3] At higher dosages and/or with long-term treatment they make increase in incidence and magnitude however.[3] A variety of uncommon and rare side effects may also occur.[3]
Interactions[edit]
Antiestrogens like aromatase inhibitors (e.g., anastrozole) and selective estrogen receptor modulators (e.g., tamoxifen, raloxifene) can interfere with and prevent the estrogenic effects of NPP.[3] 5α-Reductase inhibitors like finasteride and dutasteride can prevent the inactivation of nandrolone in so-called "androgenic" tissues like the skin, hair follicles, and prostate gland and may therefore considerably increase its androgenic side effects.[3] This is opposite to the case of most other AAS, which are either potentiated by 5α-reductase in such tissues or are not metabolized by 5α-reductase.[3] Antiandrogens like cyproterone acetate, spironolactone, and bicalutamide can block both the anabolic and androgenic effects of NPP.[19]
Pharmacology[edit]
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
| Medication | Ratioa |
|---|---|
| Testosterone | ~1:1 |
| Androstanolone (DHT) | ~1:1 |
| Methyltestosterone | ~1:1 |
| Methandriol | ~1:1 |
| Fluoxymesterone | 1:1–1:15 |
| Metandienone | 1:1–1:8 |
| Drostanolone | 1:3–1:4 |
| Metenolone | 1:2–1:30 |
| Oxymetholone | 1:2–1:9 |
| Oxandrolone | 1:3–1:13 |
| Stanozolol | 1:1–1:30 |
| Nandrolone | 1:3–1:16 |
| Ethylestrenol | 1:2–1:19 |
| Norethandrolone | 1:1–1:20 |
| Notes: In rodents. Footnotes: a = Ratio of androgenic to anabolic activity. Sources: See template. | |
NPP is a nandrolone ester, or a prodrug of nandrolone.[20][3] As such, it is an androgen and anabolic steroid, or an agonist of the androgen receptor, the biological target of androgens like testosterone.[3][20] Relative to testosterone, NPP has enhanced anabolic effects and reduced androgenic effects.[20][3] In addition to its anabolic and androgenic activity, NPP has low estrogenic activity (via its metabolite estradiol) and moderate progestogenic activity.[3] Like other AAS, NPP has antigonadotropic effects, which are due to both its androgenic and progestogenic activity.[3]
| Compound | PR | AR | ER | GR | MR | SHBG | CBG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nandrolone | 20 | 154–155 | <0.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 1–16 | 0.1 |
| Testosterone | 1.0–1.2 | 100 | <0.1 | 0.17 | 0.9 | 19–82 | 3–8 |
| Estradiol | 2.6 | 7.9 | 100 | 0.6 | 0.13 | 8.7–12 | <0.1 |
| Notes: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were progesterone for the PR, testosterone for the AR, estradiol for the ER, dexamethasone for the GR, aldosterone for the MR, dihydrotestosterone for SHBG, and cortisol for CBG. Sources: See template. | |||||||
| Compound | rAR (%) | hAR (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | 38 | 38 | ||||||
| 5α-Dihydrotestosterone | 77 | 100 | ||||||
| Nandrolone | 75 | 92 | ||||||
| 5α-Dihydronandrolone | 35 | 50 | ||||||
| Ethylestrenol | ND | 2 | ||||||
| Norethandrolone | ND | 22 | ||||||
| 5α-Dihydronorethandrolone | ND | 14 | ||||||
| Metribolone | 100 | 110 | ||||||
| Sources: See template. | ||||||||
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
NPP is converted into nandrolone in the body, which is the active form of the drug.[3] It has an extended elimination half-life in the body when administered via intramuscular injection.[20] Its duration of action is approximately one week and it is administered once every few days to once per week.[3] The elimination half-life and duration of action of NPP are much shorter than those of nandrolone decanoate.[3][21]
| Medication | Form | Major brand names | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Aqueous suspension | Andronaq, Sterotate, Virosterone | 2–3 days |
| Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | Androteston, Perandren, Testoviron | 3–4 days |
| Testosterone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Testolent | 8 days |
| Testosterone isobutyrate | Aqueous suspension | Agovirin Depot, Perandren M | 14 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersa | Oil solution | Triolandren | 10–20 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersb | Oil solution | Testosid Depot | 14–20 days |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | Delatestryl | 14–28 days |
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | Depovirin | 14–28 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersc | Oil solution | Sustanon 250 | 28 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Oil solution | Aveed, Nebido | 100 days |
| Testosterone buciclated | Aqueous suspension | 20 Aet-1, CDB-1781e | 90–120 days |
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Durabolin | 10 days |
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | Deca Durabolin | 21–28 days |
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | Notandron, Protandren | 8 days |
| Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate | Oil solution | Notandron Depot | 16 days |
| Metenolone acetate | Oil solution | Primobolan | 3 days |
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | Primobolan Depot | 14 days |
| Note: All are via i.m. injection. Footnotes: a = TP, TV, and TUe. b = TP and TKL. c = TP, TPP, TiCa, and TD. d = Studied but never marketed. e = Developmental code names. Sources: See template. | |||
-
Nandrolone levels after a single 50, 100, or 150 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate in oil solution in men.[22]
-
Nandrolone levels after a single 100 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone phenylpropionate in 4 mL or 1 mL arachis oil solution into gluteal or deltoid muscle in men.[23]
-
Nandrolone levels with a single 50 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone hexyloxyphenylpropionate in oil solution in men.[24]
-
