| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
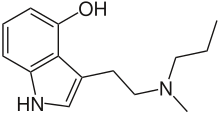
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-{2-[Methyl(propyl)amino]ethyl}-1H-indol-4-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H20N2O | |
| Molar mass | 232.327 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Hydroxy-N-methyl-N-propyltryptamine, commonly known as 4-HO-MPT or meprocin, is a psychedelic drug in the tryptamine class of chemical compounds and is a higher homologue of the naturally occurring substituted tryptamine psilocin as well as being the 4-hydroxyl analog of MPT.
History[edit]
4-HO-MPT was first synthesized and bioassayed by biochemist Alexander Shulgin and written about in his 1994 book TiHKAL.[1]
Dosage and duration[edit]
For psychedelic effects, the dosage and duration are listed as "unknown" in TiHKAL.[1]
Effects[edit]
Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 4-HO-MPT. In a single trial of 8 mg orally of 4-HO-MPT HCl from TiHKAL, it is described as producing visual distortion, vertigo, and slight insomnia.[1]
Legal status[edit]
4-HO-MPT is not scheduled by the United Nations' Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[2]
United States[edit]
4-HO-MPT is not scheduled at the federal level in the United States,[3] but it is possible that 4-HO-MPT could legally be considered an analog of psilocin, in which case, sales or possession with intent for human consumption could potentially be prosecuted under the Federal Analogue Act.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c 4-HO-MPT Entry in TIHKAL @ Erowid.org
- ^ "Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971". Archived from the original on 2022-01-19. Retrieved 2016-06-10.
- ^ "§1308.11 Schedule I." Archived from the original on 2009-08-27. Retrieved 2016-06-10.
- ^ Erowid Analog Law Vault : Federal Controlled Substance Analogue Act Summary