 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cortiphen; Kortifen; Fencoron; 11-Deoxycortisol 21-(4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)phenyl)acetate; 11-Desoxy-17α-hydroxy-21-[n-di-2(chlorethyl)aminophenyl acetate]corticosterone |
| Drug class | Cytostatic antineoplastic agent; Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
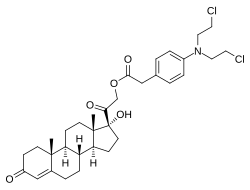
| Formula | C33H43Cl2NO5 |
| Molar mass | 604.61 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cortifen, also known as cortiphen or kortifen, as well as fencoron, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was developed in Russia for potential treatment of tumors.[1][2][3] It is a hydrophobic chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of 11-deoxycortisol (cortodoxone).[1][2][3][4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Lagova ND, Kiselev VI, Kurdiumova KN, Sof'ina ZP, Shkodinskaia EN (1989). "[Experimental study of the antitumor properties and mechanism of action of kortifen]". Voprosy Onkologii (in Russian). 35 (4): 450–456. PMID 2728387.
- ^ a b Oborotov AV, Smirnova ZS, Klochkova TI, Arzamastsev AP (1999). "Biopharmaceutical investigation of a new medicinal form of the antitumor drug cortifen". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 33 (10): 540–542. doi:10.1007/BF02508377. ISSN 0091-150X. S2CID 518576.
- ^ a b Smirnova ZS, Rodionova YV, Khalanskii AS, Gershtein ES, Gerasimova GK (1999). "Dependence of antitumor effect of hormonal cytostatic cortifen on expression of glucocorticoid receptors in brain tumor cells". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 127 (3): 299–300. doi:10.1007/BF02433363. ISSN 0007-4888. S2CID 20261670.
- ^ Oborotova NA, Smirnova ZS, Polozkova ZS, Baryshnikov AI (2002). "[Pharmacological aspects in the development of liposomal medicinal preparations for the internal injection of hydrophobic cytostatics]". Vestnik Rossiiskoi Akademii Meditsinskikh Nauk (in Russian) (1): 42–45. PMID 11882971.