Dose-normalized nandrolone exposure (serum level divided by dose administered) with nandrolone decanoate in oil solution by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in men.[25][26]
Chemistry[edit]
Nandrolone phenylpropionate, or nandrolone 17β-phenylpropionate, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of testosterone.[8][9] It is an androgen ester; specifically, it is the C17β phenylpropionate ester of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone), which itself is the 19-demethylated analogue of testosterone.[8][9]
| Anabolic steroid | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight |
Relative AAS contentb |
Durationc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Moiety | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Boldenone undecylenate | C17β | Undecylenic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | Long | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.18 | 0.84 | Short | ||
| Metenolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.14 | 0.88 | Short | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.37 | 0.73 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.56 | 0.64 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6–7) | 1.48 | 0.67 | Long | ||
| Trenbolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.16 | 0.87 | Short | ||
| Trenbolone enanthated | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | Long | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative androgen/anabolic steroid content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Duration by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in oil solution. d = Never marketed. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
History[edit]
NPP was first described in 1957 and was introduced for medical use in 1959.[3][27] It was initially used for a wide variety of indications, but starting in the 1970s its use became more restricted and its main uses became the treatment of breast cancer and osteoporosis in women.[3] Today, NPP is scarcely available.[3] The drug was the first form of nandrolone to be introduced, and was followed by nandrolone decanoate in 1962, which has been more widely used in comparison.[27]
Society and culture[edit]
Generic names[edit]
Nandrolone phenylpropionate is the generic name of the drug and its BAN while nandrolone phenpropionate is its USAN.[8][9][10][11] It has also been referred to as nandrolone phenylpropanoate or as nandrolone hydrocinnamate.[8][9][10][11]
Brand names[edit]
NPP is or has been marketed under a variety of brand names including Durabolin, Fenobolin, Activin, Deca-Durabolin, Evabolin, Grothic, Hybolin Improved, Metabol, Nerobolil, Neurabol, Norabol, Noralone, Sintabolin, Strabolene, and Superanabolon.[8][9][10][11]
Availability[edit]
NPP is or has been marketed in many countries throughout the world, including in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.[9][11]
United States[edit]
NPP was marketed previously in the United States but is no longer available in this country.[28] Nandrolone decanoate, conversely, is one of the few AAS that remains available for medical use in this country.[28]
Legal status[edit]
NPP, along with other AAS, is a schedule III controlled substance in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act.[29]
References[edit]
- ^ McEvoy JD, McVeigh CE, McCaughey WJ (December 1998). "Residues of nortestosterone esters at injection sites. Part 1. Oral bioavailability". The Analyst. 123 (12): 2475–2478. doi:10.1039/a804919j. PMID 10435281.
- ^ a b Matsumoto AM (2001). "Clinical Use and Abuse of Androgens and Antiandrogens". In Becker KL (ed.). Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1185–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 460–467, 193–194. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ^ a b Rogozkin VA (14 June 1991). "Enzymic Systems Participating in AAS Metabolism". Metabolism of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 108–. ISBN 978-0-8493-6415-0.
- ^ a b Colby HD, Longhurst PA (6 December 2012). "Fate of Anabolic Steroids in the Body". In Thomas JA (ed.). Drugs, Athletes, and Physical Performance. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 27–29. ISBN 978-1-4684-5499-4.
- ^ a b Minto CF, Howe C, Wishart S, Conway AJ, Handelsman DJ (April 1997). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nandrolone esters in oil vehicle: effects of ester, injection site and injection volume". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 281 (1): 93–102. PMID 9103484.
- ^ a b c "Decadurabolin injection Data Sheet" (PDF). Merck Sharp & Dohme (NZ) Ltd. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 January 2015. Retrieved 2017-12-13.
- ^ a b c d e f Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 660–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 716–717. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b c d Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Nandrolone - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses".
- ^ a b Kicman AT (June 2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 502–521. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
- ^ Potts GO, Arnold A, Beyler AL (6 December 2012). "Dissociation of the Androgenic and Other Hormonal Activities from the Protein Anabolic Effects of Steroids". In Kochakian CD (ed.). Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 401–. ISBN 978-3-642-66353-6.
- ^ Sneader W (23 June 2005). "Drugs from Naturally Occurring Prototypes: Biochemicals". Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 206–. ISBN 978-0-471-89979-2.
- ^ Meikle AW (1 June 1999). "Androgen Replacement Therapy of Male Hypogonadism". In Meikle AW (ed.). Hormone Replacement Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 271–. ISBN 978-1-59259-700-0.
