| Poznań Voivodeship Palatinatus Posnaniensis Województwo poznańskie | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voivodeship of Poland¹ | |||||||||
| 1320–1793 | |||||||||
 Poznań Voivodeship in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1635. | |||||||||
| Capital | Poznań | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• | 15,015 km2 (5,797 sq mi) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1320 | ||||||||
• Split off Netze District | 1772 | ||||||||
| 25 September 1793 | |||||||||
| Political subdivisions | Counties: 3, plus Wschowa Land | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Poland | ||||||||
| ¹ Voivodeship of the Polish Crown in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Voivodeship of Kingdom of Poland before 1569. | |||||||||
Poznań Voivodeship 14th century to 1793 (Latin: Palatinatus Posnaniensis, Polish: Województwo Poznańskie) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the Second Partition of Poland in 1793. It was part of the Greater Poland Province.
Geography[edit]
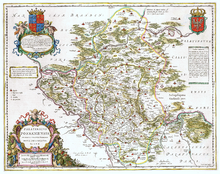
The voivodeship comprised the western part of the former Duchy of Greater Poland with its historic capital Poznań. As the westernmost part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth it bordered on the Neumark region of the Imperial Margraviate of Brandenburg in the west, the Bohemian crown land of Silesia in the south and the Duchy of Pomerania in the north. The adjacent Greater Polish area in the east belonged to the Kalisz Voivodeship.
The Northern outpost of Drahim was pawned to Brandenburg-Prussia according to the 1657 Treaty of Bromberg. In the course of the First Partition of Poland in 1772, the voivodeship lost the northern area around Wałcz to the Prussian Netze District, the remains were annexed in 1793 and incorporated into the province of South Prussia.
Zygmunt Gloger in his monumental book Historical Geography of the Lands of Old Poland provides this description of Poznań Voivodeship:
"Poznań Voivodeship, together with Kalisz and Kuyavia, was in the ancient times inhabited by the Polans. As early as the times of Bolesław Chrobry, the Land of Poznań had its own voivodes, while the city of Poznań itself was main gord of the ancient Lechia (...) When, following the Testament of Bolesław III Krzywousty Poland was divided among his sons, for more than 150 years Greater Poland was a separate duchy. In 1305 it was united with the Kingdom of Poland, by Wladyslaw Lokietek, who turned it into a voivodeship (...) In 1346, King Casimir the Great took control of the Wschowa Land, uniting it with Poznań Voivodeship.
The voivodeship, split by the Warta river into two almost equal halves, made western part of Greater Poland. Its area was 294 sq. miles, divided into Poznań County (162 sq. miles), Kościan County (92 sq. miles), Wałcz County behind the Noteć river (30 sq. miles), and the Land of Wschowa (9 sq. miles). In the mid-16th century, it had 259 Roman-Catholic parishes. Most densely populated was the Land of Wschowa, while Wałcz County was covered by vast forests.
Poznań Voivodeship had nine senators. These were: the Bishop of Poznań, the Voivode of Poznań and the Castellan of Poznań, as well as six minor castellans – those of Miedzyrzecz, Rogoźno, Srem, Przemecz, Krzywin and Santok. The Land of Wschowa had its own starosta, as well as its separate civil servants (...) The sejmiks for both Poznań and Kalisz Voivodeships took place in Środa Wielkopolska, where the two voivodeships elected 12 deputies to the Sejm, and 4 deputies to the Greater Poland Tribunal at Piotrków Trybunalski."
Major towns[edit]

The largest city of the voivodeship was the royal city of Poznań, which as one of the largest and most influential cities of entire Poland enjoyed voting rights during the Royal free elections.[1] (in alphabetical order):
Administration[edit]
Greater Poland general governor (Starosta Generalny) seat:
Voivodeship governor (Wojewoda) seat:
- Jan Opaliński, 1628–1637
- Krzysztof Opaliński, 1637–1655
- Józef Potocki, 1743–1751
- Stanisław Potocki, 1756–1760
General council (Sejmik Generalny) for Greater Poland seat:
Regional council (Sejmik) seat:
Administrative division:
- Poznań County (Powiat Poznański), Poznań
- Kościan County (Powiat Kościański), Kościan
- Wałcz County (Powiat Walecki), Wałcz
- Wschowa Land (Ziemia Wschowska), Wschowa
References[edit]
- ^ Polska encyklopedja szlachecka, Tom I (in Polish). Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Instytutu Kultury Historycznej. 1935. p. 42.

