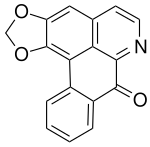
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4,5,6,6a-Tetradehydro-12-nor-2′H-[1,3]dioxolo[4′,5′:1,2]aporphin-7-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2H,8H-Benzo[g][1,3]benzodioxolo[6,5,4-de]quinolin-8-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 275.263 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Liriodenine is a bio-active isolate of the Chinese medicinal herb Zanthoxylum nitidum. It was isolated for the first time, at least with the name liriodenine, from the heartwood of Liriodendron tulipifera, the common yellow poplar of the south-eastern USA. It is found in very many other plants, notably in Annona cherimolia and Annona muricata, widely cultivated for their edible fruit.[1]
References[edit]
- ^ Chen, ZF; Liu, YC; Peng, Y; Hong, X; Wang, HH; Zhang, MM; Liang, H (February 2012). "Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antitumor properties of gold(III) compounds with the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) active ingredient liriodenine". Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry. 17 (2): 247–61. doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0846-z. PMID 21960256. S2CID 254085779.