| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorophyll b
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
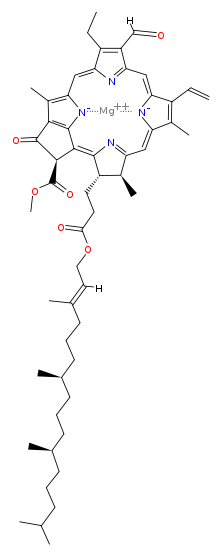
Magnesium [methyl (3S,4S,21R)-14-ethyl-13-formyl-4,8,18-trimethyl-20-oxo-3-(3-oxo-3-{[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl]oxy}propyl)-9-vinyl-21-phorbinecarboxylatato(2-)-κ2N,N′] | |
| Other names
β-Chlorophyll
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.522 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E140 (colours) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C55H70MgN4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 907.492 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting point | ~ 125 °C (257 °F; 398 K)[1] |
| Insoluble[1] | |
| Solubility | Very soluble in ethanol, ether, pyridine Soluble in methanol[1] |
| Absorbance | See text |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Chlorophyll b is a form of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll b helps in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy. It is more soluble than chlorophyll a in polar solvents because of its carbonyl group. Its color is green, and it primarily absorbs blue light.[2]
In land plants, the light-harvesting antennae around photosystem II contain the majority of chlorophyll b. Hence, in shade-adapted chloroplasts, which have an increased ratio of photosystem II to photosystem I, there is a higher ratio of chlorophyll b to chlorophyll a.[3] This is adaptive, as increasing chlorophyll b increases the range of wavelengths absorbed by the shade chloroplasts.
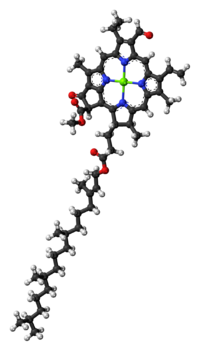 |

|
| Structure of chlorophyll b molecule showing the long hydrocarbon tail | |
Biosynthesis[edit]
The Chlorophyll b biosynthetic pathway utilizes a variety of enzymes.[4] In most plants, chlorophyll is derived from glutamate and is synthesised along a branched pathway that is shared with heme and siroheme.[5][6][7] The initial steps incorporate glutamic acid into 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA); two molecules of ALA are then reduced to porphobilinogen (PBG), and four molecules of PBG are coupled, forming protoporphyrin IX.
Chlorophyll synthase[8] is the enzyme that completes the biosynthesis of chlorophyll b[9][10] by catalysing the reaction EC 2.5.1.62
- chlorophyllide b + phytyl diphosphate chlorophyll b + diphosphate
This forms an ester of the carboxylic acid group in chlorophyllide b with the 20-carbon diterpene alcohol phytol.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ "Photosynthesis pigments". Archived from the original on 2012-09-05. Retrieved 2011-01-13.
- ^ Kitajima, Kaoru; Hogan, Kevin P (2003). "Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light". Plant, Cell & Environment. 26 (6): 857–865. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.01017.x. PMID 12803613.
- ^ Suzuki JY, Bollivar DW, Bauer CE (1997). "Genetic analysis of chlorophyll biosynthesis". Annual Review of Genetics. 31 (1): 61–89. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.31.1.61. PMID 9442890.
- ^ Battersby, A. R. (2000). "Tetrapyrroles: the Pigments of Life. A Millennium review". Nat. Prod. Rep. 17 (6): 507–526. doi:10.1039/B002635M. PMID 11152419.
- ^ Akhtar, M. (2007). "The Modification of Acetate and Propionate Side Chains During the Biosynthesis of Haem and Chlorophylls: Mechanistic and Stereochemical Studies". Ciba Foundation Symposium 180 - the Biosynthesis of the Tetrapyrrole Pigments. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 180. pp. 131–155. doi:10.1002/9780470514535.ch8. ISBN 9780470514535. PMID 7842850.
- ^ Willows, Robert D. (2003). "Biosynthesis of chlorophylls from protoporphyrin IX". Natural Product Reports. 20 (6): 327–341. doi:10.1039/B110549N. PMID 12828371.
- ^ Schmid, H. C.; Rassadina, V.; Oster, U.; Schoch, S.; Rüdiger, W. (2002). "Pre-Loading of Chlorophyll Synthase with Tetraprenyl Diphosphate is an Obligatory Step in Chlorophyll Biosynthesis" (PDF). Biological Chemistry. 383 (11): 1769–78. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.198. PMID 12530542. S2CID 3099209.
- ^ Eckhardt, Ulrich; Grimm, Bernhard; Hortensteiner, Stefan (2004). "Recent advances in chlorophyll biosynthesis and breakdown in higher plants". Plant Molecular Biology. 56 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-2331-3. PMID 15604725. S2CID 21174896.
- ^ Bollivar, David W. (2007). "Recent advances in chlorophyll biosynthesis". Photosynthesis Research. 90 (2): 173–194. doi:10.1007/s11120-006-9076-6. PMID 17370354. S2CID 23808539.