- ^ Wu C, Kovac JR (October 2016). "Novel Uses for the Anabolic Androgenic Steroids Nandrolone and Oxandrolone in the Management of Male Health". Current Urology Reports. 17 (10): 72. doi:10.1007/s11934-016-0629-8. PMID 27535042. S2CID 43199715.
- ^ Pan MM, Kovac JR (April 2016). "Beyond testosterone cypionate: evidence behind the use of nandrolone in male health and wellness". Translational Andrology and Urology. 5 (2): 213–219. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.03.03. PMC 4837307. PMID 27141449.
- ^ Handelsman DJ (25 February 2015). "Androgen Physiology, Pharmacology, and Abuse". In Jameson JL, De Groot LJ (eds.). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2388–. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.
- ^ Brown TR (27 May 2003). "Androgen Action". In Bagatell C, Bremner WJ (eds.). Androgens in Health and Disease. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 25–. ISBN 978-1-59259-388-0.
- ^ a b c d Gao W, Bohl CE, Dalton JT (September 2005). "Chemistry and structural biology of androgen receptor". Chemical Reviews. 105 (9): 3352–3370. doi:10.1021/cr020456u. PMC 2096617. PMID 16159155.
- ^ Lemke TL, Williams DA (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1362–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0.
- ^ Bagchus WM, Smeets JM, Verheul HA, De Jager-Van Der Veen SM, Port A, Geurts TB (2005). "Pharmacokinetic evaluation of three different intramuscular doses of nandrolone decanoate: analysis of serum and urine samples in healthy men". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 (5): 2624–30. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1526. PMID 15713722.
- ^ Minto CF, Howe C, Wishart S, Conway AJ, Handelsman DJ (1997). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nandrolone esters in oil vehicle: effects of ester, injection site and injection volume". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 281 (1): 93–102. PMID 9103484.
- ^ Belkien L, Schürmeyer T, Hano R, Gunnarsson PO, Nieschlag E (May 1985). "Pharmacokinetics of 19-nortestosterone esters in normal men". J. Steroid Biochem. 22 (5): 623–9. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(85)90215-8. PMID 4010287.
- ^ Kalicharan RW, Schot P, Vromans H (February 2016). "Fundamental understanding of drug absorption from a parenteral oil depot". Eur J Pharm Sci. 83: 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2015.12.011. PMID 26690043.
- ^ Kalicharan, Raween Wikesh (2017). New Insights into Drug Absorption from Oil Depots (PhD). Utrecht University.
- ^ a b Consolidated List of Products Whose Consumption And/or Sale Have Been Banned, Withdrawn, Severely Restricted Or Not Approved by Governments. United Nations Publications. 1983. pp. 153–154. ISBN 978-92-1-130230-1.
- ^ a b "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ^ Bono JP (21 December 2006). "Criminalistics: Introduction to Controlled Substances". In Karch SB (ed.). Drug Abuse Handbook, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 30–. ISBN 978-1-4200-0346-8.
Further reading[edit]
- Kicman AT (June 2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 502–521. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
- Wu C, Kovac JR (October 2016). "Novel Uses for the Anabolic Androgenic Steroids Nandrolone and Oxandrolone in the Management of Male Health". Current Urology Reports. 17 (10): 72. doi:10.1007/s11934-016-0629-8. PMID 27535042. S2CID 43199715.
- Pan MM, Kovac JR (April 2016). "Beyond testosterone cypionate: evidence behind the use of nandrolone in male health and wellness". Translational Andrology and Urology. 5 (2): 213–219. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.03.03. PMC 4837307. PMID 27141449.
![Nandrolone levels after a single 50, 100, or 150 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate in oil solution in men.[22]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/03/Nandrolone_levels_after_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_different_doses_of_nandrolone_decanoate.png/298px-Nandrolone_levels_after_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_different_doses_of_nandrolone_decanoate.png)
![Nandrolone levels after a single 100 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone phenylpropionate in 4 mL or 1 mL arachis oil solution into gluteal or deltoid muscle in men.[23]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/Nandrolone_levels_after_a_single_100_mg_intramuscular_injection_of_nandrolone_esters.png/300px-Nandrolone_levels_after_a_single_100_mg_intramuscular_injection_of_nandrolone_esters.png)
![Nandrolone levels with a single 50 mg intramuscular injection of nandrolone decanoate or nandrolone hexyloxyphenylpropionate in oil solution in men.[24]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e8/Nandrolone_levels_with_a_single_dose_of_nandrolone_decanoate_or_nandrolone_hexyloxyphenylpropionate_by_intramuscular_injection_in_men.png/300px-Nandrolone_levels_with_a_single_dose_of_nandrolone_decanoate_or_nandrolone_hexyloxyphenylpropionate_by_intramuscular_injection_in_men.png)
![Dose-normalized nandrolone exposure (serum level divided by dose administered) with nandrolone decanoate in oil solution by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in men.[25][26]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/50/Dose-normalized_nandrolone_exposure_with_nandrolone_decanoate_by_intramuscular_or_subcutaneous_injection_in_men.png/300px-Dose-normalized_nandrolone_exposure_with_nandrolone_decanoate_by_intramuscular_or_subcutaneous_injection_in_men.png)